* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA probe technology - Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Surround optical-fiber immunoassay wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
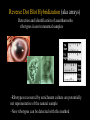
Detection of Protistan Genomes in the Environment Rebecca J. Gast Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Identification…. Detection ….. Enumeration……. ………Of marine protists Identification of cells • Morphology - Most useful for larger protists - Motility of cells also diagnostic • Sequences - Small subunit ribosomal RNA gene - Phylogenetically/taxonomically informative Detection of organisms • Indirect - detection without visual confirmation of cell - Sequences - Proteins - Lipids • Direct - Microscopy - In situ probe hybridization Oligonucleotide probes • Different levels of specificity - Extensive sequence databases are an important resource for designing probes. - Kingdom (archea, bacteria, eukaryote) - Group (methanotroph, prymnesiophyte) - Individual organism (E. coli, Paraphysomonas) • Hybridization - Southern blots, dot blots - Arrays - Whole cell - In situ (whole cell) hybridization is often considered the “gold standard” because it provides visual confirmation of a cell. Reverse Dot Blot Hybridization (aka arrays) Detection and identification of acanthamoeba ribotypes in environmental samples –Ribotypes recovered by enrichment culture are potentially not representative of the natural sample –New ribotypes can be detected with this method Fluorescence in situ hybridization Litaker et al., 2002. Journal of Phycology, 38 (3):442-463. Still difficult to address • Abundance - Quantitative analyses require the ability to retain and recover cells. • Monitoring over scales relevant to the microbial system - Spatial - there may be significant changes over very small distances - Temporal - community changes may occur rapidly in response to physical or chemical perturbation. New Technology • Automated water samplers • New probe types - Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) • New instrumentation - ESP - In situ flow cytometers What is a PNA? Behave like nucleic acid, but lack the negatively charged backbone. PNA probes are desirable for in situ hybridization shorter probes can be used (increased % mismatch) lower salt concentration (increased specificity) better cell penetration Flow cytometric detection of hybridized cells In situ hybridization chamber Increase spatial sampling capability Couple to flow cytometer Quantitative Collaborators and support • • • • • • • Robert Olson Heidi Sosik Mark Dennett Alexi Shalapyonok Ken Doherty WHOI Green Technology Award NSF Biocomplexity IDEA