* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Solar Nebula Theory
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
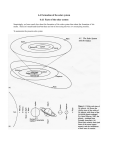
Odds and Ends – the Solar Nebula Theory Summing Up SNT Explaining the Solar System • The Solar System’s disk shape – Inherited from the motion of materials in the solar nebula. – The planets and moons mostly rotate and revolve in the same directions because they evolved from the same gas cloud. – The planet’s orbits lie in the same plane because the solar nebula collapsed into a rotating disk from which the planets were formed. SNT Is Evolutionary • The SNT is mostly evolutionary – it uses continuing processes (processes we observe in our own SS and other star systems) to describe how planets were gradually built. The SNT and Catastrophic Events • The SNT does turn to catastrophism to explain certain things such as the rotation of Uranus. • It is hypothesized that Uranus rotates on its side because of an “off-centered collision with a massive planetesimal when the planet was newly formed.” Division between Jovian and Terrestrial Worlds • This can be understood by differences in the condensation sequence. – Terrestrial planets formed in the inner part of the solar nebula with higher temperatures, which meant that the materials were solid, high density, particles like metals and silicates. – Jovian planets formed in the outer nebula with lower temperatures (beyond the frost line), which allowed gases to form large amounts of ices. The Missing Planet • The SNT predicts a planet between Mars and Jupiter. – There is no planet there but there is an asteroid belt. – Mathematical models indicate that the reason asteroids are there and not a planet is that Jupiter’s massive size disturbed the planetesimals and they did not accrete – instead they collided at high speeds. Comets and Other Objects • Comets are among the last of the planetesimals. – Comets have different origins but many, like ISON, are as old as the Solar System. • The icy Kuiper belt objects also appear to be ancient planetesimals that formed in the outer solar system but were never incorporated into a planet. They have not changed much since the SS was young. The Jovian Satellites • The Jovian planets have extensive “satellite systems.” – Some of the moons may have formed in orbit around forming planets in a miniature version of the sola nebula. – The smaller moons may have been captured asteroids or other planetesimals. The Heat of Jupiter and Saturn • The heat of formation for Jupiter and Saturn was tremendous (all of the in-falling materials would have released lots of energy). – Jupiter would have been hot enough to glow with a “luminosity” of about 1% of that of the present sun. – Fusion reactions never got going but both Jupiter and Saturn radiate more heat than they absorb from the sun – they are evidently still cooling. Common Age • The SNT has no difficulty explaining the common ages of the solar system’s bodies. – According to the theory, the planets, the sun, and all of the other inhabitants of our SS should be roughly the same age, which evidence corroborates. The SNT and Angular Momentum • If the planets formed from a contracting nebula, then the sun should have been left spinning very rapidly. – That is, it should have most of the angular momentum (moment of inertia * angular velocity) in the solar system. – Instead, it has very little. Lastly, what of the angular momentum problem? We have used the Spitzer Space Telescope to tackle this question – peering into the Orion Nebula. The SNT and Angular Momentum • To study why the sun does not spin rapidly (its rotation is quite slow), astronomers have used the Spitzer Telescope to examine 500 young stars in the Orion Nebula. – They have found that the stars that rotate slowly are 5X more likely to have a surrounding gas and dust disk than the faster rotators. The SNT and Angular Momentum – Astronomers have observed that the young, slow rotating, stars (like our sun would have been) have strong magnetic fields that extend out into their disks. – This allows the transfer of angular momentum from the young sun to the material in the disk. – The question of angular momentum is no longer a problem for the SNT. Your New Understanding • Hopefully, your new understanding of the solar system has given you a new way of thinking about our solar system – and all of its inhabitants (the sun, the planets, asteroids, comets, etc.) – As well as humanity, which of course includes you – We are as much a product of our solar system’s formation as the planets. What Science Is . . . • Science is, at its core, a new way of perceiving of the universe around you and your place in it based on the observation of natural phenomena. Understanding over time will change – it will get deeper and more complete (we have come a long way since Galileo). We are still at the beginning of our understanding.