* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download depression - Swindon General Practice Education
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Moral treatment wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Postpartum depression wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary approaches to depression wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
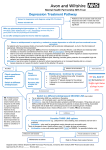
DEPRESSION NICE OCTOBER 2009 Severities of depression 1.Subthreshold depressive symptoms<5 symptoms 2.Mild depressionfew symptoms in excess of the 5,and minor functional impairment 3. Moderate depression symptoms or functional impairment between ‘mild’ and ‘severe’ 4.Severe depression most symptoms and markedly interfere with functioning. +/- psychotic symptoms STEPPED-CARE MODEL STEP 1 • RECOGNITION -feeling down, depressed or hopeless? -having little interest or pleasure? STEP 1 • Assessment and initial management -h/o depression -h/o mood elevation -response to previous treatments -social situation -suicidal ideation and intent • Risk assessment and monitoring -immediate risk refer urgently -at risk provide increased support-freq contact ref to mental health services • Advise person and family/carer -potential for increased agitation/anxiety/suicidal ideation early in treatment -vigilant for mood changes,negativity,hopelessness STEP 2 • GENERAL MEASURES -sleep hygiene -Active monitoring mild depression who do not want an intervention subthreshold symptoms who request an intervention who may recover with no formal intervention Active monitoring discuss concerns/presenting problem further assessment -2/52 provide information make contact if DNA STEP 2 • Drug treatment not routinely used,but consider if -past h/o moderate/severe depression OR -initial presentation of subthreshold symptoms for at least 2 yrs OR -subthreshold or mild depression persisting after other interventions • Depression with chronic physical health problem -as before -mild depression that complicates the care of the physical health problem • Do no prescribe or advise use of St John’s wort STEP 2 • Psychosocial and psychological interventions STEP 3 • Choosing treatments -duration of the episode -previouse illness course and response to treatment -Person’s preference -likelihood of adherence and potential SE • Persistent subthreshold/mild-moderate 1.Antidepressants OR 2.High intensity psychological intervention -CBT -IPT -Behavioural activation -Behavioural couples therapy • Moderate to severe depression combine antidepressants with high intensity psychological treatment [CBT or IPT] STEP 3 • Choosing an antidepressant -anticipated adverse events -potential interactions Efficacy and tolerability of any previous antidepressants -normally choose an SSRI in generic form -toxicity in OD for people at significant risk of suicide • Starting antidepressant treatment -explore any concerns -gradual effect -take as prescribed -need to continue beyond remission -SEs and drug interactions -risk and nature of discontinuation symptoms -addiction does not occur -see them after 2/52 -ever 2-4 weeks in the first 3/12,and then longer intervals if response is good -if risk of suicide or <30yrs see them after 1/52 and then frequently until risk is no longer clinically important • If person experiences SEs early in treatment consider, -monitoring closely if SEs are mild and acceptable OR -stopping/changing if person prefers OR -short term concomitant treatment with benzodiazepine if anxiety/agitation/insomnia are problomatic • If no improvement after 2-4 weeks-check that the drug is taken as prescribed • If response absent or minimal after 3-4 weeks with therapeutic dose -increase dose -switch • Combining psychological and drug treatment -if not responded to either consider combining antidepressants with CBT • Referral -if depression has not responded to various augmentation and combination treatments consider referral • Stopping or reducing antidepressants -discontinuation symptoms usually self limiting over about 1/52 see GP if significant monitor and reassure if mild consider reintroducing original at the dose that was effective if symptoms severe -gradually reduce the dose over 4 weeks STEP 4 • Consider reintroducing treatments that have been inadequately delivered • Assess a person referred to specialist mental health services • Develop a multi disciplinary care plan with the person -identifies roles of all professionals involved -crisis plan -shared with person/GP/other relevant people