* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neisseria gonorrheae
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Lyme disease microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
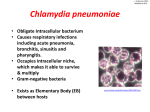
V. Ludwig F2013 Modified by DYH Neisseria gonorrhoeae Gram negative, diplococci Facultative intracellular Uses Type IV pili to adhere to surfaces and to hook to target cells to drag them closer Uses surface Opa proteins to prevent the host’s immune response Capable of conducting transformation and conjugation creating antibiotic resistant strains rapidly http://www.cytologystuff.com/learn/mole/ molecular3b.asp V. Ludwig F2013 Modified by DYH Gonorrhea AKA “The Clap” This bacteria is one of the most common STD infecting approximately 820,000 people in the US according to the CDC. If left untreated, the disease can escalate to pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, sterility, or even death. Transmitted through sexual intercourse or birth. A urine test is collected to diagnose Gonorrhea Infects warm, moist areas of the reproductive tract of males and females, and even the mouth, throat, eyes, and anus Antibiotics are generally used for treatment, but some resistant strains require other methods. Most people do not experience symptoms but those who do experience painful urination, discharge, and vaginal bleeding in women. http://textbookofbacteriology.net/pathogenesis_3.html