* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pollination - GaryTurnerScience
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
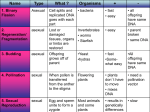
How a Flower is Pollinated The purpose of all flowers is to be pollinated and produce seeds Pollination http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xHkq1e dcbk4 What do petals do? Partly used to protect the male and female parts of the plant Some plants use wind to blow the pollen and they have small leaves Plants which use insects to transfer the pollen usually have large petals which smell and are brightly coloured What is the male part? The male part of the flower is called the stamen It has a long stalk called the filament At the top of the filament is the anther What is the anther? The anther produces pollen What is the female part? Carpels are the female parts They are made up of a stigma, style and ovary What is the stigma? It is at the top of the carpel It is sticky which helps catch pollen grains What are the ovaries? The ovaries are where the eggs are made How does pollination take place? Pollen grains brush against the insect, it flies to another plant, the grains rub on the stigma The grain of pollen grows a tube, which goes down the style until it reaches the ovary The male part joins with the female part to form a seed. This is called fertilisation. After fertilisation the petal drop off because they are no longer needed Almost 90% of all flowering plants rely on animal pollinators for fertilization, and about 200,000 species of animals act as pollinators. Of those, 1,000 are hummingbirds, bats, and small mammals such as mice. The rest are insects like beetles, bees, ants, wasps, butterflies and moths. Why Are Pollinators Important to Us? Worldwide, approximately 1,000 plants grown for food, beverages, fibers, spices, and medicines need to be pollinated by animals in order to produce the goods on which we depend. Foods and beverages produced with the help of pollinators include: apples, bananas, blueberries, chocolate, coffee, melons, peaches, potatoes, pumpkins, vanilla, almonds. Pollination can be accomplished by crosspollination or by self-pollination : Cross-pollination, also called allogamy, occurs only when pollen is delivered to a flower from a different plant. Plants adapted to outcross or cross-pollinate often have taller stamens than carpels or use other mechanisms to better ensure the spread of pollen to other plants' flowers. Self-pollination occurs when pollen from one flower pollinates the same flower or other flowers of the same individual. Plants that can pollinate themselves and produce viable offspring are called self-fertile. Plants that cannot fertilize themselves are called self-sterile, a condition which mandates cross pollination for the production of offspring.