* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download diseases of the cardiovascular system
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
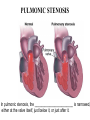
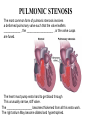
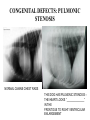
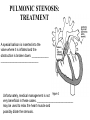
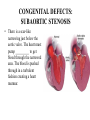
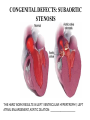
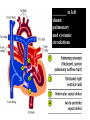
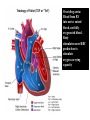
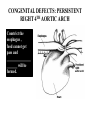
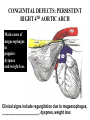
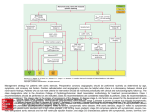
What’s your purpose? “It may be that your sole purpose in life is simply to serve as a warning to others.” -Anonymous DISEASES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: Cardiomyopathies CHF Valvular disease Cogenital malformation Infectious CONGENITAL DEFECTS: PULMONIC STENOSIS Chihuahuas, English Bulldogs, are commonly affected. CAUSE: ___________________ > 1 year PULMONIC STENOSIS In pulmonic stenosis, the _______________________ is narrowed, either at the valve itself, just below it, or just after it. PULMONIC STENOSIS The most common form of pulmonic stenosis involves a deformed pulmonary valve such that the valve leaflets ____________ , the ___________________ , or the valve cusps are fused. The heart must pump extra hard to get blood through This unusually narrow, stiff valve. The __________________ becomes thickened from all this extra work. The right atrium May become dilated and hypertrophied. CONGENITAL DEFECTS: PULMONIC STENOSIS NORMAL CANINE CHEST RADS THIS DOG HAS PULMONIC STENOSIS – THE HEART LOOKS “______________” IN THE FRONT DUE TO RIGHT VENTRICULAR ENLARGEMENT CONGENITAL DEFECTS: PULMONIC STENOSIS • CLINICAL SIGNS: – – – – – – Syncope Tiring on exercise _______________ congested heart failure ________________ basilar (base) murmur (PAM) Right ventricular enlargement Radiographs: right ventricular enlargement, dilation of the pulmonary artery, pulmonary underperfusion – Echo: right ventricular hypertrophy and enlargement, dilation of the main pulmonary artery ( __________________________________ ) PULMONIC STENOSIS: TREATMENT A special balloon is inserted into the valve where it is inflated and the obstruction is broken down: ____________ ___________________________ Unfortunately, medical management is not very beneficial in these cases. __________________________ may be used to relax the heart muscle and possibly dilate the stenosis. CLIENT EDUCATION • Do not breeding • Mild - moderate pulmonic stenosis: better __________________ • Moderate - severe pulmonic stenosis: poorer prognosis CONGENITAL DEFECTS: SUBAORTIC STENOSIS Newfoundland, Boxer, Golden Retriever, and Bull Terrier are most commonly affected LESION DEVELOPS IN THE FIRST ______________ WEEKS OF LIFE: thickening Endocardial tissue CONGENITAL DEFECTS: SUBAORTIC STENOSIS • There is a scar-like narrowing just below the aortic valve. The heart must pump _________ to get blood through the narrowed area. The blood is pushed through in a turbulent fashion creating a heart murmur. CONGENITAL DEFECTS: SUBAORTIC STENOSIS THE HARD WORK RESULTS IN LEFT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY, LEFT ATRIAL ENLARGEMENT, AORTIC DILATION: ____________________ CONGENITAL DEFECTS: SUBAORTIC STENOSIS: • CLINICAL SIGNS: – Fatigue – Exercise intolerance (low cardiac output) – ______________________ – Systolic murmur (soft – moderate) at the left heart base – ECG: evidence of left ventricular enlargement - ↑ QRS height – Echo: left ventricular hypertrophy, subvalvular fibrous ring, aortic dilation CONGENITIAL DEFECTS: SUBAORTIC STENOSIS • TREATMENT – Balloon catheter dilation – has been done with variable and temporary results – Medical management: THE GOAL IS TO SLOW THE HEART RATE AND DECREASE CONTRACTILITY; ________________ (BETA-BLOCKER WILL DO THIS) CONGENITAL DEFECTS: SUBAORTIC STENOSIS • CLIENT INFO: – Should not be used for breeding – Acute, left-sided congestive heart failure is possible – ___________________ is not uncommon DCM HCM PDA Aortic stenosis Pulmonic stenosis •1 – dogs •Enlarged Heart bronchile constriction •Dilated Flappy muscle •Nutritional: no taurin in cats •1 – Cats •Saddle thrombus •Rarely in dogs (hereditary) •Noncompliant heart muscle •Aorta – pulmonary a – lungs back L side •Stenotic aortic valve causes LV hypertrophy •High pressure in aortic valve can lead to aortic dilatation •Stenotic pulmonic valve •Pregnant heart •L sided heart failure (HF) •LV hypertrophy •RV hypertrophy •R sided HF •Increased HR •Cough •Increased HR •Weakness in hindlimbs, acute pain, rear cold feet •Pulmonary edema •Sudden death if aorta ruptures •Digoxin: increased contractibility •Beta blocker: Slow HR •Diuretic •Blood thinner •Treat surgically or die •No breeding •Balloon valvuloplasty CONGENITAL DEFECTS: TETRALOGY OF FALLOT ______________ are the most commonly affected breed, but bulldogs and cats have increased incidence as well. Cause: polygenic inheritance CONGENITAL DEFECTS: TETRALOGY OF FALLOT • THERE ARE 4 MAIN ANATOMICAL ABNORMALITIES IN THIS DISEASE! – Pulmonic stenosis – Right ventricular hypertrophy – Ventricular septal defect – Overriding aorta ________ to left shunt: pulmonary and systemic circulations Overiding aorta: Blood from RV into aorta: mixed blood, not fully oxygenated blood. Body stimulates more RBC production to stimulate oxygen carrying capacity CONGENITAL DEFECTS: TETRALOGY OF FALLOT • CLINICAL SIGNS and DIAGNOSIS: – – – – – – Affected puppies are _____________ than littermates Exercise intolerance Dyspnea, tachypnea Syncope Cyanosis _________________________: occurs as a response to the large amount of deoxygenated blood going to the systemic circulation – Systolic murmur over the pulmonic area – ECHO: right ventricular hypertrophy, subaortic ventricular septal defect, right outflow tract obstruction CONGENITAL DEFECTS: TETRALOGY OF FALLOT • TREATMENT: – ___________________: to keep PCV below 65% (replace with crystalloids) – Surgery: • Create a _______________________ shunt by doing systemic artery to pulmonary artery anastamosis • Complete correction requires cardiopulmonary bypass which is uncommon in animals CONGENITAL DEFECTS: TETRALOGY OF FALLOT • CLIENT INFO: – These dogs should not be bred – Congestive heart failure _____________ develops – Affected animals need regular phlebotomy – Limit stress and exercise – Caution when using sedatives/ tranquilizers CONGENITAL DEFECTS: PERSISTENT RIGHT 4TH AORTIC ARCH Great Danes, German Shepherds, Irish Setters are most commonly affected CONGENITAL DEFECTS: PERSISTENT RIGHT 4TH AORTIC ARCH Constrict the esophagus , food cannot get pass and ________________ _______ will be formed. CONGENITAL DEFECTS: PERSISTENT RIGHT 4TH AORTIC ARCH Main cause of megaesophagus in puppies: dyspnea and weight loss. Clinical signs include regurgitation due to megaesophagus, ______________________, dyspnea, weight loss PERSISTENT RIGHT AORTIC ARCH TH 4 • Dx: ______________________ study • Tx: Surgery (like PDA); megaesophagus maintenance; Ab’s for secondary infections • Client informations – Do not breed – Sx is needed – After sx some megaesophagus hence no boluses of food