* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Changes Within the Earth
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
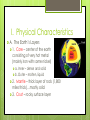
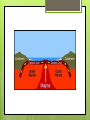
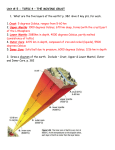
Changes Within the Earth 1-2 I. Physical Characteristics A. The Earth’s Layers 1. Core – center of the earth consisting of very hot metal (mainly iron with some nickel) a. Inner – dense and solid b. Outer – molten, liquid 2. Mantle – thick layer of rock (1,800 miles thick)…mostly solid 3. Crust – rocky surface layer B. Land, Air, and Water 1. Lithosphere – soil, rocks, landforms, & other surface features 2. Atmosphere – layer of air, water, and other substances above the surface 3. Hydrosphere – water in oceans, lakes, and rivers & under ground 4. Biosphere – world of plants, animals, and other living things that occupy the planet C. The Planet 1. 70% of earth’s surface is covered by water a. b. c. d. e. Atlantic Ocean Pacific Ocean Indian Ocean Arctic Ocean Southern Ocean 2. Continents – large landmasses in the oceans a. North America b. South America c. Africa d. Asia *largest e. Australia *smallest f. Antarctica g. Europe D. Landforms - *classified according to differences in relief (the difference in elevation between the highest and lowest points) 1. mountains – high relief at least 2,000 ft. 2. hills – lower, rounded, and less steep than mountains 3. plateaus – raised area with a generally level surface 4. plains – flat or gently rolling area with few changes in elevation II. Physical Processes A. Volcanoes 1. form when magma breaks through the earth’s crust 2. lava – molten rock B. Movements in the Crust 1. fold – when rock layers bend and buckle 2. faults – breaks in the earth’s crust *whether rock layers fold or fault is determined by the hardness of the rock and the strength of the movement *large, sudden movements that occur along a fault can cause earthquakes III. Understanding the Past A. Plate Tectonics 1. theory that suggests the earth is not one solid sheet of rock 2. instead, it’s broken into a number of moving plates 3. the plates vary in size and thickness 4. the earth’s oceans and continents ride atop the plates as they move in different directions 5. most earthquakes, volcanoes, & other geological events occur on plate boundaries B. Continental Drift 1. continental drift theory – the idea that continents slowly shift their positions due to movement of the tectonic plates on which they ride 2. proposed by Alfred Wegener who said that there once was a single “supercontinent” 3. Pangaea – the supercontinent that began to break apart 180 million years ago 4. supported his theory by finding fossils (preserved remains of ancient animals & plants) that were identical from all different continents C. Seafloor Spreading 1. using sonar, scientists mapped the floor of the Atlantic Ocean and found that the floor was not flat 2. they found mountains, deep canyons, and wide plains much like what is above water 3. samples that they took showed that the rocks on the ocean floor were much younger than the rocks above water 4. seafloor spreading – molten rock from the mantle rises beneath the underwater ridge and breaks through a split at the top of the ridge D. Plate Movement 1. convection – circular movement caused when a material is heated, expands and rises, then cools and falls 2. this happens beneath the plates and causes them to move E. When Plates Meet 1. Spreading – when plates move away from each other 2. Subduction – when one plate slides underneath another toward the mantle *the rock melts & many erupt as volcanoes (Andes) 3. Converging – when two plates collide and neither sink *likely to have rift valley, earthquakes, & volcanic activity *buckling, folding, & faulting will produce huge mountain ranges (Himalayas) 4. Faulting – when plates slip or grind past each other *causes earthquakes (San Andreas Fault) Subduction Spreading Converging Faulting F. Explaining Volcanoes 1. Ring of Fire – circle of volcanoes surrounding the Pacific Ocean 2. volcanic islands can form far away from fault lines 3. “hot spots” are regions deep in the earth’s mantle where columns of magma rise towards the earth’s surface a. The magma may heat underground water and produce hot springs or geysers (Yellowstone National Park) b. If molten rock flows out of a crack in the surface, it may produce a volcanic island chain (Hawaii)