* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
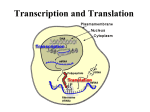
Biology 12 –DNA Review Sheet ANSWERS Answer the following questions on a separate piece of paper. 1. What are the three steps in DNA replication? Which enzyme completes each job? The three steps in the process of DNA replication are initiation, elongation and termination. See diagram below for explanations! YOU have this diagram! ENZYMES Helicase: unzips DNA, in more specific scientific terms, breaks hydrogen bonds between nucleotides. DNA Polymerase: attaches nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction Ligase: attaches Okazaki fragments together by forming covalent bonds between nucleotides RNA Primase: prepares the RNA for replication 2. Why is it called semi-conservative replication? DNA replicates by semi-conservative replication, which means that one strand of the parent double helix is conserved in each new DNA molecule. 3. Where does replication take place? In the nucleus 4. What is the purpose of replication? To make a complete copy of the organism’s DNA before the cells go through Mitosis. 5. What is an Okazaki fragment? Okazaki fragments are fragments of DNA that are produced during the process of DNA replication. They are produced on the LAGGING strand due to the fact that the enzymes can only replicate in the 5’ to 3’ direction. 6. Why is 5’ to 3’ important? One strand is opened in the 5' - 3' direction, which is the forward direction, and is called the leading strand. The other strand is opened in the 3' - 5' direction, which is the reverse direction, and is called the lagging strand. 7. Distinguish between DNA and RNA regarding nitrogen bases, pairing and sugarphosphate backbone. DNA: Double helix, Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Deoxyribose sugar RNA: Single stranded, Adenine, Guanine, Uracil, Cytosine, Ribose sugar 8. On the diagram below label: base pairing, sugar-phosphate backbone and hydrogen bonding. What is shown by the two boxes? Small box is a base pair showing the hydrogen bonds between C and G Larger box shows an entire nucleotide, Sugar phosphate backbone and guanine is the base. 9. What do the words transcription and translation mean regarding written words? How does this correspond to their meanings regarding DNA? Transcription means a written or printed representation of something. IN DNA replication the mRNA makes a transcription of a gene on the DNA that codes for a trait or protein. Translation is when one language is converted into another. The process by which a sequence of nucleotide triplets (codon) in a mRNA molecule gives rise to a specific sequence of amino acids during synthesis of a polypeptide or protein. 10. What is a codon? A codon is a three letter code that is on the mRNA strand. It corresponds to an Anticodon on a tRNA that carries a specific amino acid. 11. How do mRNA and tRNA work together to synthesis a protein? The mRNA contains the codon and the tRNA carries a specific amino acid that will join with other amino acids to make a protein (polypeptide chain) 12. What is an anti-codon? The code opposite to the codon, the snit-codon is on the tRNA strand 13. What are the three steps in translation? Initiation, Elongation, termination 14. What happens during chain initiation? See below for the answer for 14,15,16 15. What happens during chain elongation? 16. What happens during chain termination? 1 2 3 4 5 The steps in translation are: The ribosome binds to mRNA at a specific area. The ribosome starts matching tRNA anticodon sequences to the mRNA codon sequence. Each time a new tRNA comes into the ribosome, the amino acid that it was carrying gets added to the elongating polypeptide chain. The ribosome continues until it hits a stop sequence, then it releases the polypeptide and the mRNA. The polypeptide forms into its native shape and starts acting as a functional protein in the cell. (from Biology 101, link http://edtech.clas.pdx.edu/gene_expression_tutorial/translation.html, John Rueter 11/25/96) 17. Identify the amino acids that are coded for by the following mRNA strand: You need a CODON chart to do this activity. UGUGCGAUGAAGCGUGGAUGGUCUCCUAAACUUCAUUAAAGUUCU Cytosine, Alanine, START Methionine, Lysine, Arginine, Glycine, Tryptophan, Serine, Proline, Lysine, Leucine, Histidine, STOP 18. How does the ribosome tell which tRNA should contribute the next amino acid in the chain? The tRNA has an anti-codon that matches up with the codon from the mRNA strand. Each triplet codon matches up for a specific amino acid. 19. Explain how DNA, mRNA and tRNA work together to control the activities of a cell. This would be the overall explanation of ALL processes Replication transcription and translation.