* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Species richness and diversity
Survey
Document related concepts
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
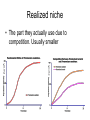
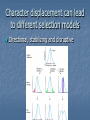
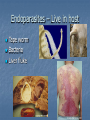
Chapter 56 Community ecology Community a group of different species living in one area Species richness The number of species in a community Increases near equator Relative abundance population of a given species in a specific size ecosystem Compares the percent of each species EX. Percent of mallards in pond compared to total bird population Species diversity Relates the number of species to the “relative abundance” of each Species area effect Larger areas usually contain more species than smaller ones Evident on islands Individualistic concept Community is made of nothing more than different species that happen to be living in same area Holistic concept Communities are an integrated unit that depend on each other for survival. “super organism” Keystone Species A species that has great influence on other species in ecosystem Ex. Sea stars Trophic cascade There is a ripple effect from one eating level to another when keystone specie is affected Orcas increase otters decease Urchins increase Kelp decreases Ex. Elk eat Aspen trees Wolves eat elk wolves influence vegetation Wolf predation near aspen trees increases Elk change browsing habits Aspen increase Community stability Resistance to change Biodiversity increases stability Biodiversity 55.2 Ecological Niche concept Niche The role an organism fills in its community Niche determined by Habitat Place in food chain Specific food types When they eat or hunt Great horned owl and red tailed hawk have different niches Both eat small rodents Both live in same area BUT owls hunt at night, hawks hunt during day Fundamental niche • Potential niche – without any competition Realized niche • The part they actually use due to competition. Usually smaller Competition exclusion One Species is eliminated from a community because of limited resources. Can not occupy same niche Example paramecium P. Caudatum paramecium declines in presence of other paramecium Resource partitioning When several similar species subdivide a niche for resources Ex. 5 different warbler species eating different areas of a tree Character displacement One Phenotype is selected because of competition Ex anoles. on same island there are populations that eat different things and occupy different niches, Character displacement can lead to different selection models Directional, stabilizing and disruptive Symbiosis and community Interactions Chp 56.3 - 56.4 Food chain One specific sequence of eating levels Food web – all the consumer interactions within ecosystem Trophic levels = eating level herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Scavenger Consumer/carnivore that does not hunt Predation +/ Predator captures and kills prey Predator Prey adaptations Predators – camouflage, sharp teeth, web, infrared sensors, etc Trap door spider Makes camouflaged lair Angler fish Spider web Green pit viper Has infra red heat sensors in pits Prey - Survival techniques camouflage – hide Aposematic – Advertize poison or impalatability by coloration Monarch butterfly Larva eats poison milk weed Monarch advertise poison. Aposematic Predators adapt to monarch poison Black backed oriole Black headed oriole Black-eared mouse Poison dart frogs Advertise poison Aposematic Camouflage Stick insect Walking leaf insect flounder Leaf Frog Mimicry One species looks like another metalmark moths mimic jumping spiders. Batesian mimicry A normal species mimics a poisonous one Monarch Batesian mimic Coral snake Batesian mimic Caterpillar mimics coral snake Batesian Müllerian mimicry More than one unpalatable /poisonous species resemble each other Bees, wasps and hornets Mimicry in Butterflies Is Seen here on These Classic “Plates” Showing Four Forms of H. numata, Two Forms of H. melpomene, and the Two Corresponding Mimicking Forms of H. erato. Multiple coral snake mimicry Batesian Plant / herbivore interactions Plants may use physical defenses Thorns Sticky Hairs Tough leaves chemical defenses secondary compounds Poisonous Irritating Bad-tasting Poisonous Mild poison Daffodils - nausea, vomiting, cramps and diarrhea Poison hemlock Deadly poison Irritating chemicals Hot peppers have capsaicin Bad-tasting Bitter melon mushrooms Parasitism +/ Like very slow predation. A parasite will feed on a host but does not result in immediate death Endoparasites – Live in host Tape worm Bacteria Liver fluke Exoparasites - External Ticks Leeches Lampreys mosquitoes Mutualism A cooperative relationship where both species benefit pos/pos Pollinators Mutualism Ex. Acacia trees and fire ants Acacia trees have thorns that secrete nectar Ants protect and defend plant from animals that would eat it Mutualism - pollinators Insects Birds and others Commensalism (+, 0 ) Benefits one species with little or no effect on the other Commensalism Birds follow army ants to find food Cape buffalo The buffalo stirs up the insects and the egrets can then feed on them parasitism and mutualism. Aphids are a major plant pest. They such the sap out of the plant and their sweet secretions may cause a heavy growth of sooty mildew on the leaf surfaces. These same aphids are ‘farmed’ by ants. The ants feed on the sugar rich secretions of the aphids, move them to better sites, and protect them from predators. Competition (-/+) or (+/-)? Only one organism will win Competition exclusion One Species is eliminated from a community because of limited resources. Can not occupy same niche Ecological succession 56.5 Succession The gradual growth of species in an area Primary succession The development of a community in an area that has not supported life previously. Primary succession occurs on bare rock, After volcanic eruption, sand dunes Primary succession Very SLOW – few minerals available can take 100s of years Stages of primary succession 1) Lichens mutualism between fungi and algae or cyanobacteria. Fungi protect, algae provides food by photosynthesis Acids from Lichens turn rock to soil (chemical weathering) Lichens eventually die and become part of soil 2) Mosses Need a little soil. Can also grow on dirty rock 3) Grasses Need thin layer of soil 4) shrubs Need thick layer of soil 5) trees Need established thick soil layer Secondary succession Occurs when an existing community has been cleared such as forest fire land slide Climax Community Stable end of succession High bio diversity High relative abundance Succession summary Eutrophication “good eating” The slow process of a lake ecosystem dying due to over growth of algae which kills other plants beneath and then the fish and animal life Eutrophication Mostly from pollution – fertilizers, detergents Algae grow on surface from HIGH nutrients, block light to other plants Plants below die O2 decreases Fish die Sediment fills in water A stream flowing in can add sediment faster Eutrophication of Caspian sea Biodiversity Increases survival of an ecosystem