* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functional Groups - La Salle University
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
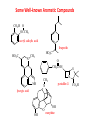
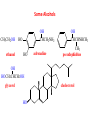
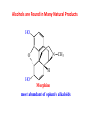
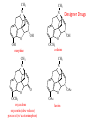
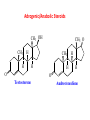
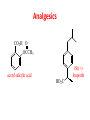
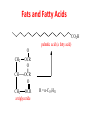
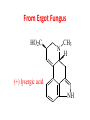
Functional Groups – Alkenes • Ethene (ethylene) is a major industrial feedstock – Used in the production of ethanol, ethylene oxide and the polymer polyethylene • Propene (propylene) is also very important in industry – Molecular formula C3H6 – Used to make the polymer polypropylene and is the starting material for acetone • Many alkenes occur naturally 2 – Alkynes • Ethyne (acetylene) is used in welding torches because it burns at high temperature • Many alkynes are of biological interest – Capillin is an antifungal agent found naturally – Dactylyne is a marine natural product – Ethinyl estradiol is a synthetic estrogen used in oral contraceptives – Benzene: A Representative Hydrocarbon • Benzene is the prototypical aromatic compound – The Kekulé structure (named after August Kekulé who formulated it) is a six-membered ring with alternating double and single bonds • Benzene does not actually have discreet single and double carbon-carbon bonds – All carbon-carbon bonds are exactly equal in length (1.38 Å) – This is between the length of a carbon-carbon single bond and a carbon-carbon double bond • Resonance theory explains this by suggesting there are two resonance hybrids that contribute equally to the real structure – The real structure is often depicted as a hexagon with a circle in the middle Some Well-known Aromatic Compounds CO2H O OCCH3 acetyl salicylic acid ibuprofin HO2C N HO2C CH3 O CH2CNH NH CH3 N lysergic acid O OH OH morphine S N penicillin G CO2H - Alkyl Halides In alkyl halides, a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces the hydrogen of an alkane – Alcohols • In alcohols the hydrogen of the alkane is replaced by the hydroxyl (-OH) group – An alcohol can be viewed as either a hydroxyl derivative of an alkane or an alkyl derivative of water • Alcohols are also classified according to the carbon the hydroxyl is directly attached to Chapter 2 Some Alcohols CH3CH2OH ethanol HO HO OH OH CHCH2NH2 CHCHNHCH3 adrenaline CH3 pseudephidrine OH HOCH2CHCH2OH glycerol cholesterol HO Alcohols are Found in Many Natural Products HO N CH3 O H HO Morphine most abundant of opium's alkaloids CH3 N O CH3 N OH OH morphine O OH OCH3 codeine CH3 N O Designer Drugs CH3 N O OCH3 oxycodone oxycontin (slow release) percocet (w/ acetominophen) O OAc heroin OAc – Ethers • Ethers have the general formula R-O-R or R-O-R’ where R’ is different from R – These can be considered organic derivatives of water in which both hydrogens are replaced by organic groups – The bond angle at oxygen is close to the tetrahedral angle – Amines • Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia – They are classified according to how many alkyl groups replace the hydrogens of ammonia – This is a different classification scheme than that used in alcohols – Aldehydes and Ketones • Both contain the carbonyl group • Aldehydes have one carbon attached to the carbonyl group • Ketones have two organic groups attached to the carbonyl group • The carbonyl carbon is sp2 hybridized – It is trigonal planar and has bond angle about 120o Adrogenic/Anabolic Steroids CH3 OH CH3 H CH3 O H CH3 H O H H H O Testosterone Androstenedione – Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Amides • All these groups contain a carbonyl group bonded to an oxygen or nitrogen • Carboxylic Acids – Contain the carboxyl (carbonyl + hydroxyl) group • Esters – A carbonyl group is bonded to an alkoxyl (OR’) group Analgesics CO2H O OCCH3 (S)(+)ibuprofin acetyl salicylic acid HO2C Fats and Fatty Acids CO2H palmitic acid (a fatty acid) O CH2 OCR O CH OCR O CH2 OCR a triglyceride R = n-C 15H31 From Ergot Fungus HO2C CH3 N H (+) lysergic acid NH Functional Groups link to Carey’s site (CH3)2N O OH C CH H2NCHCNHCHCOCH3 HOCCH2 O O Mifepristone (RU-486) O Aspartame CH2 • Amide – A carbonyl group is bonded to a nitrogen derived from ammonia or an amine – Nitriles • An alkyl group is attached to a carbon triply bonded to a nitrogen – This functional group is called a cyano group Chapter 2 Summary of Important Families of Organic Compounds Summary (cont.) From the Bark of the Pacific Yew Tree O O O NH OH O O O OH O OH O O O Taxus brevifolia O