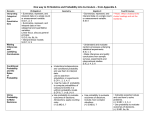
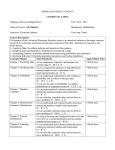
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2016 - 2017
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral economics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Dietz method wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate ceiling wikipedia , lookup
Stock selection criterion wikipedia , lookup
Financial literacy wikipedia , lookup
Business valuation wikipedia , lookup
Global saving glut wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission wikipedia , lookup
Mark-to-market accounting wikipedia , lookup
Systemically important financial institution wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2016 - 2017 Topic Ethics LOS Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) LOS 1.1.a Ethics 1.1.b Ethics 1.1.c Ethics 1.1.d Ethics 1.1.e Ethics 1.1.f Ethics 1.1.a Ethics 1.1.b Ethics 1.1.c Ethics 1.2.a Ethics 1.2.b Ethics 1.2.c Ethics 1.3.a describe the structure of the CFA Institute Professional Conduct Program and the process for the enforcement of the Code and Standards state the six components of the Code of Ethics and the seven Standards of Professional Conduct explain the ethical responsibilities required by the Code and Standards, including the sub-sections of each Standard demonstrate the application of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct to situations involving issues of professional integrity distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct explain why the GIPS standards were created, what parties the GIPS standards apply to, and who is served by the standards 1.2.a 1.2.b 1.2.c 1.3.a 1.3.b 1.3.c 1.4.a Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain ethics New describe the role of a code of ethics in New defining a profession identify challenges to ethical behavior New describe the need for high ethical New standards in the investment industry distinguish between ethical and legal New standards describe and apply a framework for New ethical decision making describe the structure of the CFA Institute Professional Conduct Program and the process for the enforcement of the Code and Standards state the six components of the Code of Ethics and the seven Standards of Professional Conduct explain the ethical responsibilities required by the Code and Standards, including the sub-sections of each Standard demonstrate the application of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct to situations involving issues of professional integrity distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct explain why the GIPS standards were created, what parties the GIPS standards apply to, and who is served by the standards Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 1 Topic LOS Ethics 1.3.b Ethics 1.3.c Ethics 1.4.a Ethics 1.4.b Ethics 1.4.c Ethics 1.4.d Quantitative 2.5.a Quantitative 2.5.b Quantitative 2.5.c Quantitative 2.5.d Quantitative 2.5.e Quantitative 2.5.f Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain the construction and purpose of composites in performance reporting explain the requirements for verification describe the key features of the GIPS standards and the fundamentals of compliance describe the scope of the GIPS standards with respect to an investment firm’s definition and historical performance record explain how the GIPS standards are implemented in countries with existing standards for performance reporting and describe the appropriate response when the GIPS standards and local regulations conflict describe the nine major sections of the GIPS standards interpret interest rates as required rates of return, discount rates, or opportunity costs explain an interest rate as the sum of a real risk-free rate, and premiums that compensate investors for bearing distinct types of risk calculate and interpret the effective annual rate, given the stated annual interest rate and the frequency of compounding solve time value of money problems for different frequencies of compounding calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity (PV only), and a series of unequal cash flows demonstrate the use of a time line in modeling and solving time value of money problems LOS 1.4.b 1.4.c 1.5.a 1.5.b 1.5.c 1.5.d 2.6.a 2.6.b 2.6.c 2.6.d 2.6.e 2.6.f Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain the construction and purpose of composites in performance reporting explain the requirements for verification describe the key features of the GIPS standards and the fundamentals of compliance describe the scope of the GIPS standards with respect to an investment firm’s definition and historical performance record explain how the GIPS standards are implemented in countries with existing standards for performance reporting and describe the appropriate response when the GIPS standards and local regulations conflict describe the nine major sections of the GIPS standards interpret interest rates as required rates of return, discount rates, or opportunity costs explain an interest rate as the sum of a real risk-free rate and premiums that compensate investors for bearing distinct types of risk calculate and interpret the effective annual rate, given the stated annual interest rate and the frequency of compounding solve time value of money problems for different frequencies of compounding calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity (PV only), and a series of unequal cash flows demonstrate the use of a time line in modeling and solving time value of money problems Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 2 Topic LOS Quantitative 2.6.a Quantitative 2.6.b Quantitative 2.6.c Quantitative 2.6.d Quantitative 2.6.e Quantitative 2.6.f Quantitative 2.7.a Quantitative 2.7.b Quantitative 2.7.c Quantitative 2.7.d Quantitative 2.7.e Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) calculate and interpret the net present value (NPV) and the internal rate of return (IRR) of an investment contrast the NPV rule to the IRR rule, and identify problems associated with the IRR rule calculate and interpret a holding period return (total return) calculate and compare the moneyweighted and time-weighted rates of return of a portfolio and evaluate the performance of portfolios based on these measures calculate and interpret the bank discount yield, holding period yield, effective annual yield, and money market yield for U.S. Treasury bills and other money market instruments convert among holding period yields, money market yields, effective annual yields, and bond equivalent yields distinguish between descriptive statistics and inferential statistics, between a population and a sample, and among the types of measurement scales define a parameter, a sample statistic, and a frequency distribution calculate and interpret relative frequencies and cumulative relative frequencies, given a frequency distribution describe the properties of a data set presented as a histogram or a frequency polygon calculate and interpret measures of central tendency, including the population mean, sample mean, arithmetic mean, weighted average or mean, geometric mean, harmonic mean, median, and mode LOS 2.7.a 2.7.b 2.7.c 2.7.d 2.7.e 2.7.f 2.8.a 2.8.b 2.8.c 2.8.d 2.8.e Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared calculate and interpret the net present value (NPV) and the internal rate of return (IRR) of an investment contrast the NPV rule to the IRR rule, and identify problems associated with the IRR rule calculate and interpret a holding period return (total return) calculate and compare the moneyweighted and time-weighted rates of return of a portfolio and evaluate the performance of portfolios based on these measures calculate and interpret the bank discount yield, holding period yield, effective annual yield, and money market yield for US Treasury bills and other money market instruments convert among holding period yields, money market yields, effective annual yields, and bond equivalent yields distinguish between descriptive statistics and inferential statistics, between a population and a sample, and among the types of measurement scales define a parameter, a sample statistic, and a frequency distribution calculate and interpret relative frequencies and cumulative relative frequencies, given a frequency distribution describe the properties of a data set presented as a histogram or a frequency polygon calculate and interpret measures of central tendency, including the population mean, sample mean, arithmetic mean, weighted average or mean, geometric mean, harmonic mean, median, and mode Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 3 Topic LOS Quantitative 2.7.f Quantitative 2.7.g Quantitative 2.7.h Quantitative 2.7.i Quantitative 2.7.j Quantitative 2.7.k Quantitative 2.7.l Quantitative 2.7.m Quantitative 2.8.a Quantitative 2.8.b Quantitative 2.8.c Quantitative 2.8.d Quantitative 2.8.e Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) calculate and interpret quartiles, quintiles, deciles, and percentiles calculate and interpret 1) a range and a mean absolute deviation and 2) the variance and standard deviation of a population and of a sample calculate and interpret the proportion of observations falling within a specified number of standard deviations of the mean using Chebyshev’s inequality calculate and interpret the coefficient of variation and the Sharpe ratio explain skewness and the meaning of a positively or negatively skewed return distribution describe the relative locations of the mean, median, and mode for a unimodal, nonsymmetrical distribution explain measures of sample skewness and kurtosis compare the use of arithmetic and geometric means when analyzing investment returns define a random variable, an outcome, an event, mutually exclusive events, and exhaustive events state the two defining properties of probability and distinguish among empirical, subjective, and a priori probabilities state the probability of an event in terms of odds for and against the event distinguish between unconditional and conditional probabilities explain the multiplication, addition, and total probability rules LOS 2.8.f 2.8.g 2.8.h 2.8.i 2.8.j 2.8.k 2.8.l 2.8.m 2.9.a 2.9.b 2.9.c 2.9.d 2.9.e Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared calculate and interpret quartiles, quintiles, deciles, and percentiles calculate and interpret 1) a range and a mean absolute deviation and 2) the variance and standard deviation of a population and of a sample calculate and interpret the proportion of observations falling within a specified number of standard deviations of the mean using Chebyshev’s inequality calculate and interpret the coefficient of variation and the Sharpe ratio explain skewness and the meaning of a positively or negatively skewed return distribution describe the relative locations of the mean, median, and mode for a unimodal, nonsymmetrical distribution explain measures of sample skewness and kurtosis compare the use of arithmetic and geometric means when analyzing investment returns define a random variable, an outcome, an event, mutually exclusive events, and exhaustive events state the two defining properties of probability and distinguish among empirical, subjective, and a priori probabilities state the probability of an event in terms of odds for and against the event distinguish between unconditional and conditional probabilities explain the multiplication, addition, and total probability rules Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 4 Topic LOS Quantitative 2.8.f Quantitative 2.8.g Quantitative 2.8.h Quantitative 2.8.i Quantitative 2.8.j Quantitative 2.8.k Quantitative 2.8.l Quantitative 2.8.m Quantitative 2.8.n Quantitative 2.8.o Quantitative 3.9.a Quantitative 3.9.b Quantitative 3.9.c Quantitative 3.9.d Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) LOS calculate and interpret 1) the joint probability of two events, 2) the probability that at least one of two events will occur, given the probability 2.9.f of each and the joint probability of the two events, and 3) a joint probability of any number of independent events distinguish between dependent and 2.9.g independent events calculate and interpret an unconditional probability using the total probability 2.9.h rule explain the use of conditional 2.9.i expectation in investment applications explain the use of a tree diagram to 2.9.j represent an investment problem calculate and interpret covariance and 2.9.k correlation calculate and interpret the expected value, variance, and standard deviation 2.9.l of a random variable and of returns on a portfolio calculate and interpret covariance given 2.9.m a joint probability function calculate and interpret an updated 2.9.n probability using Bayes’ formula identify the most appropriate method to solve a particular counting problem, and solve counting problems using 2.9.o factorial, combination, and permutation concepts define a probability distribution and distinguish between discrete and 3.10.a continuous random variables and their probability functions describe the set of possible outcomes 3.10.b of a specified discrete random variable interpret a cumulative distribution 3.10.c function calculate and interpret probabilities for a random variable, given its cumulative 3.10.d distribution function Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared calculate and interpret 1) the joint probability of two events, 2) the probability that at least one of two events will occur, given the probability of each and the joint probability of the two events, and 3) a joint probability of any number of independent events distinguish between dependent and independent events calculate and interpret an unconditional probability using the total probability rule explain the use of conditional expectation in investment applications explain the use of a tree diagram to represent an investment problem calculate and interpret covariance and correlation calculate and interpret the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of a random variable and of returns on a portfolio calculate and interpret covariance given a joint probability function calculate and interpret an updated probability using Bayes’ formula identify the most appropriate method to solve a particular counting problem and solve counting problems using factorial, combination, and permutation concepts define a probability distribution and distinguish between discrete and continuous random variables and their probability functions describe the set of possible outcomes of a specified discrete random variable interpret a cumulative distribution function calculate and interpret probabilities for a random variable, given its cumulative distribution function passingscoreforum.com 5 Topic LOS Quantitative 3.9.e Quantitative 3.9.f Quantitative 3.9.g Quantitative 3.9.h Quantitative 3.9.i Quantitative 3.9.j Quantitative 3.9.k Quantitative 3.9.l Quantitative 3.9.m Quantitative 3.9.n Quantitative 3.9.o Quantitative 3.9.p Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) define a discrete uniform random variable, a Bernoulli random variable, and a binomial random variable calculate and interpret probabilities given the discrete uniform and the binomial distribution functions construct a binomial tree to describe stock price movement calculate and interpret tracking error define the continuous uniform distribution and calculate and interpret probabilities, given a continuous uniform distribution explain the key properties of the normal distribution distinguish between a univariate and a multivariate distribution, and explain the role of correlation in the multivariate normal distribution determine the probability that a normally distributed random variable lies inside a given interval define the standard normal distribution, explain how to standardize a random variable, and calculate and interpret probabilities using the standard normal distribution define shortfall risk, calculate the safetyfirst ratio, and select an optimal portfolio using Roy’s safety-first criterion explain the relationship between normal and lognormal distributions and why the lognormal distribution is used to model asset prices distinguish between discretely and continuously compounded rates of return, and calculate and interpret a continuously compounded rate of return, given a specific holding period return LOS 3.10.e 3.10.f 3.10.g 3.10.h 3.10.i 3.10.j 3.10.k 3.10.l 3.10.m 3.10.n 3.10.o 3.10.p Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared define a discrete uniform random variable, a Bernoulli random variable, and a binomial random variable calculate and interpret probabilities given the discrete uniform and the binomial distribution functions construct a binomial tree to describe stock price movement calculate and interpret tracking error define the continuous uniform distribution and calculate and interpret probabilities, given a continuous uniform distribution explain the key properties of the normal distribution distinguish between a univariate and a multivariate distribution and explain the role of correlation in the multivariate normal distribution determine the probability that a normally distributed random variable lies inside a given interval define the standard normal distribution, explain how to standardize a random variable, and calculate and interpret probabilities using the standard normal distribution define shortfall risk, calculate the safetyfirst ratio, and select an optimal portfolio using Roy’s safety-first criterion explain the relationship between normal and lognormal distributions and why the lognormal distribution is used to model asset prices distinguish between discretely and continuously compounded rates of return and calculate and interpret a continuously compounded rate of return, given a specific holding period return Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 6 Topic LOS Quantitative 3.9.q Quantitative 3.9.r Quantitative 3.10.a Quantitative 3.10.b Quantitative 3.10.c Quantitative 3.10.d Quantitative 3.10.e Quantitative 3.10.f Quantitative 3.10.g Quantitative 3.10.h Quantitative 3.10.i Quantitative 3.10.j Quantitative 3.10.k Quantitative 3.11.a Quantitative 3.11.b Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain Monte Carlo simulation and describe its applications and limitations compare Monte Carlo simulation and historical simulation define simple random sampling and a sampling distribution explain sampling error distinguish between simple random and stratified random sampling distinguish between time-series and cross-sectional data explain the central limit theorem and its importance calculate and interpret the standard error of the sample mean identify and describe desirable properties of an estimator distinguish between a point estimate and a confidence interval estimate of a population parameter describe properties of Student’s tdistribution and calculate and interpret its degrees of freedom calculate and interpret a confidence interval for a population mean, given a normal distribution with 1) a known population variance, 2) an unknown population variance, or 3) an unknown variance and a large sample size describe the issues regarding selection of the appropriate sample size, datamining bias, sample selection bias, survivorship bias, look-ahead bias, and time-period bias define a hypothesis, describe the steps of hypothesis testing, and describe and interpret the choice of the null and alternative hypotheses distinguish between one-tailed and twotailed tests of hypotheses LOS 3.10.q 3.10.r 3.11.a 3.11.b 3.11.c 3.11.d 3.11.e 3.11.f 3.11.g 3.11.h 3.11.i 3.11.j 3.11.k 3.12.a 3.12.b Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain Monte Carlo simulation and describe its applications and limitations compare Monte Carlo simulation and historical simulation define simple random sampling and a sampling distribution explain sampling error distinguish between simple random and stratified random sampling distinguish between time-series and cross-sectional data explain the central limit theorem and its importance calculate and interpret the standard error of the sample mean identify and describe desirable properties of an estimator distinguish between a point estimate and a confidence interval estimate of a population parameter describe properties of Student’s tdistribution and calculate and interpret its degrees of freedom calculate and interpret a confidence interval for a population mean, given a normal distribution with 1) a known population variance, 2) an unknown population variance, or 3) an unknown variance and a large sample size describe the issues regarding selection of the appropriate sample size, datamining bias, sample selection bias, survivorship bias, look-ahead bias, and time-period bias define a hypothesis, describe the steps of hypothesis testing, and describe and interpret the choice of the null and alternative hypotheses distinguish between one-tailed and twotailed tests of hypotheses Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 7 Topic LOS Quantitative 3.11.c Quantitative 3.11.d Quantitative 3.11.e Quantitative 3.11.f Quantitative 3.11.g Quantitative 3.11.h Quantitative 3.11.i Quantitative 3.11.j Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain a test statistic, Type I and Type II errors, a significance level, and how significance levels are used in hypothesis testing explain a decision rule, the power of a test, and the relation between confidence intervals and hypothesis tests distinguish between a statistical result and an economically meaningful result explain and interpret the p-value as it relates to hypothesis testing identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning the population mean of both large and small samples when the population is normally or approximately normally distributed and the variance is 1) known or 2) unknown identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning the equality of the population means of two at least approximately normally distributed populations, based on independent random samples with 1) equal or 2) unequal assumed variances identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning the mean difference of two normally distributed populations identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning 1) the variance of a normally distributed population, and 2) the equality of the variances of two normally distributed populations based on two independent random samples LOS 3.12.c 3.12.d 3.12.e 3.12.f 3.12.g 3.12.h 3.12.i 3.12.j Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain a test statistic, Type I and Type II errors, a significance level, and how significance levels are used in hypothesis testing explain a decision rule, the power of a test, and the relation between confidence intervals and hypothesis tests distinguish between a statistical result and an economically meaningful result explain and interpret the p-value as it relates to hypothesis testing identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning the population mean of both large and small samples when the population is normally or approximately normally distributed and the variance is 1) known or 2) unknown identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning the equality of the population means of two at least approximately normally distributed populations, based on independent random samples with 1) equal or 2) unequal assumed variances identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning the mean difference of two normally distributed populations identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning 1) the variance of a normally distributed population, and 2) the equality of the variances of two normally distributed populations based on two independent random samples Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 8 Topic LOS Quantitative 3.11.k Quantitative 3.12.a Quantitative 3.12.b Quantitative 3.12.c Quantitative 3.12.d Quantitative 3.12.e Quantitative 3.12.f Quantitative 3.12.g Quantitative 3.12.h Economics 4.13.a Economics 4.13.b Economics 4.13.c Economics 4.13.d Economics 4.13.e Economics 4.13.f Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) distinguish between parametric and nonparametric tests and describe situations in which the use of nonparametric tests may be appropriate explain principles of technical analysis, its applications, and its underlying assumptions describe the construction of different types of technical analysis charts and interpret them explain uses of trend, support, resistance lines, and change in polarity describe common chart patterns describe common technical analysis indicators (price-based, momentum oscillators, sentiment, and flow of funds) explain how technical analysts use cycles describe the key tenets of Elliott Wave Theory and the importance of Fibonacci numbers describe intermarket analysis as it relates to technical analysis and asset allocation distinguish among types of markets explain the principles of demand and supply describe causes of shifts in and movements along demand and supply curves describe the process of aggregating demand and supply curves describe the concept of equilibrium (partial and general), and mechanisms by which markets achieve equilibrium distinguish between stable and unstable equilibria, including price bubbles, and identify instances of such equilibria LOS 3.12.k 3.13.a 3.13.b 3.13.c 3.13.d 3.13.e 3.13.f 3.13.g 3.13.h Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared distinguish between parametric and nonparametric tests and describe situations in which the use of nonparametric tests may be appropriate explain principles of technical analysis, its applications, and its underlying assumptions describe the construction of different types of technical analysis charts and interpret them explain uses of trend, support, resistance lines, and change in polarity describe common chart patterns describe common technical analysis indicators (price-based, momentum oscillators, sentiment, and flow of funds) explain how technical analysts use cycles describe the key tenets of Elliott Wave Theory and the importance of Fibonacci numbers describe intermarket analysis as it relates to technical analysis and asset allocation Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed 9 Topic LOS Economics 4.13.g Economics 4.13.h Economics 4.13.i Economics 4.13.j Economics 4.13.k Economics 4.13.l Economics 4.13.m Economics 4.14.a Economics 4.14.b Economics 4.14.c Economics 4.14.d Economics 4.14.e Economics 4.14.f Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) calculate and interpret individual and aggregate demand, and inverse demand and supply functions, and interpret individual and aggregate demand and supply curves calculate and interpret the amount of excess demand or excess supply associated with a non-equilibrium price describe types of auctions and calculate the winning price(s) of an auction calculate and interpret consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus describe how government regulation and intervention affect demand and supply forecast the effect of the introduction and the removal of a market interference (e.g., a price floor or ceiling) on price and quantity calculate and interpret price, income, and cross-price elasticities of demand and describe factors that affect each measure describe consumer choice theory and utility theory describe the use of indifference curves, opportunity sets, and budget constraints in decision making calculate and interpret a budget constraint determine a consumer’s equilibrium bundle of goods based on utility analysis compare substitution and income effects distinguish between normal goods and inferior goods, and explain Giffen goods and Veblen goods in this context Compared Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed 4.14.a calculate and interpret price, income, and cross-price elasticities of demand and describe factors that affect each measure Removed Removed Removed Removed 4.14.b 4.14.c compare substitution and income effects distinguish between normal goods and inferior goods Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com Wording Change 10 Topic LOS Economics 4.15.a Economics 4.15.b Economics 4.15.c Economics 4.15.d Economics 4.15.f Economics 4.15.h Economics 4.15.i Economics 4.15.j Economics 4.15.l Economics 4.15.k Economics 4.15.e Economics 4.15.g Economics 4.16.a Economics 4.16.b Economics 4.16.c Economics 4.16.d Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) calculate, interpret, and compare accounting profit, economic profit, normal profit, and economic rent calculate and interpret and compare total, average, and marginal revenue describe a firm’s factors of production calculate and interpret total, average, marginal, fixed, and variable costs describe approaches to determining the profit-maximizing level of output distinguish between short-run and longrun profit maximization distinguish among decreasing-cost, constant-cost, and increasing-cost industries and describe the long-run supply of each calculate and interpret total, marginal, and average product of labor determine the optimal combination of resources that minimizes cost describe the phenomenon of diminishing marginal returns and calculate and interpret the profitmaximizing utilization level of an input determine and describe breakeven and shutdown points of production describe how economies of scale and diseconomies of scale affect costs describe characteristics of perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and pure monopoly explain relationships between price, marginal revenue, marginal cost, economic profit, and the elasticity of demand under each market structure describe a firm’s supply function under each market structure describe and determine the optimal price and output for firms under each market structure LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed 4.14.d 4.14.e 4.14.f 4.15.a 4.15.b 4.15.c 4.15.d describe the phenomenon of diminishing marginal returns determine and describe breakeven and shutdown points of production describe how economies of scale and diseconomies of scale affect costs describe characteristics of perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and pure monopoly explain relationships between price, marginal revenue, marginal cost, economic profit, and the elasticity of demand under each market structure describe a firm’s supply function under each market structure describe and determine the optimal price and output for firms under each market structure Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com Wording Change 11 Topic LOS Economics 4.16.e Economics 4.16.f Economics 4.16.g Economics 4.16.h Economics 5.17.a Economics 5.17.b Economics 5.17.c Economics 5.17.d Economics 5.17.e Economics 5.17.f Economics 5.17.g Economics 5.17.h Economics 5.17.i Economics 5.17.j Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain factors affecting long-run equilibrium under each market structure describe pricing strategy under each market structure describe the use and limitations of concentration measures in identifying market structure identify the type of market structure within which a firm operates calculate and explain gross domestic product (GDP) using expenditure and income approaches compare the sum-of-value-added and value-of-final-output methods of calculating GDP LOS 4.15.e 4.15.f 4.15.g 4.15.h 4.16.a 4.16.b compare nominal and real GDP and 4.16.c calculate and interpret the GDP deflator compare GDP, national income, personal income, and personal 4.16.d disposable income explain the fundamental relationship among saving, investment, the fiscal 4.16.e balance, and the trade balance explain the IS and LM curves and how they combine to generate the 4.16.f aggregate demand curve explain the aggregate supply curve in 4.16.g the short run and long run explain causes of movements along and shifts in aggregate demand and supply 4.16.h curves describe how fluctuations in aggregate demand and aggregate supply cause 4.16.i short-run changes in the economy and the business cycle distinguish between the following types of macroeconomic equilibria: long-run full employment, short-run 4.16.j recessionary gap, short-run inflationary gap, and short-run stagflation Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain factors affecting long-run equilibrium under each market structure describe pricing strategy under each market structure describe the use and limitations of concentration measures in identifying market structure identify the type of market structure within which a firm operates calculate and explain gross domestic product (GDP) using expenditure and income approaches compare the sum-of-value-added and value-of-final-output methods of calculating GDP compare nominal and real GDP and calculate and interpret the GDP deflator compare GDP, national income, personal income, and personal disposable income explain the fundamental relationship among saving, investment, the fiscal balance, and the trade balance explain the IS and LM curves and how they combine to generate the aggregate demand curve explain the aggregate supply curve in the short run and long run explain causes of movements along and shifts in aggregate demand and supply curves describe how fluctuations in aggregate demand and aggregate supply cause short-run changes in the economy and the business cycle distinguish between the following types of macroeconomic equilibria: long-run full employment, short-run recessionary gap, short-run inflationary gap, and short-run stagflation passingscoreforum.com 12 Topic LOS Economics 5.17.k Economics 5.17.l Economics 5.17.m Economics 5.17.n Economics 5.17.o Economics 5.18.a Economics 5.18.b Economics 5.18.c Economics 5.18.d Economics 5.18.e Economics 5.18.f Economics 5.18.g Economics 5.18.h Economics 5.18.i Economics 5.19.a Economics 5.19.b Economics 5.19.c Economics 5.19.d Economics 5.19.e Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain how a short-run macroeconomic equilibrium may occur at a level above or below full employment analyze the effect of combined changes in aggregate supply and demand on the economy describe sources, measurement, and sustainability of economic growth describe the production function approach to analyzing the sources of economic growth distinguish between input growth and growth of total factor productivity as components of economic growth describe the business cycle and its phases describe how resource use, housing sector activity, and external trade sector activity vary as an economy moves through the business cycle describe theories of the business cycle describe types of unemployment and measures of unemployment explain inflation, hyperinflation, disinflation, and deflation explain the construction of indices used to measure inflation compare inflation measures, including their uses and limitations distinguish between cost-push and demand-pull inflation describe economic indicators, including their uses and limitations compare monetary and fiscal policy describe functions and definitions of money explain the money creation process describe theories of the demand for and supply of money describe the Fisher effect LOS 4.16.k 4.16.l 4.16.m 4.16.n 4.16.o 4.17.a 4.17.b 4.17.c 4.17.d 4.17.e 4.17.f 4.17.g 4.17.h 4.17.i 5.18.a 5.18.b 5.18.c 5.18.d 5.18.e Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain how a short-run macroeconomic equilibrium may occur at a level above or below full employment analyze the effect of combined changes in aggregate supply and demand on the economy describe sources, measurement, and sustainability of economic growth describe the production function approach to analyzing the sources of economic growth distinguish between input growth and growth of total factor productivity as components of economic growth describe the business cycle and its phases describe how resource use, housing sector activity, and external trade sector activity vary as an economy moves through the business cycle describe theories of the business cycle describe types of unemployment and Wording compare measures of unemployment Change explain inflation, hyperinflation, disinflation, and deflation explain the construction of indices used to measure inflation compare inflation measures, including their uses and limitations distinguish between cost-push and demand-pull inflation interpret a set of economic indicators Wording and describe their uses and limitations Change compare monetary and fiscal policy describe functions and definitions of money explain the money creation process describe theories of the demand for and supply of money describe the Fisher effect Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 13 Topic LOS Economics 5.19.f Economics 5.19.g Economics 5.19.h Economics 5.19.i Economics 5.19.j Economics 5.19.k Economics 5.19.l Economics 5.19.m Economics 5.19.n Economics 5.19.o Economics 5.19.p Economics 5.19.q Economics 5.19.r Economics 5.19.s Economics 5.19.t Economics 6.20.a Economics 6.20.b Economics 6.20.c Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe roles and objectives of central banks contrast the costs of expected and unexpected inflation describe tools used to implement monetary policy describe the monetary transmission mechanism describe qualities of effective central banks explain the relationships between monetary policy and economic growth, inflation, interest, and exchange rates contrast the use of inflation, interest rate, and exchange rate targeting by central banks determine whether a monetary policy is expansionary or contractionary describe limitations of monetary policy describe roles and objectives of fiscal policy describe tools of fiscal policy, including their advantages and disadvantages describe the arguments about whether the size of a national debt relative to GDP matters explain the implementation of fiscal policy and difficulties of implementation determine whether a fiscal policy is expansionary or contractionary explain the interaction of monetary and fiscal policy compare gross domestic product and gross national product describe benefits and costs of international trade distinguish between comparative advantage and absolute advantage LOS 5.18.f 5.18.g 5.18.h 5.18.i 5.18.j 5.18.k 5.18.l 5.18.m 5.18.n 5.18.o 5.18.p 5.18.q 5.18.r 5.18.s 5.18.t 5.19.a 5.19.b 5.19.c Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe roles and objectives of central banks contrast the costs of expected and unexpected inflation describe tools used to implement monetary policy describe the monetary transmission mechanism describe qualities of effective central banks explain the relationships between monetary policy and economic growth, inflation, interest, and exchange rates contrast the use of inflation, interest rate, and exchange rate targeting by central banks determine whether a monetary policy is expansionary or contractionary describe limitations of monetary policy describe roles and objectives of fiscal policy describe tools of fiscal policy, including their advantages and disadvantages describe the arguments about whether the size of a national debt relative to GDP matters explain the implementation of fiscal policy and difficulties of implementation determine whether a fiscal policy is expansionary or contractionary explain the interaction of monetary and fiscal policy compare gross domestic product and gross national product describe benefits and costs of international trade distinguish between comparative advantage and absolute advantage Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 14 Topic LOS Economics 6.20.d Economics 6.20.e Economics 6.20.f Economics 6.20.g Economics 6.20.h Economics 6.20.i Economics 6.20.j Economics 6.21.a Economics 6.21.b Economics 6.21.c Economics 6.21.d Economics 6.21.e Economics 6.21.f Economics 6.21.g Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) LOS explain the Ricardian and Heckscher–Ohlin models of trade and 5.19.d the source(s) of comparative advantage in each model compare types of trade and capital restrictions and their economic 5.19.e implications explain motivations for and advantages of trading blocs, common markets, and 5.19.f economic unions describe common objectives of capital 5.19.g restrictions imposed by governments describe the balance of payments 5.19.h accounts including their components explain how decisions by consumers, firms, and governments affect the 5.19.i balance of payments describe functions and objectives of the international organizations that facilitate trade, including the World 5.19.j Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the World Trade Organization define an exchange rate, and distinguish between nominal and real 5.20.a exchange rates and spot and forward exchange rates describe functions of and participants in 5.20.b the foreign exchange market calculate and interpret the percentage change in a currency relative to 5.20.c another currency calculate and interpret currency cross5.20.d rates convert forward quotations expressed on a points basis or in percentage 5.20.e terms into an outright forward quotation explain the arbitrage relationship between spot rates, forward rates, and 5.20.f interest rates calculate and interpret a forward 5.20.g discount or premium Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain the Ricardian and Heckscher–Ohlin models of trade and the source(s) of comparative advantage in each model compare types of trade and capital restrictions and their economic implications explain motivations for and advantages of trading blocs, common markets, and economic unions describe common objectives of capital restrictions imposed by governments describe the balance of payments accounts including their components explain how decisions by consumers, firms, and governments affect the balance of payments describe functions and objectives of the international organizations that facilitate trade, including the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the World Trade Organization define an exchange rate and distinguish between nominal and real exchange rates and spot and forward exchange rates describe functions of and participants in the foreign exchange market calculate and interpret the percentage change in a currency relative to another currency calculate and interpret currency crossrates convert forward quotations expressed on a points basis or in percentage terms into an outright forward quotation explain the arbitrage relationship between spot rates, forward rates, and interest rates calculate and interpret a forward discount or premium passingscoreforum.com 15 Topic LOS Economics 6.21.h Economics 6.21.i Economics 6.21.j Financial Reporting 7.22.a Financial Reporting 7.22.b Financial Reporting 7.22.c Financial Reporting 7.22.d Financial Reporting 7.22.e Financial Reporting 7.22.f Financial Reporting 7.23.a Financial Reporting 7.23.b Financial Reporting 7.23.c Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) calculate and interpret the forward rate consistent with the spot rate and the interest rate in each currency describe exchange rate regimes explain the effects of exchange rates on countries’ international trade and capital flows describe the roles of financial reporting and financial statement analysis describe the roles of the statement of financial position, statement of comprehensive income, statement of changes in equity, and statement of cash flows in evaluating a company’s performance and financial position describe the importance of financial statement notes and supplementary information—including disclosures of accounting policies, methods, and estimates— and management’s commentary describe the objective of audits of financial statements, the types of audit reports, and the importance of effective internal controls identify and describe information sources that analysts use in financial statement analysis besides annual financial statements and supplementary information describe the steps in the financial statement analysis framework describe how business activities are classified for financial reporting purposes explain the relationship of financial statement elements and accounts, and classify accounts into the financial statement elements explain the accounting equation in its basic and expanded forms LOS 5.20.h 5.20.i 5.20.j 6.21.a 6.21.b 6.21.c 6.21.d 6.21.e 6.21.f 6.22.a 6.22.b 6.22.c Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared calculate and interpret the forward rate consistent with the spot rate and the interest rate in each currency describe exchange rate regimes explain the effects of exchange rates on countries’ international trade and capital flows describe the roles of financial reporting and financial statement analysis describe the roles of the statement of financial position, statement of comprehensive income, statement of changes in equity, and statement of cash flows in evaluating a company’s performance and financial position describe the importance of financial statement notes and supplementary information—including disclosures of accounting policies, methods, and estimates— and management’s commentary describe the objective of audits of financial statements, the types of audit reports, and the importance of effective internal controls identify and describe information sources that analysts use in financial statement analysis besides annual financial statements and supplementary information describe the steps in the financial statement analysis framework describe how business activities are classified for financial reporting purposes explain the relationship of financial statement elements and accounts, and classify accounts into the financial statement elements explain the accounting equation in its basic and expanded forms Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 16 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 7.23.d Financial Reporting 7.23.e Financial Reporting 7.23.f Financial Reporting Financial Reporting 7.23.g 7.23.h Financial Reporting 7.24.a Financial Reporting 7.24.b Financial Reporting 7.24.c Financial Reporting 7.24.d Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe the process of recording business transactions using an accounting system based on the accounting equation describe the need for accruals and valuation adjustments in preparing financial statements describe the relationships among the income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of owners’ equity describe the flow of information in an accounting system describe the use of the results of the accounting process in security analysis describe the objective of financial statements and the importance of financial reporting standards in security analysis and valuation describe roles and desirable attributes of financial reporting standard-setting bodies and regulatory authorities in establishing and enforcing reporting standards, and describe the role of the International Organization of Securities Commissions describe the status of global convergence of accounting standards and ongoing barriers to developing one universally accepted set of financial reporting standards describe the International Accounting Standards Board’s conceptual framework, including the objective and qualitative characteristics of financial statements, required reporting elements, and constraints and assumptions in preparing financial statements LOS 6.22.d 6.22.e 6.22.f 6.22.g 6.22.h 6.23.a 6.23.b 6.23.c 6.23.d Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe the process of recording business transactions using an accounting system based on the accounting equation describe the need for accruals and valuation adjustments in preparing financial statements describe the relationships among the income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of owners’ equity describe the flow of information in an accounting system describe the use of the results of the accounting process in security analysis describe the objective of financial statements and the importance of financial reporting standards in security analysis and valuation describe roles and desirable attributes of financial reporting standard-setting bodies and regulatory authorities in establishing and enforcing reporting standards, and describe the role of the International Organization of Securities Commissions describe the status of global convergence of accounting standards and ongoing barriers to developing one universally accepted set of financial reporting standards describe the International Accounting Standards Board’s conceptual framework, including the objective and qualitative characteristics of financial statements, required reporting elements, and constraints and assumptions in preparing financial statements Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 17 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 7.24.e Financial Reporting 7.24.f Financial Reporting 7.24.g Financial Reporting 7.24.h Financial Reporting 7.24.i Financial Reporting 8.25.a Financial Reporting 8.25.b Financial Reporting 8.25.c Financial Reporting 8.25.d Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe general requirements for financial statements under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) compare key concepts of financial reporting standards under IFRS and US generally accepted accounting principles (US GAAP) reporting systems identify characteristics of a coherent financial reporting framework and the barriers to creating such a framework describe implications for financial analysis of differing financial reporting systems and the importance of monitoring developments in financial reporting standards analyze company disclosures of significant accounting policies describe the components of the income statement and alternative presentation formats of that statement describe general principles of revenue recognition and accrual accounting, specific revenue recognition applications (including accounting for long-term contracts, installment sales, barter transactions, gross and net reporting of revenue), and implications of revenue recognition principles for financial analysis calculate revenue given information that might influence the choice of revenue recognition method describe key aspects of the converged accounting standards issued by the International Accounting Standards Board and Financial Accounting Standards Board in May 2014 LOS 6.23.e 6.23.f 6.23.g 6.23.h 6.23.i 7.24.a 7.24.b 7.24.c 7.24.d Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe general requirements for financial statements under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) compare key concepts of financial reporting standards under IFRS and US generally accepted accounting principles (US GAAP) reporting systems identify characteristics of a coherent financial reporting framework and the barriers to creating such a framework describe implications for financial analysis of differing financial reporting systems and the importance of monitoring developments in financial reporting standards analyze company disclosures of significant accounting policies describe the components of the income statement and alternative presentation formats of that statement describe general principles of revenue recognition and accrual accounting, specific revenue recognition applications (including accounting for long-term contracts, installment sales, barter transactions, gross and net reporting of revenue), and implications of revenue recognition principles for financial analysis calculate revenue given information that might influence the choice of revenue recognition method describe key aspects of the converged accounting standards for revenue recognition issued by the International Wording Accounting Standards Board and Change Financial Accounting Standards Board in May 2014 Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 18 Topic Financial Reporting LOS 8.25.e Financial Reporting 8.25.f Financial Reporting 8.25.g Financial Reporting 8.25.h Financial Reporting 8.25.i Financial Reporting 8.25.j Financial Reporting 8.25.k Financial Reporting 8.25.l Financial Reporting 8.25.m Financial Reporting Financial Reporting Financial Reporting 8.26.a 8.26.b 8.26.c Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe general principles of expense recognition, specific expense recognition applications, and implications of expense recognition choices for financial analysis describe the financial reporting treatment and analysis of non-recurring items (including discontinued operations, extraordinary items, unusual or infrequent items) and changes in accounting policies distinguish between the operating and non-operating components of the income statement describe how earnings per share is calculated and calculate and interpret a company’s earnings per share (both basic and diluted earnings per share) for both simple and complex capital structures distinguish between dilutive and antidilutive securities, and describe the implications of each for the earnings per share calculation convert income statements to commonsize income statements evaluate a company’s financial performance using common-size income statements and financial ratios based on the income statement describe, calculate, and interpret comprehensive income describe other comprehensive income, and identify major types of items included in it describe the elements of the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, and equity describe uses and limitations of the balance sheet in financial analysis describe alternative formats of balance sheet presentation LOS 7.24.e 7.24.f 7.24.g 7.24.h 7.24.i 7.24.j 7.24.k 7.24.l 7.24.m 7.25.a 7.25.b 7.25.c Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe general principles of expense recognition, specific expense recognition applications, and implications of expense recognition choices for financial analysis describe the financial reporting treatment and analysis of non-recurring Wording items (including discontinued Change operations, unusual or infrequent items) and changes in accounting policies distinguish between the operating and non-operating components of the income statement describe how earnings per share is calculated and calculate and interpret a company’s earnings per share (both basic and diluted earnings per share) for both simple and complex capital structures distinguish between dilutive and antidilutive securities and describe the implications of each for the earnings per share calculation convert income statements to commonsize income statements evaluate a company’s financial performance using common-size income statements and financial ratios based on the income statement describe, calculate, and interpret comprehensive income describe other comprehensive income and identify major types of items included in it describe the elements of the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, and equity describe uses and limitations of the balance sheet in financial analysis describe alternative formats of balance sheet presentation Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 19 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 8.26.d Financial Reporting 8.26.e Financial Reporting 8.26.f Financial Reporting 8.26.g Financial Reporting 8.26.h Financial Reporting 8.27.a Financial Reporting 8.27.b Financial Reporting 8.27.c Financial Reporting 8.27.d Financial Reporting 8.27.e Financial Reporting 8.27.f Financial Reporting Financial Reporting 8.27.g 8.27.h Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) distinguish between current and noncurrent assets, and current and noncurrent liabilities describe different types of assets and liabilities and the measurement bases of each describe the components of shareholders’ equity convert balance sheets to common-size balance sheets and interpret commonsize balance sheets calculate and interpret liquidity and solvency ratios compare cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities and classify cash flow items as relating to one of those three categories given a description of the items describe how non-cash investing and financing activities are reported contrast cash flow statements prepared under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (U.S. GAAP) distinguish between the direct and indirect methods of presenting cash from operating activities and describe arguments in favor of each method describe how the cash flow statement is linked to the income statement and the balance sheet describe the steps in the preparation of direct and indirect cash flow statements, including how cash flows can be computed using income statement and balance sheet data convert cash flows from the indirect to direct method analyze and interpret both reported and common-size cash flow statements LOS 7.25.d 7.25.e 7.25.f 7.25.g 7.25.h 7.26.a 7.26.b 7.26.c 7.26.d 7.26.e 7.26.f 7.26.g 7.26.h Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared distinguish between current and noncurrent assets and current and noncurrent liabilities describe different types of assets and liabilities and the measurement bases of each describe the components of shareholders’ equity convert balance sheets to common-size balance sheets and interpret commonsize balance sheets calculate and interpret liquidity and solvency ratios compare cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities and classify cash flow items as relating to one of those three categories given a description of the items describe how non-cash investing and financing activities are reported contrast cash flow statements prepared under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and US generally accepted accounting principles (US GAAP) distinguish between the direct and indirect methods of presenting cash from operating activities and describe arguments in favor of each method describe how the cash flow statement is linked to the income statement and the balance sheet describe the steps in the preparation of direct and indirect cash flow statements, including how cash flows can be computed using income statement and balance sheet data convert cash flows from the indirect to direct method analyze and interpret both reported and common-size cash flow statements Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 20 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 8.27.i Financial Reporting 8.28.a Financial Reporting 8.28.b Financial Reporting 8.28.c Financial Reporting 8.28.d Financial Reporting 8.28.e Financial Reporting 8.28.f Financial Reporting 8.28.g Financial Reporting 9.29.a Financial Reporting 9.29.b Financial Reporting 9.29.c Financial Reporting 9.29.d Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) calculate and interpret free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity, and performance and coverage cash flow ratios describe tools and techniques used in financial analysis, including their uses and limitations classify, calculate, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuation ratios describe relationships among ratios and evaluate a company using ratio analysis demonstrate the application of DuPont analysis of return on equity, and calculate and interpret effects of changes in its components calculate and interpret ratios used in equity analysis and credit analysis explain the requirements for segment reporting, and calculate and interpret segment ratios describe how ratio analysis and other techniques can be used to model and forecast earnings distinguish between costs included in inventories and costs recognised as expenses in the period in which they are incurred describe different inventory valuation methods (cost formulas) calculate and compare cost of sales, gross profit, and ending inventory using different inventory valuation methods and using perpetual and periodic inventory systems calculate and explain how inflation and deflation of inventory costs affect the financial statements and ratios of companies that use different inventory valuation methods LOS 7.26.i 7.27.a 7.27.b 7.27.c 7.27.d 7.27.e 7.27.f 7.27.g 8.28.a 8.28.b 8.28.c 8.28.d Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared calculate and interpret free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity, and performance and coverage cash flow ratios describe tools and techniques used in financial analysis, including their uses and limitations classify, calculate, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuation ratios describe relationships among ratios and evaluate a company using ratio analysis demonstrate the application of DuPont analysis of return on equity and calculate and interpret effects of changes in its components calculate and interpret ratios used in equity analysis and credit analysis explain the requirements for segment reporting and calculate and interpret segment ratios describe how ratio analysis and other techniques can be used to model and forecast earnings distinguish between costs included in inventories and costs recognised as expenses in the period in which they are incurred describe different inventory valuation methods (cost formulas) calculate and compare cost of sales, gross profit, and ending inventory using different inventory valuation methods and using perpetual and periodic inventory systems calculate and explain how inflation and deflation of inventory costs affect the financial statements and ratios of companies that use different inventory valuation methods Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 21 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 9.29.e Financial Reporting 9.29.f Financial Reporting 9.29.g Financial Reporting 9.29.h Financial Reporting 9.29.i Financial Reporting 9.29.j Financial Reporting 9.29.k Financial Reporting 9.29.l Financial Reporting 9.30.a Financial Reporting 9.30.b Financial Reporting 9.30.c Financial Reporting 9.30.d Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain LIFO reserve and LIFO liquidation and their effects on financial statements and ratios convert a company’s reported financial statements from LIFO to FIFO for purposes of comparison describe the measurement of inventory at the lower of cost and net realisable value describe implications of valuing inventory at net realisable value for financial statements and ratios describe the financial statement presentation of and disclosures relating to inventories explain issues that analysts should consider when examining a company’s inventory disclosures and other sources of information calculate and compare ratios of companies, including companies that use different inventory methods analyze and compare the financial statements of companies, including companies that use different inventory methods distinguish between costs that are capitalised and costs that are expensed in the period in which they are incurred compare the financial reporting of the following types of intangible assets: purchased, internally developed, acquired in a business combination explain and evaluate how capitalising versus expensing costs in the period in which they are incurred affects financial statements and ratios describe the different depreciation methods for property, plant, and equipment and calculate depreciation expense LOS 8.28.e 8.28.f 8.28.g 8.28.h 8.28.i 8.28.j 8.28.k 8.28.l 8.29.a 8.29.b 8.29.c 8.29.d Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain LIFO reserve and LIFO liquidation and their effects on financial statements and ratios convert a company’s reported financial statements from LIFO to FIFO for purposes of comparison describe the measurement of inventory at the lower of cost and net realisable value describe implications of valuing inventory at net realisable value for financial statements and ratios describe the financial statement presentation of and disclosures relating to inventories explain issues that analysts should consider when examining a company’s inventory disclosures and other sources of information calculate and compare ratios of companies, including companies that use different inventory methods analyze and compare the financial statements of companies, including companies that use different inventory methods distinguish between costs that are capitalised and costs that are expensed in the period in which they are incurred compare the financial reporting of the following types of intangible assets: purchased, internally developed, acquired in a business combination explain and evaluate how capitalising versus expensing costs in the period in which they are incurred affects financial statements and ratios describe the different depreciation methods for property, plant, and equipment and calculate depreciation expense Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 22 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 9.30.e Financial Reporting 9.30.f Financial Reporting 9.30.g Financial Reporting 9.30.h Financial Reporting 9.30.i Financial Reporting 9.30.j Financial Reporting 9.30.k Financial Reporting 9.30.l Financial Reporting 9.30.m Financial Reporting 9.30.n Financial Reporting 9.30.o Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe how the choice of depreciation method and assumptions concerning useful life and residual value affect depreciation expense, financial statements, and ratios describe the different amortisation methods for intangible assets with finite lives and calculate amortisation expense describe how the choice of amortisation method and assumptions concerning useful life and residual value affect amortisation expense, financial statements, and ratios describe the revaluation model explain the impairment of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets explain the derecognition of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets explain and evaluate how impairment, revaluation, and derecognition of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets affect financial statements and ratios describe the financial statement presentation of and disclosures relating to property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets analyze and interpret financial statement disclosures regarding property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets compare the financial reporting of investment property with that of property, plant, and equipment explain and evaluate how leasing rather than purchasing assets affects financial statements and ratios LOS 8.29.e 8.29.f 8.29.g 8.29.h 8.29.i 8.29.j 8.29.k 8.29.l 8.29.m 8.29.n 8.29.o Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe how the choice of depreciation method and assumptions concerning useful life and residual value affect depreciation expense, financial statements, and ratios describe the different amortisation methods for intangible assets with finite lives and calculate amortisation expense describe how the choice of amortisation method and assumptions concerning useful life and residual value affect amortisation expense, financial statements, and ratios describe the revaluation model explain the impairment of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets explain the derecognition of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets explain and evaluate how impairment, revaluation, and derecognition of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets affect financial statements and ratios describe the financial statement presentation of and disclosures relating to property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets analyze and interpret financial statement disclosures regarding property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets compare the financial reporting of investment property with that of property, plant, and equipment explain and evaluate how leasing rather than purchasing assets affects financial statements and ratios Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 23 Topic Financial Reporting LOS 9.30.p Financial Reporting 9.31.a Financial Reporting 9.31.b Financial Reporting 9.31.c Financial Reporting 9.31.d Financial Reporting 9.31.e Financial Reporting 9.31.f Financial Reporting 9.31.g Financial Reporting 9.31.h Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain and evaluate how finance leases and operating leases affect financial statements and ratios from the perspective of both the lessor and the lessee describe the differences between accounting profit and taxable income, and define key terms, including deferred tax assets, deferred tax liabilities, valuation allowance, taxes payable, and income tax expense explain how deferred tax liabilities and assets are created and the factors that determine how a company’s deferred tax liabilities and assets should be treated for the purposes of financial analysis calculate the tax base of a company’s assets and liabilities calculate income tax expense, income taxes payable, deferred tax assets, and deferred tax liabilities, and calculate and interpret the adjustment to the financial statements related to a change in the income tax rate evaluate the impact of tax rate changes on a company’s financial statements and ratios distinguish between temporary and permanent differences in pre-tax accounting income and taxable income describe the valuation allowance for deferred tax assets—when it is required and what impact it has on financial statements explain recognition and measurement of current and deferred tax items LOS 8.29.p 8.30.a 8.30.b 8.30.c 8.30.d 8.30.e 8.30.f 8.30.g 8.30.h Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain and evaluate how finance leases and operating leases affect financial statements and ratios from the perspective of both the lessor and the lessee describe the differences between accounting profit and taxable income and define key terms, including deferred tax assets, deferred tax liabilities, valuation allowance, taxes payable, and income tax expense explain how deferred tax liabilities and assets are created and the factors that determine how a company’s deferred tax liabilities and assets should be treated for the purposes of financial analysis calculate the tax base of a company’s assets and liabilities calculate income tax expense, income taxes payable, deferred tax assets, and deferred tax liabilities, and calculate and interpret the adjustment to the financial statements related to a change in the income tax rate evaluate the impact of tax rate changes on a company’s financial statements and ratios distinguish between temporary and permanent differences in pre-tax accounting income and taxable income describe the valuation allowance for deferred tax assets—when it is required and what impact it has on financial statements explain recognition and measurement of current and deferred tax items Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 24 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 9.31.i Financial Reporting 9.31.j Financial Reporting 9.32.a Financial Reporting 9.32.b Financial Reporting Financial Reporting 9.32.c 9.32.d Financial Reporting 9.32.e Financial Reporting 9.32.f Financial Reporting 9.32.g Financial Reporting 9.32.h Financial Reporting 9.32.i Financial Reporting 9.32.j Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) analyze disclosures relating to deferred tax items and the effective tax rate reconciliation, and explain how information included in these disclosures affects a company’s financial statements and financial ratios identify the key provisions of and differences between income tax accounting under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and US generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) determine the initial recognition, initial measurement and subsequent measurement of bonds describe the effective interest method and calculate interest expense, amortisation of bond discounts/premiums, and interest payments LOS 8.30.i 8.30.j 8.31.a 8.31.b 8.31.c explain the derecognition of debt describe the role of debt covenants in 8.31.d protecting creditors describe the financial statement presentation of and disclosures relating 8.31.e to debt explain motivations for leasing assets 8.31.f instead of purchasing them distinguish between a finance lease and an operating lease from the 8.31.g perspectives of the lessor and the lessee determine the initial recognition, initial measurement, and subsequent 8.31.h measurement of finance leases compare the disclosures relating to 8.31.i finance and operating leases compare the presentation and disclosure of defined contribution and 8.31.j defined benefit pension plans Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared analyze disclosures relating to deferred tax items and the effective tax rate reconciliation and explain how information included in these disclosures affects a company’s financial statements and financial ratios identify the key provisions of and differences between income tax accounting under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and US generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) determine the initial recognition, initial measurement and subsequent measurement of bonds describe the effective interest method and calculate interest expense, amortisation of bond discounts/premiums, and interest payments explain the derecognition of debt describe the role of debt covenants in protecting creditors describe the financial statement presentation of and disclosures relating to debt explain motivations for leasing assets instead of purchasing them distinguish between a finance lease and an operating lease from the perspectives of the lessor and the lessee determine the initial recognition, initial measurement, and subsequent measurement of finance leases compare the disclosures relating to finance and operating leases compare the presentation and disclosure of defined contribution and defined benefit pension plans passingscoreforum.com 25 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 9.32.k Financial Reporting 10.33.a Financial Reporting Financial Reporting 10.33.b 10.33.c Financial Reporting 10.33.d Financial Reporting 10.33.e Financial Reporting 10.33.f Financial Reporting 10.33.g Financial Reporting 10.33.h Financial Reporting 10.33.i Financial Reporting 10.34.a Financial Reporting 10.34.b Financial Reporting 10.34.c Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) calculate and interpret leverage and coverage ratios distinguish between financial reporting quality and quality of reported results (including quality of earnings, cash flow, and balance sheet items) describe a spectrum for assessing financial reporting quality distinguish between conservative and aggressive accounting describe motivations that might cause management to issue financial reports that are not high quality describe conditions that are conducive to issuing low-quality, or even fraudulent, financial reports describe mechanisms that discipline financial reporting quality and the potential limitations of those mechanisms describe presentation choices, including non-GAAP measures, that could be used to influence an analyst’s opinion describe accounting methods (choices and estimates) that could be used to manage earnings, cash flow, and balance sheet items describe accounting warning signs and methods for detecting manipulation of information in financial reports evaluate a company’s past financial performance and explain how a company’s strategy is reflected in past financial performance forecast a company’s future net income and cash flow describe the role of financial statement analysis in assessing the credit quality of a potential debt investment LOS 8.31.k 9.32.a 9.32.b 9.32.c 9.32.d 9.32.e 9.32.f 9.32.g 9.32.h 9.32.i 9.33.a 9.33.b 9.33.c Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared calculate and interpret leverage and coverage ratios distinguish between financial reporting quality and quality of reported results (including quality of earnings, cash flow, and balance sheet items) describe a spectrum for assessing financial reporting quality distinguish between conservative and aggressive accounting describe motivations that might cause management to issue financial reports that are not high quality describe conditions that are conducive to issuing low-quality, or even fraudulent, financial reports describe mechanisms that discipline financial reporting quality and the potential limitations of those mechanisms describe presentation choices, including non-GAAP measures, that could be used to influence an analyst’s opinion describe accounting methods (choices and estimates) that could be used to manage earnings, cash flow, and balance sheet items describe accounting warning signs and methods for detecting manipulation of information in financial reports evaluate a company’s past financial performance and explain how a company’s strategy is reflected in past financial performance forecast a company’s future net income and cash flow describe the role of financial statement analysis in assessing the credit quality of a potential debt investment Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 26 Topic LOS Financial Reporting 10.34.d Financial Reporting 10.34.e Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe the use of financial statement analysis in screening for potential equity investments explain appropriate analyst adjustments to a company’s financial statements to facilitate comparison with another company LOS 9.33.d 9.33.e Financial Reporting 10.34.a Financial Reporting 10.34.b Financial Reporting 10.34.c Financial Reporting 10.34.d Financial Reporting 10.34.e Financial Reporting 10.34.f Financial Reporting 10.34.g Financial Reporting 10.34.h Financial Reporting 10.34.i Financial Reporting 10.34.j Financial Reporting 10.34.k Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe the use of financial statement analysis in screening for potential equity investments explain appropriate analyst adjustments to a company’s financial statements to facilitate comparison with another company describe corporate governance describe a company’s stakeholder groups and compare interests of stakeholder groups describe principal–agent and other relationships in corporate governance and the conflicts that may arise in these relationships describe stakeholder management describe mechanisms to manage stakeholder relationships and mitigate associated risks describe functions and responsibilities of a company’s board of directors and its committees describe market and non-market factors that can affect stakeholder relationships and corporate governance identify potential risks of poor corporate governance and stakeholder management and identify benefits from effective corporate governance and stakeholder management describe factors relevant to the analysis of corporate governance and stakeholder management describe environmental and social considerations in investment analysis describe how environmental, social, and governance factors may be used in investment analysis Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com New New New New New New New New New New New 27 Topic LOS Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) LOS Financial Reporting 10.35.a Financial Reporting 10.35.b Financial Reporting 10.35.c Financial Reporting 10.35.d Financial Reporting 10.35.e Financial Reporting 10.35.f Corporate Finance 11.35.a Corporate Finance 11.35.b Corporate Finance 11.35.c Corporate Finance 11.35.d Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) describe the capital budgeting process and distinguish among the various categories of capital projects describe the basic principles of capital budgeting explain how the evaluation and selection of capital projects is affected by mutually exclusive projects, project sequencing, and capital rationing calculate and interpret net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, discounted payback period, and profitability index (PI) of a single capital project explain the NPV profile, compare the NPV and IRR methods when evaluating independent and mutually exclusive projects, and describe the problems associated with each of the evaluation methods describe expected relations among an investment’s NPV, company value, and share price describe the capital budgeting process and distinguish among the various categories of capital projects describe the basic principles of capital budgeting explain how the evaluation and selection of capital projects is affected by mutually exclusive projects, project sequencing, and capital rationing calculate and interpret net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, discounted payback period, and profitability index (PI) of a single capital project Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com Compared New New New New New New Removed Removed Removed Removed 28 Topic LOS Corporate Finance 11.35.e Corporate Finance 11.35.f Corporate Finance 11.36.a Corporate Finance 11.36.b Corporate Finance 11.36.c Corporate Finance 11.36.d Corporate Finance 11.36.e Corporate Finance 11.36.f Corporate Finance 11.36.g Corporate Finance 11.36.h Corporate Finance Corporate Finance 11.36.i 11.36.j Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain the NPV profile, compare the NPV and IRR methods when evaluating independent and mutually exclusive projects, and describe the problems associated with each of the evaluation methods describe expected relations among an investment’s NPV, company value, and share price calculate and interpret the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of a company describe how taxes affect the cost of capital from different capital sources describe the use of target capital structure in estimating WACC and how target capital structure weights may be determined explain how the marginal cost of capital and the investment opportunity schedule are used to determine the optimal capital budget explain the marginal cost of capital’s role in determining the net present value of a project calculate and interpret the cost of debt capital using the yield-to-maturity approach and the debt-rating approach calculate and interpret the cost of noncallable, nonconvertible preferred stock calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount model approach, and the bondyield-plus risk-premium approach calculate and interpret the beta and cost of capital for a project describe uses of country risk premiums in estimating the cost of equity LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared Removed Removed 10.36.a 10.36.b 10.36.c 10.36.d 10.36.e 10.36.f 10.36.g 10.36.h 10.36.i 10.36.j calculate and interpret the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of a company describe how taxes affect the cost of capital from different capital sources describe the use of target capital structure in estimating WACC and how target capital structure weights may be determined explain how the marginal cost of capital and the investment opportunity schedule are used to determine the optimal capital budget explain the marginal cost of capital’s role in determining the net present value of a project calculate and interpret the cost of debt capital using the yield-to-maturity approach and the debt-rating approach calculate and interpret the cost of noncallable, nonconvertible preferred stock calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount model approach, and the bondyield-plus risk-premium approach calculate and interpret the beta and cost of capital for a project describe uses of country risk premiums in estimating the cost of equity Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 29 Topic LOS Corporate Finance 11.36.k Corporate Finance 11.36.l Corporate Finance 11.37.a Corporate Finance 11.37.b Corporate Finance 11.37.c Corporate Finance 11.37.d Corporate Finance 11.37.e Corporate Finance 11.38.a Corporate Finance 11.38.b Corporate Finance 11.38.c Corporate Finance 11.38.d Corporate Finance 11.38.e Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe the marginal cost of capital schedule, explain why it may be upward-sloping with respect to additional capital, and calculate and interpret its break-points explain and demonstrate the correct treatment of flotation costs define and explain leverage, business risk, sales risk, operating risk, and financial risk, and classify a risk calculate and interpret the degree of operating leverage, the degree of financial leverage, and the degree of total leverage analyze the effect of financial leverage on a company’s net income and return on equity calculate the breakeven quantity of sales and determine the company’s net income at various sales levels calculate and interpret the operating breakeven quantity of sales describe regular cash dividends, extra dividends, liquidating dividends, stock dividends, stock splits, and reverse stock splits, including their expected effect on shareholders’ wealth and a company’s financial ratios describe dividend payment chronology, including the significance of declaration, holder-of-record, exdividend, and payment dates LOS 10.36.k 10.36.l 11.37.a 11.37.b 11.37.c 11.37.d 11.37.e 11.38.a 11.38.b 11.38.c compare share repurchase methods calculate and compare the effect of a share repurchase on earnings per share when 1) the repurchase is financed 11.38.d with the company’s excess cash and 2) the company uses debt to finance the repurchase calculate the effect of a share 11.38.e repurchase on book value per share Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe the marginal cost of capital schedule, explain why it may be upwardsloping with respect to additional capital, and calculate and interpret its break-points explain and demonstrate the correct treatment of flotation costs define and explain leverage, business risk, sales risk, operating risk, and financial risk and classify a risk calculate and interpret the degree of operating leverage, the degree of financial leverage, and the degree of total leverage analyze the effect of financial leverage on a company’s net income and return on equity calculate the breakeven quantity of sales and determine the company’s net income at various sales levels calculate and interpret the operating breakeven quantity of sales describe regular cash dividends, extra dividends, liquidating dividends, stock dividends, stock splits, and reverse stock splits, including their expected effect on shareholders’ wealth and a company’s financial ratios describe dividend payment chronology, including the significance of declaration, holder-of-record, ex-dividend, and payment dates compare share repurchase methods calculate and compare the effect of a share repurchase on earnings per share when 1) the repurchase is financed with the company’s excess cash and 2) the company uses debt to finance the repurchase calculate the effect of a share repurchase on book value per share passingscoreforum.com 30 Topic LOS Corporate Finance 11.38.f Corporate Finance 11.39.a Corporate Finance 11.39.b Corporate Finance 11.39.c Corporate Finance 11.39.d Corporate Finance 11.39.e Corporate Finance 11.39.f Corporate Finance 11.39.g Corporate Finance 11.40.a Corporate Finance 11.40.b Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain why a cash dividend and a share repurchase of the same amount are equivalent in terms of the effect on shareholders’ wealth, all else being equal describe primary and secondary sources of liquidity and factors that influence a company’s liquidity position compare a company’s liquidity measures with those of peer companies evaluate working capital effectiveness of a company based on its operating and cash conversion cycles, and compare the company’s effectiveness with that of peer companies describe how different types of cash flows affect a company’s net daily cash position calculate and interpret comparable yields on various securities, compare portfolio returns against a standard benchmark, and evaluate a company’s short-term investment policy guidelines evaluate a company’s management of accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable over time and compared to peer companies evaluate the choices of short-term funding available to a company and recommend a financing method LOS 11.38.f 11.39.a 11.39.b 11.39.c 11.39.d 11.39.e 11.39.f 11.39.g Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain why a cash dividend and a share repurchase of the same amount are equivalent in terms of the effect on shareholders’ wealth, all else being equal describe primary and secondary sources of liquidity and factors that influence a company’s liquidity position compare a company’s liquidity measures with those of peer companies evaluate working capital effectiveness of a company based on its operating and cash conversion cycles and compare the company’s effectiveness with that of peer companies describe how different types of cash flows affect a company’s net daily cash position calculate and interpret comparable yields on various securities, compare portfolio returns against a standard benchmark, and evaluate a company’s short-term investment policy guidelines evaluate a company’s management of accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable over time and compared to peer companies evaluate the choices of short-term funding available to a company and recommend a financing method define corporate governance describe practices related to board and committee independence, experience, compensation, external consultants, and frequency of elections, and determine whether they are supportive of shareowner protection Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com Removed Removed 31 Topic LOS Corporate Finance 11.40.c Corporate Finance 11.40.d Corporate Finance 11.40.e Corporate Finance 11.40.f Corporate Finance 11.40.g Portfolio Management 12.41.a Portfolio Management 12.41.b Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management 12.41.c 12.41.d 12.41.e 12.42.a 12.42.b 12.42.c 12.42.d Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe board independence and explain the importance of independent board members in corporate governance identify factors that an analyst should consider when evaluating the qualifications of board members describe responsibilities of the audit, compensation, and nominations committees and identify factors an investor should consider when evaluating the quality of each committee describe provisions that should be included in a strong corporate code of ethics evaluate, from a shareowner’s perspective, company policies related to voting rules, shareowner sponsored proposals, common stock classes, and takeover defenses describe the portfolio approach to investing describe types of investors and distinctive characteristics and needs of each describe defined contribution and defined benefit pension plans describe the steps in the portfolio management process describe mutual funds and compare them with other pooled investment products define risk management describe features of a risk management framework define risk governance and describe elements of effective risk governance explain how risk tolerance affects risk management LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared Removed Removed Removed Removed Removed 12.40.a 12.40.b 12.40.c 12.40.d 12.40.e 12.41.a 12.41.b 12.41.c 12.41.d describe the portfolio approach to investing describe types of investors and distinctive characteristics and needs of each describe defined contribution and defined benefit pension plans describe the steps in the portfolio management process describe mutual funds and compare them with other pooled investment products define risk management describe features of a risk management framework define risk governance and describe elements of effective risk governance explain how risk tolerance affects risk management Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 32 Topic LOS Portfolio Management 12.42.e Portfolio Management 12.42.f Portfolio Management 12.42.g Portfolio Management 12.43.a Portfolio Management 12.43.b Portfolio Management 12.43.c Portfolio Management Portfolio Management 12.43.d 12.43.e Portfolio Management 12.43.f Portfolio Management 12.43.g Portfolio Management 12.43.h Portfolio Management 12.44.a Portfolio Management 12.44.b Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe risk budgeting and its role in risk governance identify financial and non-financial sources of risk and describe how they may interact describe methods for measuring and modifying risk exposures and factors to consider in choosing among the methods calculate and interpret major return measures and describe their appropriate uses describe characteristics of the major asset classes that investors consider in forming portfolios calculate and interpret the mean, variance, and covariance (or correlation) of asset returns based on historical data explain risk aversion and its implications for portfolio selection calculate and interpret portfolio standard deviation describe the effect on a portfolio’s risk of investing in assets that are less than perfectly correlated describe and interpret the minimumvariance and efficient frontiers of risky assets and the global minimumvariance portfolio explain the selection of an optimal portfolio, given an investor’s utility (or risk aversion) and the capital allocation line describe the implications of combining a risk-free asset with a portfolio of risky assets explain the capital allocation line (CAL) and the capital market line (CML) LOS 12.41.e 12.41.f 12.41.g 12.42.a 12.42.b 12.42.c 12.42.d 12.42.e 12.42.f 12.42.g 12.42.h 12.43.a 12.43.b Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe risk budgeting and its role in risk governance identify financial and non-financial sources of risk and describe how they may interact describe methods for measuring and modifying risk exposures and factors to consider in choosing among the methods calculate and interpret major return measures and describe their appropriate uses describe characteristics of the major asset classes that investors consider in forming portfolios calculate and interpret the mean, variance, and covariance (or correlation) of asset returns based on historical data explain risk aversion and its implications for portfolio selection calculate and interpret portfolio standard deviation describe the effect on a portfolio’s risk of investing in assets that are less than perfectly correlated describe and interpret the minimumvariance and efficient frontiers of risky assets and the global minimum-variance portfolio explain the selection of an optimal portfolio, given an investor’s utility (or risk aversion) and the capital allocation line describe the implications of combining a risk-free asset with a portfolio of risky assets explain the capital allocation line (CAL) and the capital market line (CML) Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 33 Topic LOS Portfolio Management 12.44.c Portfolio Management 12.44.d Portfolio Management 12.44.e Portfolio Management 12.44.f Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management 12.44.g 12.44.h 12.45.a 12.45.b 12.45.c 12.45.d Portfolio Management 12.45.e Portfolio Management 12.45.f Portfolio Management 12.45.g Equity 13.46.a Equity 13.46.b Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) explain systematic and nonsystematic risk, including why an investor should not expect to receive additional return for bearing nonsystematic risk explain return generating models (including the market model) and their uses calculate and interpret beta explain the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), including its assumptions, and the security market line (SML) calculate and interpret the expected return of an asset using the CAPM describe and demonstrate applications of the CAPM and the SML describe the reasons for a written investment policy statement (IPS) describe the major components of an IPS describe risk and return objectives and how they may be developed for a client distinguish between the willingness and the ability (capacity) to take risk in analyzing an investor’s financial risk tolerance describe the investment constraints of liquidity, time horizon, tax concerns, legal and regulatory factors, and unique circumstances and their implications for the choice of portfolio assets explain the specification of asset classes in relation to asset allocation describe the principles of portfolio construction and the role of asset allocation in relation to the IPS explain the main functions of the financial system describe classifications of assets and markets LOS 12.43.c 12.43.d 12.43.e 12.43.f 12.43.g 12.43.h 12.44.a 12.44.b 12.44.c 12.44.d 12.44.e 12.44.f 12.44.g 13.45.a 13.45.b Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared explain systematic and nonsystematic risk, including why an investor should not expect to receive additional return for bearing nonsystematic risk explain return generating models (including the market model) and their uses calculate and interpret beta explain the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), including its assumptions, and the security market line (SML) calculate and interpret the expected return of an asset using the CAPM describe and demonstrate applications of the CAPM and the SML describe the reasons for a written investment policy statement (IPS) describe the major components of an IPS describe risk and return objectives and how they may be developed for a client distinguish between the willingness and the ability (capacity) to take risk in analyzing an investor’s financial risk tolerance describe the investment constraints of liquidity, time horizon, tax concerns, legal and regulatory factors, and unique circumstances and their implications for the choice of portfolio assets explain the specification of asset classes in relation to asset allocation describe the principles of portfolio construction and the role of asset allocation in relation to the IPS explain the main functions of the financial system describe classifications of assets and markets Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 34 Topic LOS Equity 13.46.c Equity 13.46.d Equity 13.46.e Equity 13.46.f Equity 13.46.g Equity 13.46.h Equity 13.46.i Equity 13.46.j Equity 13.46.k Equity 13.46.l Equity 13.47.a Equity 13.47.b Equity 13.47.c Equity 13.47.d Equity 13.47.e Equity 13.47.f Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe the major types of securities, currencies, contracts, commodities, and real assets that trade in organized markets, including their distinguishing characteristics and major subtypes describe types of financial intermediaries and services that they provide compare positions an investor can take in an asset calculate and interpret the leverage ratio, the rate of return on a margin transaction, and the security price at which the investor would receive a margin call compare execution, validity, and clearing instructions compare market orders with limit orders define primary and secondary markets and explain how secondary markets support primary markets describe how securities, contracts, and currencies are traded in quote-driven, order-driven, and brokered markets describe characteristics of a wellfunctioning financial system describe objectives of market regulation describe a security market index calculate and interpret the value, price return, and total return of an index describe the choices and issues in index construction and management compare the different weighting methods used in index construction calculate and analyze the value and return of an index given its weighting method describe rebalancing and reconstitution of an index LOS 13.45.c 13.45.d 13.45.e 13.45.f 13.45.g 13.45.h 13.45.i 13.45.j 13.45.k 13.45.l 13.46.a 13.46.b 13.46.c 13.46.d 13.46.e 13.46.f Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe the major types of securities, currencies, contracts, commodities, and real assets that trade in organized markets, including their distinguishing characteristics and major subtypes describe types of financial intermediaries and services that they provide compare positions an investor can take in an asset calculate and interpret the leverage ratio, the rate of return on a margin transaction, and the security price at which the investor would receive a margin call compare execution, validity, and clearing instructions compare market orders with limit orders define primary and secondary markets and explain how secondary markets support primary markets describe how securities, contracts, and currencies are traded in quote-driven, order-driven, and brokered markets describe characteristics of a wellfunctioning financial system describe objectives of market regulation describe a security market index calculate and interpret the value, price return, and total return of an index describe the choices and issues in index construction and management compare the different weighting methods used in index construction calculate and analyze the value and return of an index given its weighting method describe rebalancing and reconstitution of an index Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 35 Topic LOS Equity 13.47.g Equity Equity 13.47.h 13.47.i Equity 13.47.j Equity 13.47.k Equity 13.48.a Equity 13.48.b Equity 13.48.c Equity 13.48.d Equity 13.48.e Equity 13.48.f Equity 13.48.g Equity 14.49.a Equity 14.49.b Equity 14.49.c Equity 14.49.d Equity 14.49.e Equity 14.49.f Equity 14.49.g Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) LOS 13.46.g describe uses of security market indices describe types of equity indices 13.46.h describe types of fixed-income indices 13.46.i describe indices representing 13.46.j alternative investments compare types of security market 13.46.k indices describe market efficiency and related concepts, including their importance to 13.47.a investment practitioners distinguish between market value and 13.47.b intrinsic value explain factors that affect a market’s 13.47.c efficiency contrast weak-form, semi-strong-form, 13.47.d and strong-form market efficiency explain the implications of each form of market efficiency for fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and the 13.47.e choice between active and passive portfolio management describe market anomalies 13.47.f describe behavioral finance and its potential relevance to understanding 13.47.g market anomalies describe characteristics of types of 14.48.a equity securities describe differences in voting rights and other ownership characteristics among 14.48.b different equity classes distinguish between public and private 14.48.c equity securities describe methods for investing in non14.48.d domestic equity securities compare the risk and return characteristics of different types of 14.48.e equity securities explain the role of equity securities in 14.48.f the financing of a company’s assets distinguish between the market value 14.48.g and book value of equity securities Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) describe uses of security market indices describe types of equity indices describe types of fixed-income indices describe indices representing alternative investments compare types of security market indices describe market efficiency and related concepts, including their importance to investment practitioners distinguish between market value and intrinsic value explain factors that affect a market’s efficiency contrast weak-form, semi-strong-form, and strong-form market efficiency explain the implications of each form of market efficiency for fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and the choice between active and passive portfolio management describe market anomalies describe behavioral finance and its potential relevance to understanding market anomalies describe characteristics of types of equity securities describe differences in voting rights and other ownership characteristics among different equity classes distinguish between public and private equity securities describe methods for investing in nondomestic equity securities compare the risk and return characteristics of different types of equity securities explain the role of equity securities in the financing of a company’s assets distinguish between the market value and book value of equity securities passingscoreforum.com Compared 36 Topic LOS Equity 14.49.h Equity 14.50.a Equity 14.50.b Equity 14.50.c Equity 14.50.d Equity 14.50.e Equity 14.50.f Equity 14.50.g Equity 14.50.h Equity 14.50.i Equity 14.50.j Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) compare a company’s cost of equity, its (accounting) return on equity, and investors’ required rates of return explain uses of industry analysis and the relation of industry analysis to company analysis compare methods by which companies can be grouped, current industry classification systems, and classify a company, given a description of its activities and the classification system explain the factors that affect the sensitivity of a company to the business cycle and the uses and limitations of industry and company descriptors such as “growth,” “defensive,” and “cyclical” explain how a company’s industry classification can be used to identify a potential “peer group” for equity valuation describe the elements that need to be covered in a thorough industry analysis describe the principles of strategic analysis of an industry explain the effects of barriers to entry, industry concentration, industry capacity, and market share stability on pricing power and price competition describe industry life cycle models, classify an industry as to life cycle stage, and describe limitations of the life-cycle concept in forecasting industry performance compare characteristics of representative industries from the various economic sectors describe macroeconomic, technological, demographic, governmental, and social influences on industry growth, profitability, and risk LOS 14.48.h 14.49.a 14.49.b 14.49.c 14.49.d 14.49.e 14.49.f 14.49.g 14.49.h 14.49.i 14.49.j Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared compare a company’s cost of equity, its (accounting) return on equity, and investors’ required rates of return explain uses of industry analysis and the relation of industry analysis to company analysis compare methods by which companies can be grouped, current industry classification systems, and classify a company, given a description of its activities and the classification system explain the factors that affect the sensitivity of a company to the business cycle and the uses and limitations of industry and company descriptors such as “growth,” “defensive,” and “cyclical” explain how a company’s industry classification can be used to identify a potential “peer group” for equity valuation describe the elements that need to be covered in a thorough industry analysis describe the principles of strategic analysis of an industry explain the effects of barriers to entry, industry concentration, industry capacity, and market share stability on pricing power and price competition describe industry life cycle models, classify an industry as to life cycle stage, and describe limitations of the life-cycle concept in forecasting industry performance compare characteristics of representative industries from the various economic sectors describe macroeconomic, technological, demographic, governmental, and social influences on industry growth, profitability, and risk Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 37 Topic LOS Equity 14.50.k Equity 14.51.a Equity 14.51.b Equity 14.51.c Equity 14.51.d Equity 14.51.e Equity 14.51.f Equity 14.51.g Equity 14.51.h Equity 14.51.i Equity 14.51.j Equity 14.51.k Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe the elements that should be covered in a thorough company analysis evaluate whether a security, given its current market price and a value estimate, is overvalued, fairly valued, or undervalued by the market describe major categories of equity valuation models explain the rationale for using present value models to value equity and describe the dividend discount and freecash-flow-to-equity models calculate the intrinsic value of a noncallable, non-convertible preferred stock calculate and interpret the intrinsic value of an equity security based on the Gordon (constant) growth dividend discount model or a two-stage dividend discount model, as appropriate identify characteristics of companies for which the constant growth or a multistage dividend discount model is appropriate explain the rationale for using price multiples to value equity, how the price to earnings multiple relates to fundamentals, and the use of multiples based on comparables calculate and interpret the following multiples: price to earnings, price to an estimate of operating cash flow, price to sales, and price to book value describe enterprise value multiples and their use in estimating equity value describe asset-based valuation models and their use in estimating equity value explain advantages and disadvantages of each category of valuation model LOS 14.49.k 14.50.a 14.50.b 14.50.c 14.50.d 14.50.e 14.50.f 14.50.g 14.50.h 14.50.i 14.50.j 14.50.k Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe the elements that should be covered in a thorough company analysis evaluate whether a security, given its current market price and a value estimate, is overvalued, fairly valued, or undervalued by the market describe major categories of equity valuation models explain the rationale for using present value models to value equity and describe the dividend discount and freecash-flow-to-equity models calculate the intrinsic value of a noncallable, non-convertible preferred stock calculate and interpret the intrinsic value of an equity security based on the Gordon (constant) growth dividend discount model or a two-stage dividend discount model, as appropriate identify characteristics of companies for which the constant growth or a multistage dividend discount model is appropriate explain the rationale for using price multiples to value equity, how the price to earnings multiple relates to fundamentals, and the use of multiples based on comparables calculate and interpret the following multiples: price to earnings, price to an estimate of operating cash flow, price to sales, and price to book value describe enterprise value multiples and their use in estimating equity value describe asset-based valuation models and their use in estimating equity value explain advantages and disadvantages of each category of valuation model Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 38 Topic LOS Fixed Income 15.52.a Fixed Income 15.52.b Fixed Income 15.52.c Fixed Income 15.52.d Fixed Income 15.52.e Fixed Income 15.52.f Fixed Income 15.53.a Fixed Income 15.53.b Fixed Income 15.53.c Fixed Income 15.53.d Fixed Income 15.53.e Fixed Income 15.53.f Fixed Income 15.53.g Fixed Income 15.53.h Fixed Income 15.53.i Fixed Income 15.54.a Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe basic features of a fixedincome security describe content of a bond indenture compare affirmative and negative covenants and identify examples of each describe how legal, regulatory, and tax considerations affect the issuance and trading of fixed-income securities describe how cash flows of fixedincome securities are structured describe contingency provisions affecting the timing and/or nature of cash flows of fixed-income securities and identify whether such provisions benefit the borrower or the lender describe classifications of global fixedincome markets describe the use of interbank offered rates as reference rates in floating-rate debt describe mechanisms available for issuing bonds in primary markets describe secondary markets for bonds describe securities issued by sovereign governments describe securities issued by nonsovereign governments, quasigovernment entities, and supranational agencies describe types of debt issued by corporations describe short-term funding alternatives available to banks describe repurchase agreements (repos) and the risks associated with them calculate a bond’s price given a market discount rate LOS 15.51.a 15.51.b 15.51.c 15.51.d 15.51.e 15.51.f 15.52.a 15.52.b 15.52.c 15.52.d 15.52.e 15.52.f 15.52.g 15.52.h 15.52.i 15.53.a Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe basic features of a fixedincome security describe content of a bond indenture compare affirmative and negative covenants and identify examples of each describe how legal, regulatory, and tax considerations affect the issuance and trading of fixed-income securities describe how cash flows of fixed-income securities are structured describe contingency provisions affecting the timing and/or nature of cash flows of fixed-income securities and identify whether such provisions benefit the borrower or the lender describe classifications of global fixedincome markets describe the use of interbank offered rates as reference rates in floating-rate debt describe mechanisms available for issuing bonds in primary markets describe secondary markets for bonds describe securities issued by sovereign governments describe securities issued by nonsovereign governments, quasigovernment entities, and supranational agencies describe types of debt issued by corporations describe short-term funding alternatives available to banks describe repurchase agreements (repos) and the risks associated with them calculate a bond’s price given a market discount rate Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 39 Topic LOS Fixed Income 15.54.b Fixed Income 15.54.c Fixed Income 15.54.d Fixed Income 15.54.e Fixed Income 15.54.f Fixed Income 15.54.g Fixed Income 15.54.h Fixed Income 15.54.i Fixed Income 15.55.a Fixed Income 15.55.b Fixed Income 15.55.c Fixed Income 15.55.d Fixed Income 15.55.e Fixed Income 15.55.f Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) LOS identify the relationships among a bond’s price, coupon rate, maturity, 15.53.b and market discount rate (yield-tomaturity) define spot rates and calculate the 15.53.c price of a bond using spot rates describe and calculate the flat price, accrued interest, and the full price of a 15.53.d bond describe matrix pricing 15.53.e calculate and interpret yield measures for fixed-rate bonds, floating-rate 15.53.f notes, and money market instruments define and compare the spot curve, yield curve on coupon bonds, par 15.53.g curve, and forward curve define forward rates and calculate spot rates from forward rates, forward rates 15.53.h from spot rates, and the price of a bond using forward rates compare, calculate, and interpret yield 15.53.i spread measures explain benefits of securitization for 15.54.a economies and financial markets describe securitization, including the parties involved in the process and the 15.54.b roles they play describe typical structures of securitizations, including credit 15.54.c tranching and time tranching describe types and characteristics of residential mortgage loans that are 15.54.d typically securitized describe types and characteristics of residential mortgage-backed securities, including mortgage pass-through 15.54.e securities and collateralized mortgage obligations, and explain the cash flows and risks for each type define prepayment risk and describe the prepayment risk of mortgage15.54.f backed securities Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) identify the relationships among a bond’s price, coupon rate, maturity, and market discount rate (yield-to-maturity) define spot rates and calculate the price of a bond using spot rates describe and calculate the flat price, accrued interest, and the full price of a bond describe matrix pricing calculate and interpret yield measures for fixed-rate bonds, floating-rate notes, and money market instruments define and compare the spot curve, yield curve on coupon bonds, par curve, and forward curve define forward rates and calculate spot rates from forward rates, forward rates from spot rates, and the price of a bond using forward rates compare, calculate, and interpret yield spread measures explain benefits of securitization for economies and financial markets describe securitization, including the parties involved in the process and the roles they play describe typical structures of securitizations, including credit tranching and time tranching describe types and characteristics of residential mortgage loans that are typically securitized describe types and characteristics of residential mortgage-backed securities, including mortgage pass-through securities and collateralized mortgage obligations, and explain the cash flows and risks for each type define prepayment risk and describe the prepayment risk of mortgage-backed securities passingscoreforum.com Compared 40 Topic LOS Fixed Income 15.55.g Fixed Income 15.55.h Fixed Income 15.55.i Fixed Income 16.56.a Fixed Income 16.56.b Fixed Income 16.56.c Fixed Income 16.56.d Fixed Income 16.56.e Fixed Income 16.56.f Fixed Income 16.56.g Fixed Income 16.56.h Fixed Income 16.56.i Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe characteristics and risks of commercial mortgage-backed securities describe types and characteristics of non-mortgage asset-backed securities, including the cash flows and risks of each type describe collateralized debt obligations, including their cash flows and risks calculate and interpret the sources of return from investing in a fixed-rate bond define, calculate, and interpret Macaulay, modified, and effective durations explain why effective duration is the most appropriate measure of interest rate risk for bonds with embedded options define key rate duration and describe the use of key rate durations in measuring the sensitivity of bonds to changes in the shape of the benchmark yield curve explain how a bond’s maturity, coupon, and yield level affect its interest rate risk calculate the duration of a portfolio and explain the limitations of portfolio duration calculate and interpret the money duration of a bond and price value of a basis point (PVBP) calculate and interpret approximate convexity and distinguish between approximate and effective convexity estimate the percentage price change of a bond for a specified change in yield, given the bond’s approximate duration and convexity LOS 15.54.g 15.54.h 15.54.i 16.55.a 16.55.b 16.55.c 16.55.d 16.55.e 16.55.f 16.55.g 16.55.h 16.55.i Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe characteristics and risks of commercial mortgage-backed securities describe types and characteristics of non-mortgage asset-backed securities, including the cash flows and risks of each type describe collateralized debt obligations, including their cash flows and risks calculate and interpret the sources of return from investing in a fixed-rate bond define, calculate, and interpret Macaulay, modified, and effective durations explain why effective duration is the most appropriate measure of interest rate risk for bonds with embedded options define key rate duration and describe the use of key rate durations in measuring the sensitivity of bonds to changes in the shape of the benchmark yield curve explain how a bond’s maturity, coupon, and yield level affect its interest rate risk calculate the duration of a portfolio and explain the limitations of portfolio duration calculate and interpret the money duration of a bond and price value of a basis point (PVBP) calculate and interpret approximate convexity and distinguish between approximate and effective convexity estimate the percentage price change of a bond for a specified change in yield, given the bond’s approximate duration and convexity Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 41 Topic LOS Fixed Income 16.56.j Fixed Income 16.56.k Fixed Income 16.56.l Fixed Income 16.57.a Fixed Income 16.57.b Fixed Income 16.57.c Fixed Income 16.57.d Fixed Income 16.57.e Fixed Income 16.57.f Fixed Income 16.57.g Fixed Income 16.57.h Fixed Income 16.57.i Fixed Income 16.57.j Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe how the term structure of yield volatility affects the interest rate risk of a bond describe the relationships among a bond’s holding period return, its duration, and the investment horizon explain how changes in credit spread and liquidity affect yield-to-maturity of a bond and how duration and convexity can be used to estimate the price effect of the changes describe credit risk and credit-related risks affecting corporate bonds describe default probability and loss severity as components of credit risk describe seniority rankings of corporate debt and explain the potential violation of the priority of claims in a bankruptcy proceeding distinguish between corporate issuer credit ratings and issue credit ratings and describe the rating agency practice of “notching” explain risks in relying on ratings from credit rating agencies explain the four Cs (Capacity, Collateral, Covenants, and Character) of traditional credit analysis calculate and interpret financial ratios used in credit analysis evaluate the credit quality of a corporate bond issuer and a bond of that issuer, given key financial ratios of the issuer and the industry describe factors that influence the level and volatility of yield spreads explain special considerations when evaluating the credit of high yield, sovereign, and non-sovereign government debt issuers and issues LOS 16.55.j 16.55.k 16.55.l 16.56.a 16.56.b 16.56.c 16.56.d 16.56.e 16.56.f 16.56.g 16.56.h 16.56.i 16.56.j Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe how the term structure of yield volatility affects the interest rate risk of a bond describe the relationships among a bond’s holding period return, its duration, and the investment horizon explain how changes in credit spread and liquidity affect yield-to-maturity of a bond and how duration and convexity can be used to estimate the price effect of the changes describe credit risk and credit-related risks affecting corporate bonds describe default probability and loss severity as components of credit risk describe seniority rankings of corporate debt and explain the potential violation of the priority of claims in a bankruptcy proceeding distinguish between corporate issuer credit ratings and issue credit ratings and describe the rating agency practice of “notching” explain risks in relying on ratings from credit rating agencies explain the four Cs (Capacity, Collateral, Covenants, and Character) of traditional credit analysis calculate and interpret financial ratios used in credit analysis evaluate the credit quality of a corporate bond issuer and a bond of that issuer, given key financial ratios of the issuer and the industry describe factors that influence the level and volatility of yield spreads explain special considerations when evaluating the credit of high yield, sovereign, and non-sovereign government debt issuers and issues Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 42 Topic LOS Derivatives 17.58.a Derivatives 17.58.b Derivatives 17.58.c Derivatives 17.58.d Derivatives 17.58.e Derivatives 17.59.a Derivatives 17.59.b Derivatives 17.59.c Derivatives 17.59.d Derivatives 17.59.e Derivatives 17.59.f Derivatives 17.59.g Derivatives 17.59.h Derivatives 17.59.i Derivatives 17.59.j Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) define a derivative, and distinguish between exchange-traded and over-thecounter derivatives contrast forward commitments with contingent claims define forward contracts, futures contracts, options (calls and puts), swaps, and credit derivatives, and compare their basic characteristics LOS 17.57.a 17.57.b 17.57.c describe purposes of, and controversies 17.57.d related to, derivative markets explain arbitrage and the role it plays in determining prices and promoting 17.57.e market efficiency explain how the concepts of arbitrage, replication, and risk neutrality are used 17.58.a in pricing derivatives distinguish between value and price of 17.58.b forward and futures contracts explain how the value and price of a forward contract are determined at 17.58.c expiration, during the life of the contract, and at initiation describe monetary and nonmonetary benefits and costs associated with holding the underlying asset, and 17.58.d explain how they affect the value and price of a forward contract define a forward rate agreement and 17.58.e describe its uses explain why forward and futures prices 17.58.f differ explain how swap contracts are similar to but different from a series of forward 17.58.g contracts distinguish between the value and price 17.58.h of swaps explain how the value of a European 17.58.i option is determined at expiration explain the exercise value, time value, 17.58.j and moneyness of an option Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared define a derivative and distinguish between exchange-traded and over-thecounter derivatives contrast forward commitments with contingent claims define forward contracts, futures contracts, options (calls and puts), swaps, and credit derivatives and compare their basic characteristics describe purposes of, and controversies related to, derivative markets explain arbitrage and the role it plays in determining prices and promoting market efficiency explain how the concepts of arbitrage, replication, and risk neutrality are used in pricing derivatives distinguish between value and price of forward and futures contracts explain how the value and price of a forward contract are determined at expiration, during the life of the contract, and at initiation describe monetary and nonmonetary benefits and costs associated with holding the underlying asset and explain how they affect the value and price of a forward contract define a forward rate agreement and describe its uses explain why forward and futures prices differ explain how swap contracts are similar to but different from a series of forward contracts distinguish between the value and price of swaps explain how the value of a European option is determined at expiration explain the exercise value, time value, and moneyness of an option passingscoreforum.com 43 Topic Derivatives Derivatives Derivatives Derivatives Derivatives Derivatives Derivatives Alternative Investments Alternative Investments Alternative Investments LOS Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) identify the factors that determine the value of an option, and explain how 17.59.k each factor affects the value of an option explain put–call parity for European 17.59.l options explain put–call–forward parity for 17.59.m European options explain how the value of an option is 17.59.n determined using a one-period binomial model explain under which circumstances the 17.59.o values of European and American options differ determine the value at expiration, the profit, maximum profit, maximum loss, breakeven underlying price at expiration, and payoff graph of the 17.60.a strategies of buying and selling calls and puts and determine the potential outcomes for investors using these strategies determine the value at expiration, profit, maximum profit, maximum loss, breakeven underlying price at expiration, and payoff graph of a 17.60.b covered call strategy and a protective put strategy, and explain the risk management application of each strategy compare alternative investments with 18.61.a traditional investments describe categories of alternative 18.61.b investments describe potential benefits of 18.61.c alternative investments in the context of portfolio management LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared identify the factors that determine the value of an option and explain how each factor affects the value of an option explain put–call parity for European 17.58.l options explain put–call–forward parity for 17.58.m European options explain how the value of an option is 17.58.n determined using a one-period binomial model explain under which circumstances the 17.58.o values of European and American options differ determine the value at expiration, the profit, maximum profit, maximum loss, breakeven underlying price at expiration, and payoff graph of the 17.59.a strategies of buying and selling calls and puts and determine the potential outcomes for investors using these strategies determine the value at expiration, profit, maximum profit, maximum loss, breakeven underlying price at expiration, and payoff graph of a 17.59.b covered call strategy and a protective put strategy, and explain the risk management application of each strategy compare alternative investments with 18.60.a traditional investments describe categories of alternative 18.60.b investments describe potential benefits of alternative 18.60.c investments in the context of portfolio management 17.58.k Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 44 Topic LOS Alternative Investments 18.61.d Alternative Investments 18.61.e Alternative Investments 18.61.f Alternative Investments 18.61.g Level I - 2016 (549 LOS) describe hedge funds, private equity, real estate, commodities, infrastructure, and other alternative investments, including, as applicable, strategies, sub-categories, potential benefits and risks, fee structures, and due diligence describe, calculate, and interpret management and incentive fees and net-of-fees returns to hedge funds describe issues in valuing, and calculating returns on, hedge funds, private equity, real estate, commodities, and infrastructure describe risk management of alternative investments LOS 18.60.d 18.60.e 18.60.f 18.60.g Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) Compared describe hedge funds, private equity, real estate, commodities, infrastructure, and other alternative investments, including, as applicable, strategies, subcategories, potential benefits and risks, fee structures, and due diligence describe, calculate, and interpret management and incentive fees and netof-fees returns to hedge funds describe issues in valuing and calculating returns on hedge funds, private equity, real estate, commodities, and infrastructure describe risk management of alternative investments Finance or Accounting Questions? Go to passingscoreforum.com 45