* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Changes in chromosome number
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
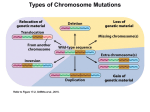
Course Overview Changes in chromosome number http://www.erin.utoronto.ca/~w3bio/bio207/index.htm February 1 Outline Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Topic Course objectives and Introduction to genetics Human Pedigrees Patterns of Inheritance: sex-linkage Chromosomal basis of inheritance Changes in chromosome number Gene Mapping Gene to Phenotype Modified Mendelian ratios Model organisms and mutants Genetics of Plant Development (Arabidopsis) Genetics of Animal Development (Drosophila) Behaviour Genetics/Quantitative genetics Drosophila Calvin Bridges’ cross • Drosophila melanogaster has 4 chromosomes: 1 pair of sex chromosomes and 3 pairs of autosomes • semi-colons are used to indicate when genes are on different chromosomes • What is the expected ratio of progeny from the cross: w/w X +/Y White-eyed females X red-eyed males ? X+ – Eg: w;+;+;+ 1;2;3;4 Chapter Ch. 1 & Ch. 2 Ch. 2 Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Ch. 15 Ch. 4 (Ch. 16) Ch. 6 Ch. 6 Ch. 6 (Ch. 16) Ch. 18 Ch. 18 Ch. 16 + papers 4 3 2 Y Xw Xw Xw X+ (red ♀) Xw Y (white ♂) Xw Xw Xw X+ (red ♀) Xw Y (white ♂) 1 Sex determination • In Drosophila sex is determined by the X:A ratio – 1X:2A is male – 2X:2A is female – 2X:3A is intersex • In Drosophila melanogaster dosage compensation is by hyperactivation of the X in males Text p. 79 1 Text p. 491 Aneuploidy • Aneuploid: an individual organism whose chromosome number that differs from wildtype by part of a chromosome set – E.g. Drosophila nullo X (X0) sterile males differ from wildtype males by the loss of Y Text p.490-494 Stages in the production of mature male and female gametes 2n Spermatogonium 2n Oogonium 2n Primary Oocyte 2n Primary Spermatocyte Meiosis I 2n Secondary Spermatocytes 2n Secondary Oocyte 2n First Polar body Meiosis II n n n n Spermatids Spermatozoa (sperm) n n n n n Ootid n n n Three polar bodies Ovum (egg) n Text p. 86 2 Monosomic (2n-1) • The absence of one copy of a chromosome from a pair – E.g. Turner syndrome (45 X) • Phenotype is female Trisomy (2n+1) • Trisomics have an extra copy of one chromosome • Autosomal trisomies: – trisomy 13 Patau syndrome – trisomy 18 Edwards syndrome – trisomy 21 Down syndrome • Sex chromosome trisomies: – Klinefelter syndrome (XXY) – XYY – XXX Trisomic: e.g. 47 XXY • Klinefelter syndrome 47 XXY karyotype – Phenotype male but Barr bodies present Trisomy 21 • Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) – have an extra copy of chromosome 21 Text p.494 3 Text p.493 Trisomic • Gametic ratio : e.g. for gene A on a trivalent chromosome – – – – 1/6 A 2/6 a 2/6 A/a 1/6 a/a Dosage compensation • X-chromosome inactivation: – In early development of female mammals one X-chromosome becomes in activated and this inactivation persists throughout all subsequent mitotic divisions – Barr bodies: an inactivated Xchromosome highly condensed and visible as a dark staining spot XX Mitosis XX XX Mitosis XX XX XX XX Many Mitoses Cell line with inactive maternal X X- inactivation Cell line with inactive paternal X X- inactivation E.g. Calico cats – In early development of female mammals one X-chromosome becomes in activated and this inactivation persists throughout all subsequent mitotic divisions Text p.495 and p.324 Text p.495 and p.324 4 12 possible trisomics • The effects of one extra chromosome – In humans trisomics form almost half of chromosomally abnormal spontaneous abortuses. For example trisomy 16 is most common in abortions and not seen among live births – In Datura plants the effects an extra chromosome can be seen from the shape of the fruit The jimsonweed plant (Datura stramonium) Text p.77 Euploidy • Euploid: having multiples of the basic chromosome set Text p.486 Text p.486 5 Chromosome structure • Duplication: the replication of a segment of chromosome A. B C D E becomes A. B CC D E • Inversion: a chromosomal rearrangement in which the chromosome is broken twice and flipped 180 degrees then rejoined – A. B C D E becomes A. C B D E • Translocation: the segment of one chromosome moved to another chromosome – A. B C D E becomes A. B C H I • Deletion the loss of a segment within one chromosome and the juxtaposition of the two segments on either side of the deleted segment – A. B C D E becomes A. B E 6 Inversions • Inversion: a chromosomal rearrangement in which the chromosome is broken twice and flipped 180 degrees then rejoined • The loops in these polytene chromosomes reveal the breakpoints of the inversions Translocation • Translocation: the segment of one chromosome moved to another chromosome Inversion picture from Text p.618 Deletions • Deletion the loss of a segment within one chromosome and the juxtaposition of the two segments on either side of the deleted segment – E.g. cri du chat syndrome (5p15.2 and 15.3 are deleted) 7 Naming chromosomal aberrations • Drosophila melanogaster : Duplication -Dp(3L) (i.e. a duplication in the left arm of chromosome-3) Inversion- In(1) (i.e. Inversion in chromosome-1) Translocation- T(3R) (i.e. translocation in the right arm of chromosome-3) Transposition-Tp(2L) (i.e. transposition in the left arm of chromosome-2) Deficiency- Df(3R) (i.e. deficiency in the right arm of chromosome-3) More details can be found at: http://fly.bio.indiana.edu/nomenclature.htm Human sex chromosomes SRY Introduction to genetic analysis Griffiths, A., Wessler, S.R., Lewontin,R.C., Gelbart, W.M.,Suzuki, D.T. and Miller, J.H. Eighth Edition, W.H. Freeman and Company NY • Part I Transmission genetic analysis – Chapter 1: all questions p. 24-26 – Chapter 2: all the questions p. 62-72 – Chapter 3: questions #1-12,18,19, 22, 25-27, 29, 30, 32, 40-42. • Part IV The nature of heritable change • Chapter 15: sections 15.1 and 15.3; questions #13,11-13,19,21,22, 32, 38, 52. 8