* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part One
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
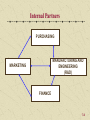
Chapter Seven Weaving Marketing into the Fabric of the Firm LEARNING OBJECTIVES Introduce market orientation concept Describe the internal partnerships that must be developed with marketing Discuss how marketing learns 7-2 MARKET ORIENTATION CONCEPT What is a Market Orientation Components of Market Orientation How Market Orientation Impacts Performance Spanning Process 7-3 What is Market Orientation 1. 2. 3. The systematic gathering of information on customers and competitors, both present and potential The systematic analysis of the information for the purpose of developing market knowledge The systematic use of such knowledge to guide strategy recognition, understanding, selection, implementation and modification A market-oriented firm should - benefit from better marketing programs; be difficult for competitors to identify; be unique 7-4 Components of Marketing Orientation 1. Establish a corporate culture where every employee values their customers 2. Listening to the voice of the customer throughout the entire company 3. Developing superior skills to understand and satisfy customers A market orientation must exist in the culture of the organization (part of the values & norms of the organization) A company needs a market orientation in order to learn successfully. 7-5 How Market Orientation Impacts Performance 1. Do a better job of market sensing 2. Anticipating market requirements ahead of competition Marketing research is one form of market sensing Can be achieved through listening to the salesforce, observing competition at trade shows, and developing stronger ties with innovative customers and suppliers Be able to develop stronger relationships With customers With channels of distribution 7-6 Spanning Process CUSTOMER NEEDS Inputs by customers through sales, service, information seeking LINKS Spanning activities that provide decision-making information COMPANY CAPABILITIES Defined by all organization functions - Spanning processes link the firm’s internal processes with the customer - Market oriented firms must have adequate spanning processes 7-7 EXTERNAL EMPHASIS INTERNAL EMPHASIS Outside-in Process Inside-Out Process Spanning Process • Market Sensing • Customer Linking • Channel Bonding •Technology Monitoring • Customer Order Fulfillment • Pricing • Purchasing • Customer Service Delivery • New Product / Service Development • Strategy Development • Financial Management • Cost Control • Technology Development • Integrated Logistics • Manufacturing/Transformation Process • Human Resources Management • Environmental Safety Health and Safety 7-8 PARTNERSHIP IN MARKETING Internal Partnering – The process of creating partnerships with other functional areas within the firm Partnerships are characterized by open communication, trust and commitment to the partner. − − − Partners are able to align their goals with the goals of the other Silo structure is with high walls built around the departments and no ability or desire to go between the departments The creation of internal partnerships Internal Partners 7-9 Stages of Internal & External Partnering AWARENESS EXPLORATION EXPANSION COMMITMENT ACHIEVING THE SUPRAGOAL: CUSTOMER SATISFACTION 7-10 Internal Partners PURCHASING MANUFACTURING AND ENGINEERING (R&D) MARKETING FINANCE 7-11 Encouraging Integration in Marketing Operations Develop & Articulate Strategic Decisions that Will Be Implemented Pursue Personnel Stability to Enhance Long Term Rapport Level the Budget and Compensation Playing Field That Supports Marketing Efforts Establish Clear and Formalized Communication / Organizations Structures 7-12 Typical Marketing Organizational Structure MARKETING DIRECTOR SALES PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT MARCOMM MARKETING RESEARCH 7-13 Customer Focused Team Structure Sales Account Manager Engineering Engineering Rep Customer Mfg. Rep Shipping Rep Purchasing Agent Purchasing Manufacturing Shipping Finance Rep Finance 7-14 HOW BUSINESS MARKETERS LEARN THE THREE-STEP PROCESS 1 INFORMATION ACQUISITION Marketing Research Sales and Service Feedback Environmental Scanning Competitive Intelligence Accounting Systems Information Systems Experiments Benchmarking Joint Venture Lead Customers Organizational Memory 2 INFORMATION DISSEMINATION To: Marketing Management Senior Management Manufacturing Engineering and R&D Finance 3 SHARED INTERPRETATION Through: Brainstorming Planning Other Processes 7-15 Tools to Generate New Knowledge • COGNITIVE MAPPING – Finding links of cause and effect through exploring beliefs and assumptions • EXPERIMENTS – Research that tests cognitive maps • LEARNING LABORATORIES – A physical environment set aside for learning through experiments, simulations, models and role playing • LEARNING FROM OTHERS – Getting knowledge from partners, consultants, seminars, and competitors. 7-16 Cognitive Maps—MAP 1 Example: Kinko’s Observation More competitors means less business per store + Observation Observation Kinko’s stores compete with each other when located in the same city because of free delivery service Have fewer stores in a city = 7-17 Two Cognitive Maps—MAP 2 Observation Observation Advertising drives awareness Each store has signage or advertising Assumption Observation Conclusion 2 More stores mean more awareness Higher awareness means more business Have more stores in a city = 7-18