* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Communicating in Groups & Teams
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
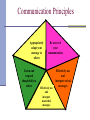
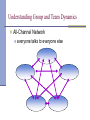
UNIT III: COMMUNICATING IN GROUPS AND TEAMS . Chapter 9 Understanding Group and Team Communication Communication Principles Appropriately adapt your message to others Listen and respond thoughtfully to others Be aware of your communication Effectively use and interpret nonverbal messages Effectively use and interpret verbal messages Understanding Group and Team Communication Groups and Teams Defined Types of Groups and Teams Group and Team Dynamics Group and Team Phases of Development Diversity in Groups and Teams: Adapting to Differences Groups and Teams Defined Communicating In Small Groups consists of a small number of people common purpose sense of belonging members exert influence on others in the group Small group communication is the transactive process of creating meaning among 3 to 15 people who share a common purpose, who feel a sense of belonging, and who exert influence on each other. Groups and Teams Defined Communicating In Teams A team is a coordinated group of people organized to work together to achieve a specific, common goal. Groups and Teams Defined Distinctions Between Groups and Teams Teams develop clearly defined responsibilities for team members. Teams have clearly defined rules for team operation. Teams develop clear goals. Teams develop a way of coordinating their efforts. Characteristics of Effective Team Members Experience Problem-Solving Ability Openness Supportiveness Action Oriented Positive Personal Style Understanding Types of Groups and Teams Primary Groups exist to fulfill the basic human need of associating with others Study Groups meet to learn new ideas Therapy Groups exist to provide treatment for the personal problems that group members may have Understanding Types of Groups and Teams Problem Solving Groups exist to resolve an issue or overcome an unsatisfactory situation or obstacle to achieve a goal Focus Groups small groups of people who are asked to discuss a particular topic or issue Social Groups exist just for the joy of socializing with others Chapter 9: Understanding Group and Team Communication Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Roles consistent ways you communicate with others in a group Types of Roles task social individual Chapter 9: Understanding Group and Team Communication Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Rules team ground rules Norms standards that determine what is appropriate and inappropriate behavior in a group Status an individual’s importance and prestige Chapter 9: Understanding Group and Team Communication Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Power the ability to influence others’ behavior Types of Power legitimate (respect for position) referent (based on attraction) expert (influence from a person’s knowledge) reward (ability to satisfy needs) coercive (sanctions and punishment) Chapter 9: Understanding Group and Team Communication Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Cohesiveness degree of attraction that members of a group feel toward one another and the group Chapter 9: Understanding Group and Team Communication Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Cohesive Groups Emphasize “we” rather than “I” Reinforce good attendance Establish group traditions Set clear goals Encourage participation Celebrate accomplishing goals Stress teamwork and collaboration Uncohesive Groups Emphasize individual contributions Less emphasis on attendance Less effort to develop traditions Avoid setting goals Limit participation Discourage group celebration Stress individual accomplishment Chapter 9: Understanding Group and Team Communication Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Communication Interaction Patterns a pattern of communication that identifies the frequency of who talks to whom Networks of Communication all-channel chain wheel Understanding Group and Team Dynamics All-Channel Network everyone talks to everyone else Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Chain Network people convey a message through one person at a time Understanding Group and Team Dynamics Wheel Network one person receives most of the messages Understanding Group and Team Phases of Development Orientation primary tension Conflict secondary tension Emergence conflict is reduced Reinforcement group develops a sense of “we” Process Nature of Group Phases Understanding Diversity in Groups and Teams Differences in Working Collectively or Individually individualism and collectivism Differences in the Use of Time monochronic/polychronic Differences in the Use of Personal Space high-contact/low-contact