* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 1: Marketing Intro
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
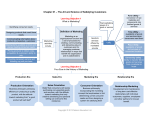
CHAPTER 1: Marketing: The Art and Science of Satisfying Customers 2 BASIC OPERATING FUNCTIONS OF EVERY ORGANIZATION 1. Production of a good, service, organization, person, or idea 2. Marketing of the good, service, organization, person or idea Utility • want satisfying power of a good or service 4 TYPES OF UTILITY 1. FORM – created by production – convert raw materials into finished goods & services Ex. Metal Shelves, Ford Explorer Utility (Cont.) 2. TIME – created by marketing – availability of goods & services when consumers want to buy them Ex.: Dominos 30 minute guarantee Federal Express Utility (Cont.) 3. PLACE – created by marketing – availability of goods & services where consumers want to buy them • Ex.: vending machines, Taco Bell Express 4. OWNERSHIP – created by marketing – transfer title time of purchase • Ex.: retail outlets (in exchange for $ or credit card payment) WHAT IS MARKETING? • American Marketing Assoc. (1985) – "process of planning & executing the conception, pricing, promotion, & distribution of ideas, goods, & services to create exchanges that will satisfy individual & organizational objectives" •Marketing does not begin at the end of the loading dock! Marketing should be involved from the conception of the product to the ultimate user. 4 Eras in Marketing 1. PRODUCTION ERA: – "A good product will sell itself" – Prior to 1920's – production oriented: make product and then sell it (Henry Ford) 2. SALES ERA: – "Creative advertising & selling will overcome customer resistance & convince them to buy” – between 1925 & early 1950's – selling was main focus of marketing 3. MARKETING ERA: – "The consumer is king! Find a need & fill it!” – early 1950's to early 1990’s • Emergence of the Marketing Concept – *CONSUMER ORIENTATION • Seller’s Market vs. Buyer’s Market 4. RELATIONSHIP MARKETING ERA – – – long-term, value added relationships developed over time with customers and suppliers 1990-Today Strategic Alliances • Ex. UPS What era do you think is next?? AVOIDING MARKETING MYOPIA • Management failure to recognize scope of its business – EX. Amtrak – AT&T and TCI • chart on pg 11 gives good examples of focusing on benefits 5 Types of Nontraditional Marketing 1. Person Marketing – to cultivate attention, interest, & preference of a target market toward a person Ex.: pro athletes 2. Place Marketing – attract visitors to a particular area – Ex.: “Wake Up to Missouri” or Pumpkin License Plate 3. Cause Marketing – identification & marketing of a social issue, cause, or idea to selected target markets Ex.: "Save the Whales" literacy Milk 4. Event Marketing – mkt of sporting, cultural, & charitable activities to selected target markets • Ex. Visa & Olympics or TWA Dome 5. Organizational Marketing – seek to influence others to accept the goods of, receive the services of, or contribute in some way to an organization - Ex.: “Be All that You Can Be” – Ex: “An Army of One” ELEMENTS OF A MARKETING STRATEGY 1. THE TARGET MARKET – who firm will direct marketing efforts toward • Ex. Baby-boomers, children, women • Ex.: Stouffers Lean Cuisine 2. THE MARKETING MIX VARIABLES (4P’s) – Once target market is chosen, how these variables are "mixed" determines success of marketing. Marketing Mix A. PRODUCT: package design, branding, trademarks, warranties, product life cycles & new product development B. PRICING: one of most difficult marketing decisions C. DISTRIBUTION: ensures that product arrives in right place, in right quantity at the right time D. PROMOTION: communications link between sellers & buyers Ex.: advertising, sales people, sales promotions 3. THE MARKETING ENVIRONMENT – The marketing environment is important because it provides a framework for all marketing activity. – 5 Forces 1. COMPETITION 2. POLITICAL-LEGAL 3. ECONOMIC 4. TECHNOLOGICAL 5. SOCIAL-CULTURAL • Strategic Alliances: partnership that creates competitive advantages ex. Delta and Disney UPS and Bradfield’s Pepsi and Apple’s iTunes • Marketing Costs – creating time, place & ownership utility costs $ – most estimate that marketing costs are 40 - 60% of overall product cost Internet and Marketing • It was the future and is now the present! ETHICS AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY • Most business people are ethical but there are a few rotten ones. Ex. ADM, Enron, Worldcom