* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain Flashcards
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
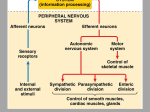
Brain Flashcards 1. What are the 4 major anatomical regions of the brain? 2. What are the two regions in the diencephalon? 3. What are the three regions of the brain stem? 4. Why is proper nutrition important to the brain, and what is the main nutrient it requires? Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brain stem, and Cerebellum 5. Thalamus and hypothalamus Midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. Cerebrum What region of the brain is responsible for logical thought and conscious awareness? 6. What region of the brain is responsible for the highest sensory and motor activity? 7. What is the purpose of having gyri and sulci in the brain? 8. What structure separates the two cerebral 9. hemispheres? 10. What is the largest portion of the brain? 11. What is the second largest portion of the brain? 12. Is the CEREBRUM made of grey matter or white matter? 13. What is grey matter made up of? 14. What is white matter made up of? 15. What are the two halves of the cerebrum called? 16. What area connects the right and left halves of the brain? 17. What would be the effect of cutting the corpus callosum? 18. What disorder has problems with communication between the right and left halves of the brain? 19. What does the left side of the brain control? 20. What does the right side of the brain control? 21. What part of the brain sorts out all the unnecessary sensory information? 22. What region of the brain provides homeostatic control over the body? 23. What part of the brain that exerts more control over autonomic functioning than any other part? 24. What is the main visceral control center of the brain? Cerebrum The gyri and sulci increase the surface area, and the surface is where the information processing is. Longitudinal fissure CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain Cerebrum is made of grey matter Grey matter is made of cell bodies, dendrites, neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons. White matter is made of myelinated axons CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES. CORPUS CALLOSUM The right cerebral hemisphere cannot communicate directly with the left hemisphere. It does not interfere with vision or hearing, and does not cause paralysis. However, it does interfere with being able to speak for a while after the surgery. Autism is a neurological disease that includes problems with communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres. Critical thinking. NOTE: planning and judgment are NOT in the left side of the brain…that is the entire frontal lobe. Emotions THALAMUS Hypothalamus The hypothalamus hypothalamus. Brain Flashcards 25. What does the hypothalamus control? 26. What are the three parts of the brain stem? 27. What part of the brain controls automatic behaviors, such as fight-or-flight? 28. What part of the brain controls visual and 29. audio REFLEXES? 30. What part of the brain is involved in addictions and in initiating body movement? Where is it located? 31. What neurotransmitter does it secrete? 32. Damage to the substantia nigra causes 33. What are two symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease? 34. What part of the brain relays sensory information between the cerebellum and cerebrum? 35. What part of the brain controls autonomic functions such as breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate? 36. What part of the brain plays a role in rousing and maintaining consciousness? Where is it located? 37. What does melatonin do in humans? 38. What part of the brain makes melatonin? 39. What part of the brain is the BIOLOGICAL CLOCK and is responsible for jet lag? 40. What is the second largest portion of the brain? What’s its function? 41. The PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX contains what type of neurons? 42. What does the PRIMARY MOTOR ASSOCIATION AREA do? 43. What area of the brain contains the motor homunculus? 44. What is the motor homunculus? 45. Are all body parts equally represented by cell Temperature, autonomic nervous reflexes, glucose and hormone levels, and the visceral reflexes (digestion, sweating, hunger, thirst, and sleep). It does NOT control blood pressure directly. Brain stem: PONS, MIDBRAIN, and MEDULLA OBLONGATA MIDBRAIN The CORPORA QUADRAGEMINI They send the information to the MIDBRAIN for processing The SUBSTANTIA NIGRA, which is in the MIDBRAIN Substatia nigra secretes DOPAMINE PARKINSON’S DISEASE Trouble starting movements Pill-rolling tremor at rest PONS MEDULLA OBLONGATA (note: it does NOT control hunger and sleep) RETICULAR FORMATION. It is located throughout the brainstem Allows circadian rhythms (sleep cycles; what time of day you feel like sleeping or waking) Pineal gland (pineal body) PINEAL GLAND (pineal body) The CEREBELLUM is the second largest portion of the brain, and is responsible for being able to balance. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX : UPPER MOTOR NEURONS Leaned motor skills and Planning movement PRECENTRAL GYRUS A drawing of a man that represents how many neuron cell bodies we have that innervate each region of our body. No. For instance, the lips and hands are drawn large to Brain Flashcards density in the motor area in proportion to their size in the body? 46. What area of the brain receives signals for touch, temperature, pressure, and pain? 47. What area of the brain interprets signals for touch, temperature, pressure, and pain? 48. The center for vision in the cerebral cortex is located in which lobe of the brain? 49. What area of the brain receives signals from the eyes by way of CN II? 50. What area of the brain interprets signals from the eyes? 51. What is the effect of damage to Brodmann areas 18 and 19? 52. What area of the brain receives signals from sounds from the cochlear nerve? 53. What area of the brain interprets signals from sounds? 54. What region of the brain allows for speech? Stroke in this area can cause what? 55. What region of the brain allows for understanding of words? 56. Where is the primary gustatory (taste) cortex? 57. Which lobe coordinates PLANNING AND JUDGMENT? represent the many cells in the motor area that innervate those regions. PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX 58. What procedure was done to people who were overly aggressive? Frontal lobotomy 59. Do neurons regenerate? No 60. What part of the brain controls memory of events? HIPPOCAMPUS 61. Where are memories stored in the brain? SOMATOSENSORY ASSOCIATION AREA occipital lobe PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX VISUAL ASSOCIATION AREA Damage to Brodmann areas 18 and 19 causes inability to recognize what one sees PRIMARY AUDITORY CORTEX AUDITORY ASSOCIATION AREA Broca’s area Stroke here can cause aphasia (unable to speak) Wernicke’s area In the insula of the temporal lobe of the cerebrum Frontal lobe They are stored throughout the brain, especially in the cerebral cortex and cerebellum. 62. What is anterograde amnesia? 63. What is retrograde amnesia? 64. What is a stroke? can’t remember anything new can’t remember the past Something which deprives an area of the brain of oxygen; usually from a blood clot or hemorrhage in the brain (broken blood vessel) 65. What is the most likely cause of amnesia? 66. What is dementia? Stroke Dementia is loss of memory. It is a symptom, not a disease Brain Flashcards 67. What is Alzheimer’s Disease? 68. In what system of the brain is memory, emotion, and smell linked? 69. The mammillary bodies are part of what region of the brain? 70. What is the function of the mammillary bodies? 71. How can you damage the mammillary bodies, and what disorder does it cause? 72. What does the fornix do? 73. What part of the brain controls balance and coordination? 74. What is the tough meningeal layer called? Alzheimer’s Disease is the most common form of dementia. The LIMBIC SYSTEM They are part of the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus area). They are also part of the limbic system. They relay recognition memory and add the sense of smell to memories. They are damaged by thiamine (vitamin B) deficiency or by alcohol. The disorder is Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (anterograde amnesia) Carries signals from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies CEREBELLUM dura mater. 75. What meningeal layer is between the dura mater ARACHNOID MATER and pia mater? 76. Which one of the meninges follows the brain surface into a cerebral sulcus? 77. Where is Cerebrospinal fluid located? 78. The subaracbnoid space lies between 79. what two layers of meninges 80. What type of injection is between L3 and 81. L4, above the dura mater, so only the 82. nerves are affected? 83. What makes CEREBRAL SPINAL FLUID? 84. Where is CSF located? 85. What are the functions of CSF? 86. What causes HYDROCEPHALY? 87. What two types of organisms cause MENINGITIS? Which one is worse? 88. What is the main symptom of meningitis? 89. What test is done to diagnose meningitis? 90. What is infection of the brain called and how is pia mater Ventricles and subarachnoid space arachnoid and pia An epidural. Ependymal cells in the choroid plexus, which is in the ventricles. Ventricles and the subarachnoid space. 1. Allows the brain to float. 2. It cushions. 3. Acts as the lymphatic system of the brain (it doesn’t have one). This is usually congenital, caused by a blockage of the cerebral aqueduct. Can be caused by a tumor in adults Can be caused from virus (not that bad) or bacteria (can be fatal). The main symptom is a headache SPINAL TAP ENCEPHALITIS Brain Flashcards it caused? 91. Define subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage 92. Name the main ventricles of the brain, and which is largest? 93. Define CSF: What fluid is it similar to? 94. Where is it made? 95. What structure makes it? 96. What type of capillaries does it come out of, and to where does it spread 97. Define closed head injury 98. What are four ways that aging affects the nervous system? 99. What machine is used to measure brain wave activity? 100. What are the 4 types of brain waves? 101. What are alpha waves? 102. What are beta waves? 103. What are theta waves? 104. What are delta waves? 105. What are two main therapies for brain tumors? 106. What does Avastin do? 107. What is VEGF? 108. What part of the brain is first affected by alcohol? 109. What does alcohol do to a fetus 110. What are some problems with nicotine? 111. What effect does cocaine have on the brain? 112. What are the withdrawal symptoms of heroin? 113. What are some negative effects of marijuana on the nervous system? It can be caused by mosquito-borne illnesses, or bacteria The dura and arachnoid mater both have lots Of blood vessels, which might rupture Potentially fatal – blood accumulates and squeezes the brain. Tx = drill a hole Lateral ventricle (largest) Third ventricle Cerebral Aqueduct Fourth ventricle Similar to plasma be/c it is derived from plasma Made in the 3rd and 4th ventricle by the CHOROID PLEXUS There are fenestrated capillaries there; the fluid spreads into the subarachnoid space Brain hits inside of the skull Decline in sensory functions, motor function, short term memory, and insomnia EEG (electroencephalogram) Alpha Beta Theta Delta Active during wakeful relaxation (meditation, prayer) Active when learning, thinking Active when just falling asleep Active during deep sleep Gamma knife radiation therapy Tumor-starving medicines (Avastin) Blocks VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) A chemical our cells make that causes blood vessels to grow toward the cell to feed it. This chemical is made in excess by cancer cells which need excess nutrients. Cerebellum Fetal alcohol syndrome (most common cause of mental retardation in the USA) It is highly addictive. It also increases the heart rate and blood pressure. Withdrawal symptoms include headache, irritability, and insomnia. Depletes dopamine (causes Parkinson’s symptoms) sweating, shakes, abdominal cramps, and an increase in heart rate alteration in vision, judgment, and motor coordination Brain Flashcards