* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Early Development
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
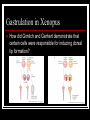
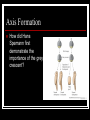
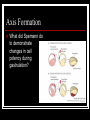
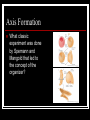
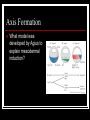
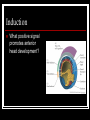
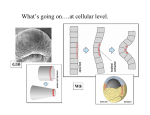
Early Development Amphibians Cleavage in a frog Describe the progression of events. Gastrulation in Xenopus What have fate maps told us about tissue origins? Gastrulation in Xenopus What are VegT and Vg1 and what influcence do they have? Gastrulation in Xenopus What type of cell movement initiates gastrulation? Gastrulation in Xenopus What happens next? Gastrulation in Xenopus What happens at the mid-blastula transition in preparation for gastrulation? How is dorsal-ventral axis established? What happens if cortical rotation is blocked? Gastrulation in Xenopus How did Gimlich and Gerhart demonstrate that certain cells were responsible for inducing dorsal lip formation? Gastrulation in Xenopus What appears to be the major factor directing movement of cells into embryo? Gastrulation in Xenopus What other cell movements occur? Gastrulation in Xenopus What two factors appear to drive convergent extension? adhesion proteins paraxial and axial protocadherin are expressed changes in calcium concentrations Gastrulation in Xenopus At what point in gatrulation do notocordal cells become distinct? Gastrulation in Xenopus What mechanism appears to be responsible for epiboly of the ectoderm? Axis Formation How did Hans Spemann first demonstrate the importance of the grey crescent? Axis Formation What did Spemann do to demonstrate changes in cell potency during gastrulation? Axis Formation What classic experiment was done by Spemann and Mangold that led to the concept of the organizer? Axis Formation How did work of Nieuwkoop and Nakamura contribute to an understanding of how the “organizer” worked? Axis Formation What is the Nieuwkoop center? How is it formed? Axis Formation What is involved in the mechanism of induction of mesoderm by endoderm? What appears to be the role of β-catenin? What is the connection between β-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase – 3 (GSK3)? Axis Formation How does β-catenin become concentrated in dorsal cells of embryo? Axis Formation How does β-catenin contribute to formation of the organizer? Axis Formation What model was developed by Agius to explain mesodermal induction? The Organizer What are the four major functions of this tissue? differentiate into dorsal mesoderm induce formation of paraxial mesoderm induce formation of neural tube initiate gastrulation movements The Organizer What is the role of the goosecoid gene? The Organizer How does the organizer actually induce formation of neural tissue? The Organizer What are the proteins secreted by the organizer? The Organizer What can the secreted protein noggin do? What other proteins exhibit similar effects? The Organizer What are some of the important effects of BMP-4? The Organizer What are the functions of the diffusable proteins cerberus, dickkopf and Frzb? How do these proteins work? The Organizer The Organizer Why is neurogenin so important? Induction How did Otto Mangold demonstrate the regional specificity of neural induction? Induction Toivonen and Saxen postulated two gradients in amphibian embryos dorsal gradient – “neuralizing” activity caudal gradient – “posteriorizing” activity What is the primary protein involved in posteriorizing the neural tube? Induction What positive signal promotes anterior head development? Left-Right Axis What appears to be major event in leftright axis formation in Xenopus?