* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
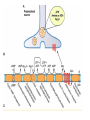
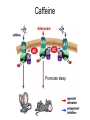
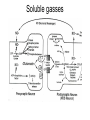
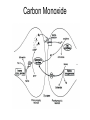
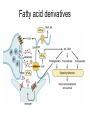
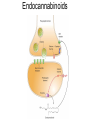
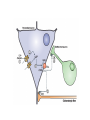
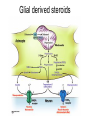
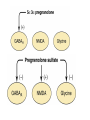
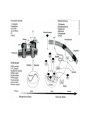
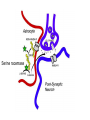
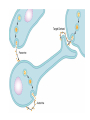
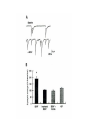
What is a neurotransmitter? • • • • • • Secreted factor from neurons Limited to a specific population Regulated synthesis, enzyme Produce a measurable effect Bind a specific, saturable receptor Release in response to stimulus from axon terminal • Storage in vesicles • Degradation and/or re-uptake Alternative transmitters • • • • • Purines, nucleosides: ATP and adenosine Gases: NO and CO Fatty acid metabolites, endocannabinoids Neurotrophic factors: NGF, BDNF, etc. D-amino acids: D-serine Functions of ATP • Released in response to hypoxia, mechanical stress, injury • Recruits microglia and macrophages • Spinal nociception-neuropathic pain • Regulates breathing in response to pH changes • Short half life, most degraded to adenosine in < 1 sec Functions of adenosine • Released especially by stressed cells – Seems non-exocytotic, non-Na+ or Ca2+ dependent – Stimulated release of ATP is TTX sensitive and Ca2+ dependent • Increases oxygen delivery by dilating vessels • Decrease cell energy usage (reduce cellular oxygen requirements) – Decrease firing rate, NT release, etc. Caffeine Promotes sleep Adenosine transport Soluble gasses Carbon Monoxide Fatty acid derivatives Endocannabinoids Glial derived steroids Serine racemase Knockouts of all these NTs, and their receptors, are lethal. Acute roles for NT in adult brain • Application of NT to brain leads to seizure activity (coordinated neural discharge) • NGF application to PNS leads to painful sensation • Neuronal activity likewise regulates NT synthesis (BDNF and NGF by seizure)