* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth Surfaces Chapter 1 Study Guide The inner core is . A. layers
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
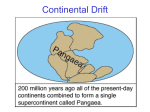
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
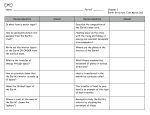
Earth Surfaces Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. The inner core is _________________________________. 2. Direct evidence about Earth’s interior is _______________. 3. Water vapor is a _____________________. A. layers B. radiation C. dense ball of Solid metal D. studying rocks 4. The transfer of energy through empty space is _______________. 5. Write the Earth’s layers in order from the middle to the surface._________________________________________________________________ 6. Geologists have used indirect evidence from seismic waves to learn more E. convection About the Earth’s interior _______________________. 7. Transfer of heat in fluid is ______________________________. F. gas 8. When you touch a hot stove, that is an example of ___________. G. convection current 9. The ________________ if the part of Earth that contains plates. H. conduction 10. Hot soup rises slowly to the top and as it cools it sinks to the bottom I. lithosphere forming constant movement that moves energy toward the surface of the pot. This constant movement is a ___________________. 11. The upper layer of Earth is broken into a dozen ______________ which J. destructive move slowly in various directions. 12. Pressure _________ from Earth’s surface toward the center of Earth. K. radiation 13. Earth’s ____________ is the thin envelope of gases that surrounds the Earth L. Lithosphere 14. The outermost layer of Earth is called the _______________. M. asthenosphere 15. Mantle material rises in convection currents because heated materials N. conduction become ____________ dense. 16. When geologists study Earth’s interior, they rely on ________ methods O. indirect such as seismic waves to study layers. 17. When sun warms your face it is a form of heat transfer ______. P. outer core 18. There is a theory that the ______________ moves to produce Earth’s Q. convection currents magnetic field. 19. The transfer of heat by the movement of heated fluid is called____. R. tectonics 20. Heat is transferred in the mantle as soft rock flows slowly in cycle called S. earthquakes _______. 21. When you touch a hot plate the transfer of heat is called _________. T. inner core 22. The _____ is part of the mantle that is made of soft rock that bends. U. less 23. Oceanic crust is made of _______ rock. V. increases 24. ______ produce seismic waves that travel through the Earth. W. plates 25. Erosion and Weathering are examples of _____ forces that shape the Earth. X. crust 26. Plate ________ is the theory that plates move very slowly in various Y. atmosphere directions. 27. The layer of Earth’s interior that is made up of crust and the upper part of Z. basaltic the mantle is the ________. 28. The most pressure would occur in the ___________. AA. convection 29. Compare and contrast the inner core and the outer core. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 30. Contrast oceanic crust and continental crust.____________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 31. Contrast between radiation, conduction, and convection. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________