* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 4 ppt
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
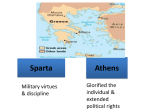
4 The Civilization of the Greeks Early Greece Importance of geography in Greek history Sea Topography (Map 4.1) Minoan Crete, 2000-1450 B.C.E. Height between 2000 and 1450 B.C.E. Knossus Sudden and catastrophic collapse around 1450 B.C.E. Mycenaean Greeks, 1600-1100 B.C.E. Flourished between 1400 and 1200 B.C.E. Indo-European / warrior people Agememnon Mycenae torched about 1190 B.C.E. Ancient Greece (c. 750 – 338) Mycenae Although not much of the site remains today, Mycenaean civilization erected several fortified palace complexes on these hills in the fifteen century B.C.E. The Greek Dark Age (c. 1100-c. 750 B.C.E.) Collapse of agricultural production Migration east across the Aegean Sea Ionian Greeks Two other major groups Aeolian Greeks Dorians Homer Iliad Odyssey Heroic values form the core of aristocratic virtue The Greek City-States: (c. 750 – c. 500 B.C.E.): The Polis The polis is a small but autonomous political unit in which all major political, social, and religious activities are carried out in a central location Acropolis and Agora Citizens, non-citizens, and responsibilities Military system Hoplites (heavily armed infantrymen) formed into phalanx Political and military repercussions Colonization and the Rise of Tyrants Colonization Gulf between rich and poor, overpopulation, and trade Founded as a polis Cultural diffusion Trade and commerce Tyrants A tyrant was someone who came to rule by unconstitutional ways in 7th and 6th centuries B.C.E. Support came from the new rich from trade and industry who opposed the old aristocracy Poor peasants becoming indebted to the landholding aristocrats Tyrants favored merchants and traders Extinguished by end of 6th century B.C.E. • Ended the rule of aristocratic oligarchies • Opened the door to open participation by the citizens Sparta Southwestern Peloponnesus Conquered neighboring Laconia and Messenia Helots (a type of serf) Reforms by Lycurgus Military society Women Government Two kings share power with the gerousia (council of 28 elders over the age of 60 serving for life) Apella – assembly of all male citizens Athens Established about 700 B.C.E. End of the 7th century B.C.E., farmers sold into slavery for not paying debts Solon (c. 640-c. 560 B.C.E.) 594 B.C.E. canceled all debts, outlawed new loans based on human collateral, freed people who had fallen into slavery for debts Did not initiate land redistribution Pisistratus seize power in 560 B.C.E. and pursued policies to aid trade Cleisthenes seized power in 508 B.C.E. Creates Council of 500 that was responsible for the administration of foreign and financial affairs Athenian assembly had final authority in passing laws Creates the foundation of Athenian democracy The Parthenon The Parthenon, which dominated the Acropolis of fifth century B.C.E. Greece and the Athens of today, represents the glory that was Greece in the age of Pericles. The Challenge of Persia Darius Unsuccessful revolt of Ionian cities Attacks the mainland Greeks Battle of Marathon, 490 B.C.E. Xerxes (522-486 B.C.E.) (486-465 B.C.E.) Invasion of Greece, 480-479 B.C.E. • Spartan league and Athenian navy • Battle of Thermopylae, 480 B.C.E. • Battle of Salamis, 480 B.C.E. • Battle of Plataea, 479 B.C.E. The Growth of an Athenian Empire in the Age of Pericles Delian League formed 478-77 B.C.E. Under the leadership of Athens, the Persians attacked and virtually all Greek city-states in the Aegean freed Athens comes to control the League and forbids any state to withdraw Pericles Expanded democracy at home and an empire abroad Elected to generalship 30 times between 461 and 429 B.C.E. The Great Peloponnesian War and the Decline of the Greek States (431404 B.C.E.) Sparta and allies v. Athens and allies Athens stays behind its walls and Sparta ravages the land of Attica Plague in 429, B.C.E., takes Pericles Battle of Aegospotami, 405 B.C.E. Surrender of Athens, 404 B.C Effects of the wars ©2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning ™ is a trademark used herein under license. Classical Greece Culture of Classical Greece History Greek Drama Tragedy Comedy The Arts: The Classical Ideal Architecture • Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian columns • Temples • Parthenon Sculpture • Subjects of male nudity • Proportional and life-like Theater at Epidaurus The acoustics at this great outdoor theater at Epidaurus are so clear that a whisper on stage could be heard from any of its 14,000 seats. The Greek Love of Wisdom Philosophy meant “love of wisdom” Socrates (469-399 B.C.E.) Socratic method Goal of education was to improve the individual Questioned authority Plato (c. 429-347 B.C.E.) The Republic The Academy Aristotle (384-322 B.C.E.) Politics Importance of his ideas on Western thought Greek Religion Was necessary for the well-being of the state Mount Olympus No body of doctrine or focus on morality Festivals Oracle of Apollo at Delphi Daily Life in Classical Athens 150,000 citizens, 43,000 of which were adult males who exercised political power Economy based on agriculture and trade Family the central institution Women kept under strict control Male homosexuality a prominent feature Rise of Macedonia and the Conquests of Alexander Philip II (359-336 B.C.E.) The Battle of Chaeronea Assassinated in 336 B.C.E. Alexander the Great (336-323 B.C.E.) Persian Empire • Battle of Granicus River, 334 B.C.E. • Battle of Issus, 333 B.C.E. • Battle of Gaugamela, 331 B.C.E. • Persepolis, 330 B.C.E. • Alexander in India, 327 B.C.E. • Death of Alexander, 323 B.C.E. The Conquests of Alexander the Great The Legacy of Alexander Hellenistic Age (“to imitate Greeks”) Destruction of Persia Benefits Greek engineers, intellectuals, merchants, administrators, and soldiers Political unity based on monarchy Culture Art, architecture, language, literature Cities The Hellenistic Kingdoms Four Hellenistic kingdoms emerged Macedonia under the Antigonid dynasty Syria and the east under the Seleucids Attalid kingdom of Pergamum in western Asia Minor Egypt under the Ptolemies Greeks and Macedonians formed the new ruling class Hellenizing an urban phenomenon Greeks and Macedonians colonists provided a pool for civilian administrators and workers Agriculture and trade Agriculture was central to Hellenistic economy Trade and commerce experienced considerable expansion ©2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. The World of the Hellenistic Monarchs Culture in the Hellenistic World Greeks provided sense of unity Hellenistic era was time of accomplishments Scholars Art Golden Age of Science Separation of science and philosophy Archimedes (287-212 B.C.E.) Philosophy Athens still the center of philosophy Epicurus (341-270 B.C.E.) Zeno (335-263 B.C.E.) and Stoicism ©2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. The World According to Erathosthenes Discussion Questions How did geography and the sea help to shape Greek culture? Compare and contrast the city-states of Sparta and Athens. How would you explain their divergent development? What did “democracy” mean to the ancient Greeks? What groups were excluded from Athenian democracy? How would you explain the rise of kingdoms and the demise of independent city-states during the Hellenistic period?