* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alzheimer Disease - Bellarmine University
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
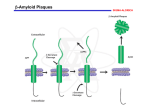
Healthy Alzheimers 1) Loss of neurons (cortical degeneration) 3 Prevents tubulin 2 Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) • 10 different isoforms (alternative splicing) • Transmembrane region at the Carboxyl end allows shorter isoforms to localize to the neuronal membrane, and in the Golgi bodies • Longer isoforms are found in non-neuronal cells • Normal function = Receptor? Adhesion? Amyloid Precursor Protein The enzymes that cut these are called ‘Secretases’ (specific proteases) Normally cut In healthy cells Figure 14.9 Neuron Amyloid Precursor Protein No AD Normally cut In healthy cells Figure 14.9 Neuron Amyloid Precursor Protein No AD No AD Normally cut In healthy cells Figure 14.9 Neuron Amyloid Precursor Protein No AD No AD AD Normally cut In healthy cells Figure 14.9 Neuron Amyloid proteins (40 or 42 amino acid) cause plaques to form in the brain Check out this link to photo from the brain of a 76 year old with Alzheimers http://vm.cclcm.ccf.org/slide.jsp?instGUID=90ADFDBE-7CAA-4925-2FE3-6E26EB6B33A6 Plaque Neurofibrillary Tangles (tau Tangles) They look like flames (or tadpoles) tau protein normally helps microtubule assembly and stability Phosphorylation of tau Microtubules help transfer vesicles & send signals down the axon http://www.uphs.upenn.edu/news/News_Releases/dec04/paclitaxel.htm < Animation Two Types of AD: Early Onset (before 65 years of age) = less than 10% of AD; caused by dominant mutations on Chromosomes 1, 14 or 21… even if one of these genes are inherited > AD Chromosome 21 = Amyloid Precursor Protein Early Onset AD: Phenotype the same as Late Onset AD, except shows up between ages of 45-60. Late Onset AD don’t have mutation on APP Chromosome 21 = Amyloid Precursor Protein Missense mutations V717I V717G V717F I716V K670N M671L This somehow encourages the removal of the Beta-Amyloid segment What comes first? The disease? The plaques? The tau Tangles? Two Types of AD: Early Onset (before 65 years of age) = less than 10% of AD; caused by dominant mutations on Chromosomes 1, 14 or 21… even if one of these genes are inherited > AD Chromosome 21 = Amyloid Precursor Protein Chromosome 14 = Presenilin-1 (helps γ-Secretase) Chromosome 1 = Presenilin-2 (rare; helps Secretases) By 1995, researchers knew that there were three proteases that were cleaving the β-Amyloid fragment and set about to find the genes involved. Most of the searching was done by pharmaceutical companies…. Finally, in 1999 GlaxoSmithKline announced they had cloned β-Secretase ! Two Types of AD: Late Onset (after 65 years) = 90% of cases; often due to sporadic mutations, but can be inherited (not one gene in particular, probably multigenes). Example = Apolipoprotein E (Chromo. 19) …called a “risk factor” The Amyloid Precursor Protein is not mutated In most cases of Late Onset AD Two Types of AD: Late Onset Apolipoprotein E (Chromo. 19) Synthesized by Astrocytes (non-neuronal cells) that control passage of things, like cholesterol, to the brain…Blood-Brain Barrier) • Published in February 2006 • Twin Study (done in Sweden) • 2800 set of twins over the age of 65 were tested for dementia and AD Gatz, M. et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006;63:168-174. Copyright restrictions may apply. Prevalence of Total Dementia and Alzheimer Disease, Probandwise Concordance Rates, and Tetrachoric Correlations (With 95% Confidence Intervals) by Zygosity and Sex See pages 10-11 of our book Of twins (where one has AD) how often do both have AD? Gatz, M. et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006;63:168-174. Copyright restrictions may apply. They also calculated heritability Calculated heritability of AD to be 58% Prevalence of Total Dementia and Alzheimer Disease, Probandwise Concordance Rates, and Tetrachoric Correlations (With 95% Confidence Intervals) by Zygosity and Sex Gatz, M. et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006;63:168-174. Copyright restrictions may apply. Canadian Family Physician Feb. 2006 • Controlling menopause with estrogen doesn’t help • Currently, no great pharmaceutical advances But, these things help: • Controlling high blood pressure • Healthy lifestyle (diet, sleep, • Ongoing education (‘new learning’) • Regular physical activity • Lowering cholesterol (Apolipoprotein E) • Preventing early head trauma But drug development is underway Four million Americans have Alzheimers. What sort of medicines might be designed to fight Alzheimers Disease? What doesn’t help: Megadoses of antioxidants Vitamin E and Vitamin C….. …they actually appear to hurt! Auburn University, 2005 1) Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that is important in the parasympathetic nervous system (autonomous system that is responsible for returning body functions back to normal after stimulation). Neurotransmitters released into ‘cleft’ Examples: • Glutamate (most common in brain) • Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) • Dopamine • Acetylcholine • Epinephrine • Histamine • Serotonin • Neurotensin • Nitric Oxide • Neuropeptide Y Acetylcholinesterase is the enzyme that breaks down Acetylcholine. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors increase the amount of Acetylcholine. This seems to help AD patients. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Tacrine (Tetrahydroaminoacridine) was the 1st treatment approved for Alzheimers (1995). Now, have several other drugs that act the same way…..basically increasing the levels of Acetylcholine. 2) High levels of the neurotransmitter, Glutamate occur in AD patients. This overstimulates the Calcium channels to let in too much Ca+. What if you could block the Glutamate Receptor? Memantine (a drug used in Germany for 20 years to treat brain disease) does just that. Approved in U.S. in 2003. Really helps patient with severe AD….. doesn’t help as much in early stages Hyperlink > 3) Is exposure to Aluminum associated with AD? Controversial…but it is increasingly looking to be true! Β-Amyloid shape is affected by Iron, Zinc, Copper, Iron & Aluminum Aluminum also causes accumulation of tau protein Kyushu University of Health and Welfare, Japan, 2005 Clioquinol Originally used against skin infections Chelates Zinc & Copper and reduces tau tangles & plaques in mice… …but contains an impurity so has been taken off the market. Insert Joke Here 4) Voyager Pharmaceutical Corp. observed an AD patient with unusual levels of a hormone called “Gonadotropin”…. …….which regulates estrogen and testosterone level. They are investigating ways to modify levels of this hormone in AD patients. North Carolina, 2006 5) Lipitor (the anti-cholesterol drug) appears to help AD patients 6) Anti-Psychotic Drug to treat Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disease Used for AD in nursing homes. Actually makes AD worse. King’s College, London, February, 2005 7) γ-Secretase Developing drugs to inhibit gamma-Secretase. But finding that this enzyme has roles in healthy tissue. For instance: embryonic development (Notch), T-cell development, intestines. University of Tokyo, 2006 γ-Secretase Some anti-inflammatory medicines (like Ibuprofen) reduce γ-Secretase activity. But others (like Naproxen, Celebrex, Vioxx) don’t. University of Tokyo, 2006 8) β-Secretase Developing drugs to inhibit beta-Secretase. Has fewer side effects in animals. 2006 9) Alzhemed Binds to ß-amyloid protein after it is made but prevents it from aggregating into plaques. Clinical trials in Canada & Europe right now 10) Amyloid Plaques first form inside Acetylcholine-responsive neurons. So researchers are looking for ways to block the movement of Amyloid protein into these Neurons. 11) Vaccination against Alzheimers Injecting people with small amounts of β-amyloid protein to raise an immunity to it. But 6% of test patients got seriously ill. 12) Isolate skin cells and insert the gene for Nerve Growth Factor (linked to a promoter that induces high levels of transcription). Then these cells are implanted in the brain. Seems to be working. At a recent meeting of AD researchers and M.D.s at John Hopkins University there were vigorous questions from physicians about what they should actually prescribe for AD. One researcher estimated that the current treatments on the market might be 10% effective. Another expert gave better odds….. “All you can do is look into your soul and do the best you can” said one expert. Heritability of Lung Cancer = 25% The seven warning signs of Alzheimer's Disease: 1. Asking the same question over and over. 2. Repeating the same story, word for word. 3. Forgetting how to do activities that were previously easy (like cooking, playing cards, etc.). 4. Losing one's ability to pay bills or balance one's checkbook. 5. Getting lost in familiar surroundings, or misplacing common objects. 6. Neglecting to bathe, or wearing the same clothes over and over. 7. Relying on someone else, such as a spouse, to make decisions or answer questions. http://www.nia.nih.gov/Alzheimers/Publications/sevensigns.htm