* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network.
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
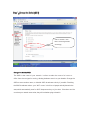
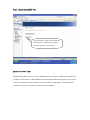
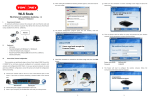
9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network. Step 1: Change the Default Password of Modem / Router After opening modem page click on management access control – password. Select username, confirm old password and put new desired password. Change the default password Each router has a default username and password, and you should always change these the moment you start configuring the router. If the router's password is either unchanged common or weak, a hacker might be able to reconfigure the router and wipe out all your other security measures, making them useless. You should try to use a good mix of numbers and characters to be on the safe side. Tips in setting a new password • Always use combinations of letters (upper and lower case), numbers, and symbols in your passwords. • Avoid using common words, which are known to friends and neighbors. • Change your passwords frequently. Step 2: Disable the DHCP services Click on Advance Setup - LAN and Disable DHCP services. Then save & apply. Disable the DHCP service DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) enables remote computers connected to the router to obtain an IP address and connect to the network without needing to know the IP and router address information. Disabling the DHCP services is a simple add effective way of keeping intruders away. As far as possible, set up the computers on your network with static IP addresses. If you still want to use DHCP to make your own configuration easier, restrict the number of DHCP IP users to the number of computers on your network. For example, if you have five laptops running on the network, limit the DHCP IP addresses to 5 from the default 50. Step 3: Change the Default SSID Click on wireless – click basic- and changed SSID accordingly Change the default SSID The SSID is the name of your network. It often reveals the name of a house or office from where signal is coming, allowing hackers to zero in on your location. Change the SSID to some random name, or disable SSID broadcast entirely if possible. Disabling the SSID broadcast makes your WiFi router invisible to laptops and cell phones in the area, which automatically scan for Wi-Fi hotspots and try to join them. If hackers can't be sure that your network even exists, they will not bother trying to break in. Step 4: Opt for WPA2 or PSK security Click on Wireless - security – change network authentication WPA2-PSK, enter WPA pre-shared key, as shown in the figure. Opt for WPA2 or PSK security over WEP WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) keys can be cracked with relative ease, so opt for WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), which uses 64-bit or 128-bit encryption. PSKs are Pre-Shared Keys, which provide stronger security than WEP or WPA. The encrypted keys are shared by the router and your Wi-Fi devices. The higher the encryption bit rate, the more difficult it is to crack. Step 5: Enable the MAC filter Click on Wireless – MAC Filter and ADD the MAC address to authenticate or restrict a particular computer on the network. En ab le the M AC F ilte r Enable MAC (Media Access Control) address filtering to restrict or authenticate a particular computer on the network. A MAC address is a unique physical address assigned to every piece of network equipment, which the router can use to restrict or authenticate it. If an unauthorized computer tries to join the network, it will simply be rejected. Step 6: Disable the Remote Administration Disable remote administration Remote management features can be helpful and convenient if you are constantly on the move, but can also be a window for hackers. Enable this feature only when you are actually traveling and really need it. Step 7: Use the Router's firewall Enable the firewall feature if your router has one. Usually, routers use SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection), which reviews the packets of data entering your network. If your router has an Internet Filter, enable it too. This rejects anonymous Internet requests and keeps your network from being "pinged", or detected by other users over the Internet. Step 8: Switch off the router when not in use If you only need Wi-Fi for home or office networking and do not need to use the Internet at all times, you could simply disconnect the ISP's cable from your router or switch off your ADSL/cable modem. Step 9: Position your Router carefully As far as possible, position the router in the center of your room or office. If your router allows you to reduce its signal strength, keep it at a level sufficient for your usage area. You never know how many people are actually able to detect and use your network. Keeping the router at a height increases the area of broadcast, so keep that in mind.