* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory Tract Infection
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
1793 Philadelphia yellow fever epidemic wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Mycoplasma pneumoniae wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever in Buenos Aires wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
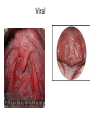
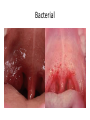
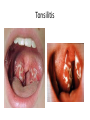
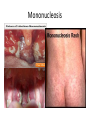
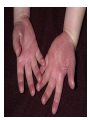
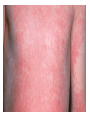
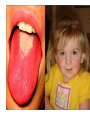
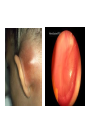
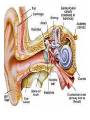
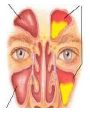
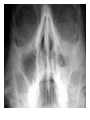
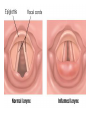
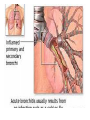
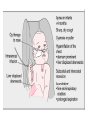
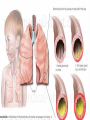
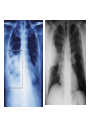
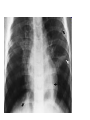
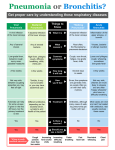
Respiratory tract infectious Respiratory tract infectious Upper Common cold Pharyngitis Laryngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Lower Bronchitis Bronchiolitis Pneumonia Upper respiratory tract infection • Etiology: Viruses: e.g rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, RSV, enteroviruses, EBV, Bacteria: e.g Streptococcus. Pnumococcus, Hemophilus influezna,moraxella catarrhalis Fungi: e.g Candida albicans, Common cold -coryza • Viral ethiology • Clear or mucopurulent nasal discharge or nasal blockage • Fever may occur • Other symptoms : tiredness , headache, • Treatment : paracetamol, ibupropfen, Pharyngitis Symtoms: Throat pain, Fever Physical exam: Inflammed,red pharynx , lymph nodes can be enlarged Etiology: 2/3 viral, 1/3 bacterial Viral Bacterial drops of dew- like accompanying coryza pharynx distinctly red coryza lymph nodes slightly enlarged or not enlarged lymph nodes prominently enlarged and tender Laboratory test Usually low CRP,WBC, Lymphocyte in Blood film High CRP, WBC low or high Neutrophil granulocyte Viral Bacterial Tonsilitis • • • • • • • • Fever red and/or swollen tonsils white or yellow patches on the tonsils tender, stiff, and/or swollen neck(swollen lymph nodes) painful or difficult swallowing Sore throat Abdominal pain , vomiting Antibiotic should be given (penicillin, macrolid) Tonsilitis Mononucleosis(glandular fever) • • • • • • • fever tonsilitis (sometimes causing airway narrowing) prominent lymphadenopathy (Neron’s neck) hepatosplemomegaly a maculopapullar rash no positive reaction to antibiotic most commonly contracted by adolescents and young adults ages • Etiology: mostly EBV Mononucleosis Scarlet fever • acute, bacterial, rash disease of childhood • caused by β hemolytic streptoccoccus, group B • incubation period 1-7 days ( average-3 days) acute onset, fever,vomiting, abdominal pain, • pharyngitis , tonsilitis • rash appears on 1 or 2 day- macular ,punctate intensively red • characteristic location on face- paleness around mouth, spreading downwords Scarlet fever • characteristic tongue ( white strawberry tongue→ red strawberry tongue • haemorrhagic lesions in articular fossae ( Pastia lines) • Desquamation begins after a week from face to limbs Acute infection of the middle ear • fever , pain in ear, irritation, loss of appetite • examination of tympanic membrane: loss of normal light reflection, bulging, red membrane acute infection of the middle ear Complications: • mastoiditis • meningitis Reccurent ear infection may cause chronic secretory otitis media( glue ear), leading to hearing loss Sinusitis • Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses Most cases are due to a viral infection • Pain, swelling, tendreness over a cheek, nasal blockage, headache • Treatment: antibiotics, histamine blockers, decongestants, Laryngitis • • • • • • • • • • • • • Symptoms Hoarseness or no voice at all Dry, sore burning, throat Coughing, barking cough stridor Difficulty swallowing Sensation of swelling in the area of the larynx Cold or flu-like symptoms Swollen lymph nodes Fever Difficulty breathing (mostly in children) Difficulty eating Increased production of saliva in mouth Comparison of clinical features of subglottic laryngitis and epiglottitis • Onset Subglottic laryngitis over days Preceding coryza Cough + severe, barking Epiglottitis over hours slight or absent Ablity to swallow + - Drooling saliva - + Appearence Fever unwell <38,5 Stridor Voice,cry toxic, very ill >38,5 harsh, rasping soft,whispering hoarse Reluctant to speak Treatment of suglottic laryngitis Nebulised steroids and 0,9 % NaClsaline Systemic steroids Oxygen therapy Usually no antibiotics are needed Etiology: mostly viral or allergens Epiglottic laryngitis Etiology: Haemophilus influenzae HIB, rare after HIB vaccinations Treatment of epiglottitis • In intensive care unit • Intubation • Antibiotic (cephalosporin II, III generation) LTRI • Bronchitis (acute, obturative) • Bronchiolitis • Pneumonia Bronchitis • Bronchitis is inflammation of the mucous membranes of the bronchi • Etiology: • Viruses ( Parainfluenzae, Adenovirus, RS-virus, Rhinovirus) • Bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus) • Atopy Symtoms of bronchitis • • • • • • • • non-productive cough productive cough dyspnoe (due to obturation) fever vomiting wheezing dry rale coarse rattling Treatment mucolitycs (eg cysteine derivates, Ambroksol) bronchodilating drugs- Beta Agonist, Ipratropii bromidum Steroids Antibiotics- mainly used in newborns and small chlildren when bacterial infection is suspected (eg Amoxicilline, Cephalosporin antibiotics I, II generation- Cefalotin, Cefuroxim) Broncholitis Etiology: • viruses (RS virus, Parainfluenzae, Influenzae, Adenovirus) One of the most danger LRTI due to lifethreatening respiratory insufficiency Bronchiolitis • • • • • • Typical childhood infection Most often in infancy Cough,expiratory dyspnoe, fever Involvment of bronchioli Respiratory insufficinecy Wheezing , crackles Bronchiolatis • • • • • Oxygen therapy, Bronchodilators- Berodual, Ventolin, Atrovent Steroids-nebulized and/or systemic Nebulized epinephrine Nebulized hypertonic saline (3%) dyspnoe • Sternal, subcostal and intercostal recession • Nasal flaring • Hyperinflation of chest (sternum prominent, liver displaced downward) • Dyscoordination of chest and abdomen movment Pneumonia • Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs. It is a serious infection in which air sacs in the lungs fill with pus and other liquid. • Pneumonia may be lobar or bronchial • Pneumonia is most common in winter and spring. • About 10 to 15 percent of children with a respiratory infection have pneumonia. Pneumonia • The pathogens causing pneumonia vary according to the child's age: • Newborn - organisms from the mother's genital tract, particularly group B streptococcus, but also Gram-negative enterococci Pneumonia • Infants and young children -mostly respiratory viruses, particularly RSV, are most common, but olso bacterial infections include Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae. Bordetella pertussis and Chlamydia trachomatis can also cause pneumonia at this age. An infrequent but serious cause is Staphylococcus aureus • Children over 5 years - Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae are the main causes. • At all ages Mycobacterium tuberculosis should be considered Pneumonia-symptoms: • fever and cough are the first to develop • persistent cough that may last three to four weeks • severe cough that may produce some mucus • chest or stomach pain • decrease in appetite • chills • breathing fast or hard • vomiting • headache • not feeling well Pneumonia • • • • • • • tachypnoea, nasal flaring chest indrawing crackles over the affected area dullness on percussion, decreased breath sounds bronchial breathing Pneumonia-diagnosis • chest x ray- segmental involvement,diffuse peribronchiolar densities,effusion • blood tests- e.g. blood cell count, CRP, • sputum culture • pulse oximetry Treatment • • • • antibiotics Increased fluid intake oxygen therapy frequent suctioning of your child's nose and mouth (to help get rid of thick secretions) • medication for cough • sometimes bronchdilators Pneumonia Complications: • most common: abscesses, empyema • less common: peritonitis, pericarditis,