* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wheat Amylase Trypsin Inhibitors as Triggers of
Survey
Document related concepts
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Coeliac disease wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
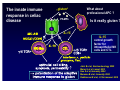
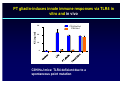
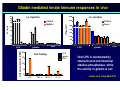
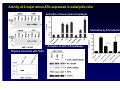
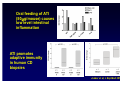
Wheat Amylase Trypsin Inhibitors as Triggers of Innate Immunity Detlef Schuppan Molecular and Translational Medicine, Dept. Medicine I, Univ. of Mainz, Germany Division of Gastroenterology and Celiac Center, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, USA 2nd International Expert Meeting on Gluten Sensitivity Munich Nov.30 – Dec. 2, 2012 HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Food intolerances 1. Lactose or fructose intolerance 2. “Histamine intolerance” 3. Food allergy 4. Celiac disease (gluten: wheat, barley, rye) Recent – very common 5. Non-celiac “gluten” sensitivity 6. FODMAP intolerance Frequently associated 6. Irritable bowel syndrome 7. Pathological intestinal microbiota Mesopotamia Egypt Moderner Massenanbau Hallmarks of celiac disease • Dietary gluten from wheat, barley, or rye as trigger of adaptive (T cell) immunity • Genetic Predisposition (HLA-DQ2 or -DQ8) • IgA autoantibodies to tissue transglutaminase • A wheat component that drives innate immunity Role of the Innate Immune System in celiac disease – prior work • Stimulation of biopsies from CD patients with PT gliadin or α2 gliadin p31-43 enhances IL-15 positive cells in the lamina propria (Maiuri et al, Lancet 2003) • p31-43 induces MICA on intestinal epithelial cells via IL-15, serving as target for cytotoxic IELs (Hue et al, Immunity 2004) • PT gliadin and different gliadin peptides induce activation & maturation of monocytes, macrophages & DCs (Tuckova et al, J Leuk Biol 2002; Palova- Jelinkova et al, FEBS Lett 2004, J Immunol 2005; Nikulina et al, J Immunol 2004; Cinova et al, J Clin Immunol 2007; Rakhimova et al, J Clin Immunol 2008) • Gliadin enhances intestinal permeability and DC activation via MyD88 (CXCR3 on intestinal epithelial cells as gliadin receptor) (Thomas et al, J Immunol, 2006; Lammert et al, Gastroenterology 2008) 1. LPS contamination not strictly ruled out ? 2. No reproducible identification of a certain (set of) gliadin peptide(s) 3. No plausible receptor identified The innate immune response in celiac disease „gluten“ PAMPs IL-15 What about professional APC ? Is it really gluten ? IL-15 central growth factor for intraepithelial NK cells and CTL Jabri B et al, Gastroenterology 2000 Maiuri L et al, Lancet 2003 Hue S et al, Immunity 2004 Meresse B et al, Immunity 2004 Rakhimova M et al, J Clin Immunol 2008 p31-43 and PT gliadin do not stimulate intestinal epithelial cells, monocytes, macrophages or DCs Medium 6000 p31-43 20g/ml scrambled p31-43 20g/ml 4000 scrambled p31-43 40g/ml 2000 7 U- 93 1 PTH -2 9 0 HT IL-8 (pg/ml) p31-43 40g/ml Junker et al, J Exp Med 2012 10 ng /m l 5000 TN Fa 5n g/ m l 50 0 g/ m l LP S gl ia di n LPS is not a contaminant M ed iu m g /m l 10 ng /m l 25 0 0 l 0 g/ m 5 0 iu m 5 25 M ed 10 IL-8 (ng/ml) 20 15 LP S l 25 ze in gl ia di n g /m /m l 10 ng /m l 25 0 LP S ze in g gfd PT PT PT 25 0 30 P T 0 gl ia di n 5 M ed iu m 10 IL-8 (ng/ml) healthy ctr PT IL-8 (ng/ml) 15 IL-8 (pg/ml) gl M ed PT iadi n iu gl 1 00 m ia PT di n g/ 25 m gl ia d i 0 g l PT n 5 /m ze 00 l PT in 1 g/m z e 00 l PT in 2 g/m ze 50 l in g 50 /m l L P 0 g S / 10 ml ng /m l PT PT gliadin stimulates monocyte derived DCs from controls and celiac patients 20 15 regular diet 10 w/o proteinase K + proteinase K 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 Junker et al, J Exp Med 2012 PT gliadin-induces innate immune responses via TLR4 in vitro and in vivo KC KC(ng/ml) (ng/ml) 30 C3H/HeOuJ C3H/HeOuJ C3H/HeJ C3H/HeJ 20 10 0 C3H/HeJ mice: TLR4 deficient due to a spontaneous point mutation Gliadin mediated innate immune responses in vivo 80 60 40 C57BL/6 MyD88-/- TNF- (pg/ml) 2000 20 15 10 C57BL/6 Rag1-/- 1000 400 300 fold x-fold mucosal induction (mRNA) 20 LPS oral feeding LPS gliadin PBS 15 10 5 0 KC TNF- MCP-1 IL-1 gliadin zein Oral LPS is inactivated by stomach acid and intestinal alkaline phosphatase, while the activity in gliadin is not Junker et al, J Exp Med 2012 8 7 1 8 6 5 2 7 6 4 3 3 4 5 6 zein gliadin LPS 0 0 9 0 4 100 9 0 1 2 5 5 200 1 2 3 4 S S S KC (ng/ml) 25 i.p. injection 3000 i.p. injection The activity is contained in the ω-gliadin fraction 50 293-hTLR4/MD2-CD14 IL-8 (ng/ml) 8000 6000 4000 30 10 8 6 overlapping 20mers 4 2 2000 0 0 M ed iu m LP S P PT MA R ek tor -g lia di n gl i 1. adi n 2gl i adi n 5gl ia di n IL-8 (pg/ml) 12000 40 5 LP Me g Pa lia S diu m din 10n m 3C 1 g SK 00 /m 4 mg l 10 /m m l g/ m 1 l 10 to 9 to 19 18 to 28 27 to 38 36 to 1 43 to 43 16000 Comparison of the gliadin fractions by SDS-PAGE showed a minor component of 15kDa associated only with ω-gliadins There is a little hidden bird on this foto – find it ! Wheat amylase-trypsin Inhibitors (ATIs) trigger intestinal innate immunity in macrophages and dendritic cells via TLR4 Junker Y et al, J Exp Med 2012 Oda Y et al, Biochemistry 1997 Characteristics und function of wheat ATIs • • • • • Family of up to 11 similar, small and compact proteins 5(4) intramolecular SS-bonds, resistant to intestinal degradation Pest control (inhibition of parasite enzymes) Tatham & Shewry, Clin Exp Allergy 2008 Zevallos VF et al, DDW 2012, #1309 Known major allergens of baker‘s asthma Content paralles that of gluten – association with omega-gliadins Activity of 2 major wheat ATIs expressed in eukaryotic cells Activation of monocytes-macrophages Inactivation by S-S reduction Activation of both TLR4 pathways Physical interaction with TLR4 Oral feeding of ATI (50g/mouse) causes low level intestinal inflammation ATI promotes adaptive immunity in human CD biopsies Junker et al, J Exp Med 2012 Classification of plants according to their relative potency to induce innate immunity IL8 (1 unit= 100 pg) Units of IL-8/g of flour in U937 cells 300 250 234,18 208,80 200 Wheat Triticum aestivum Barley Hordeum vulgare L. Rye Secale cereale 155,27 150 100 High: gluten containing 79,40 71,89 Medium: gluten-free (gluten-poor) 78,89 50 0 Soya Glycine Max Quinoa Chenopodium quinoa Buckwheat Fagopyrum esculentum IL8 (1 unit= 100 pg) 25 22,62 20 16,60 Peas Pisum sativum Early Crops Einkorn<Emmer<Spelt 15 Low: gluten free 10 Rice Oryza sativa Millet Panicum miliaceum Oats Avena sativa Maize Zea mays L. Amaranth Amaranthus caudatus 5 0 1,69 2,42 1,18 1,23 Zevallos VF et al, unpublished Emmer Einkorn Spelt Modern wheat Origin of Wheat Breeding Crossing Chromosome sets Goat wheat Increase of content of immunogenic gluten epitopes and ATIs with resistance breeding and higher ploidity Breeder‘s dilemma Breeding for high yield and high pest resistance • Reduction of nutritional value (essential amino acids, minerals, vitamins) • Increase in pest resistance proteins/ molecules potentially harmful to man Morris CE and Sands DC, Nat Biotechnol 2006 Non-celiac „gluten“ sensitivity „Gluten sensitivity“ without overt small intestinal damage or auto-Abs Estimated prevalence 3-10% Role of ATIs ? Studies in IBS, autoimmune-, metabolic, cardiovascular…… diseases are warranted Intestinal lumen Intestinal epithelium Basement membrane IEL activation Lamina propria PMN attraction/activation Stimulation of TLR4 on MΦ & DC Fuelling inflammation & autoimmunity in the gut and at distant sites Potentiation of already existing intestinal adaptive immune activation ATI Antigen MΦ attraction/activation Intestine and lymph nodes Recirculation and homing to other sites adipose ↓ SERIAL KILLERS Innate Immunity in Celiac Disease The mechanism by which certain gluten peptides (p31-43) may elicit innate mechanisms in biopsies ex vivo remains to be defined ATIs of gluten containing grains are strong inducers of innate immunity in DCs > macrophages > monocytes via TLR4 Ingested ATIs induce low level intestinal inflammation in vivo ATI content of modern wheat has increased due to resistance breeding ATIs of gluten free foods have much less stimulatory activity Innate immunity to ATIs likely impacts other intestinal and non-intestinal inflammatory diseases Research and Clinical Team Acknowledgements BIDMC GI: Donatella Barisani Melinda Dennis Tobias Freitag Yvonne Junker Ciaran Kelly Daniel Leffler Seong-Jun Kim BWH: Sebastian Zeissig BIDMC Immunology: Ulrich v. Andrian Cox Terhorst Svend Rietdijk BIDMC Proteomics Center: Towia Liberman Simon Dillon MGH: Atul Bhan Hans-Chr. Reinecker Celiac Center Boston Germany: Walburga Dieterich Minna Hietikko Martin Hils George Kahaly Norbert Krauss Moises Laparra Ralf Pasternack Martin Rosenthal Mareike Roth Nina Rüssel Nicole Voltz Herbert Wieser Jessy Willim Victor Zevallos Stanford: Grete Sønderstrup Chaitan Khosla Support NIH-NIAID BMBF DFG German and US Celiac Sprue Associations Celiac Center Mainz