* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disease-Causing Viruses and Microorganisms
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Swine influenza wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
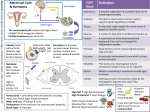
Disease-Causing Viruses and Microorganisms Disease-Causing Viruses & Microorganisms (pathogens) Viruses • Structure of Virusesgenetic material surrounded by protein shell Protein shell (capsid) Viral DNA/RNA Another kind of viral structure (Capsid) Viruses View from a microscope Viruses • Much smaller than bacteria Viruses • Not considered to be living because they cannot survive alone • They can reproduce only inside of other living things. A single infected cell may replicate thousands of viruses. The new viruses go on to infect other cells. Viruses Viruses • Mutations of Viruses- Some viruses’ DNA can mutate at a very high rate, making it difficult to treat them with medicines. This is why new medicines and vaccines have to be discovered constantly. Examples of Viruses • HIV- causes AIDS; attacks white blood cells/immune system; death usually occurs from getting sick from another disease; high rate of mutation Kaposi’s sarcoma HIV: the AIDS Virus Transmitted by: • Blood-contaminated products •Contaminated blood •Sexual intercourse Origins: Scientists are still uncertain where the virus came from, but have noted a similar virus (SIV) in monkeys, which may have mutated. Patient 0: a Canadian flight attendant E:\Biology\HIV_and_AIDS. asf Examples of Viruses • Influenza- many different strains; high mutation rate; fever, muscle aches, chills, extreme fatigue Influenza Virus Flu Epidemics: • First epidemic recorded in Europe? 1173 • Russian Flu (1889-1890)- 1 million deaths • Spanish Flu (1918-1919)- over 50 million died • Asian Flu Pandemic (1957-1958)- about 2 million deaths • Hong Kong Flu Pandemic (1968-1969)- about 1 million deaths • Avian Flu discovered (1996) • E:\Biology\The_Influenza_Pandemic_of_1918.asf Should you get a flu shot? • Flu vaccines are chancy. They include parts of dead flu viruses that scientists believe are the “most likely suspects” to cause the flu this year. Your immune system learns to recognize them and fight them. (You can actually feel a little sick after getting the shot.) • However, the flu virus mutates quickly, and may look nothing like anything in the shot. • Effectiveness of the vaccine varies from year to year. Doctors recommend it for young children, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems. Examples of Viruses • Smallpox- once eradicated; may come back via bioterrorism. Vaccine is being developed again; causes fever, fatigue, body ache, rash, pustules Examples of Viruses • Herpes Simplex- two types; type I causes cold sores; type II causes genital herpes It is transmitted by sexual intercourse. Currently there is no cure for Herpes. Examples of Viruses • Chicken pox- small red, itching spots; can recur in adults as Shingles Children in the U.S. may now be vaccinated for chicken pox. Examples of Viruses • West Nile Viruscarried by mosquitos; may show no symptoms (80%) or fever, headache, vomiting, coma, tremors, vision loss, paralysis (20%) Examples of Viruses • Rabies- transmitted by bite of rabid animal; fatigue, headache, fever, disorientation, hallucinations, seizures, death or coma After bitten, victim must be treated with a series of vaccinations. Other Nasty Viruses Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever- one strain is 90% fatal, extremely virulent, liquefies internal organs, patients “bleed out” of every orifice Other Nasty Viruses Hantavirus- carried by mice (mice feces), 50% fatal, one strain causes respiratory infection & failure, another causes hemorrhagic fever (SW U.S. has had cases!) Other Nasty Viruses Lassa Fever- carried by rats, 50% fatal, can cause fever, hearing loss, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, facial swelling, mucosal bleeding, tremors. Bacteria Mutations of Bacteria – bacteria that are repeatedly exposed to antibiotics are likely to mutate and become resistant (Show Video clip- HHMI Infectious Diseases- Bacterial Growth) Examples of Bacteria • Streptococcus/strep throat – severe and sudden sore throat without coughing or sneezing, fever, white or yellow spots on throat/tonsils Strepto = chain Coccus = round Examples of Bacteria • E.coli – watery/bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, anemia; 2-6 days; usually results from eating undercooked beef meat Most strains of E.coli are harmless, and live in large intestines of humans and animals. A few strains cause the food poisoning above. Movie: see Fast Food Nation Examples of Bacteria • Salmonella – usually results from eating undercooked chicken/eggs or egg products, diarrhea and vomiting for 2 weeks. Also found on some turtles! Examples of Bacteria • Botulism – bacteria produces toxin; homecanned foods and honey (infants); flaccid muscles, double/blurred vision, slurred speech; toxin is used for cosmetic purposes (botox) Do not open cans/canned food that looks “inflated”. Examples of Bacteria • Anthrax – produces white spores; 3 types 1. Cutaneous (skin) – itchy bump, then pustule with black center; usually contracted from hides and wool; 20% fatal if not treated Often affects animal (livestock) handlers- aka “Ragpicker’s Disease” or “Wool sorter’s Disease” Examples of Bacteria Anthrax types: 2. Inhalational – agent of bioterrorism; flu symptoms (muscle aches, fever), then difficulty breathing, shock, usually death X-ray of infected lungs Examples of Bacteria Anthrax types: 3. Gastrointestinal – contaminated meat; nausea, vomiting (w/ blood), severe diarrhea Examples of Bacteria • Tetanus – “rusty nail”; bacteria lives in soil; lockjaw, difficulty swallowing, muscle spasms, continual contracting of muscles, airway obstruction Examples of Bacteria • Cholera – caused by drinking water contaminated with feces; explosive diarrhea, ricewater stool, dehydration Can also be caused by eating undercooked shellfish Cholera bed Examples of Bacteria • Lyme Disease – carried by ticks; rash (sometimes fades to a bull’s eye shape), fever, chills, muscle ache, fatigue, sometimes irregular or slow heart beat Other Nasty Bacteria Typhoid fever- Salmonella typhi, causes abdominal pain, blinding headache, rash, high fever, the tale of Typhoid Mary- some people can be carriers & not get sick Typhoid Mary Other Nasty Bacteria Tuberculosis- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, most common form is pulmonary TB, spread by airborne droplets, causes bloody cough, pain, & breathlessness, victims waste away. http://www.schs.state.nc.us/SCHS/gis/atlas/tb.html Protists Examples: • Plasmodium – causes malaria – Headache, nausea, fever, vomiting, chills, dizziness, abdominal cramps, muscle pain, dry cough Examples of Protists • Giardia – contracted by drinking contaminated water (rivers, lakes, etc.) – USE A GOOD WATER FILTER AND/OR BOIL WATER IF BACKPACKING!); diarrhea, bloating, farting, stomach cramps, fatigue, and weight loss Giardia is a parasite! Fungus Examples: • Athlete’s foot – itching and burning feet, skin peeling, cracking, pain, and bleeding; usually associated with locker rooms; up to 70% of the population will have it sometime in their lives!; can be treated with OTC (over the counter) meds Examples of Fungus • Ringworm – itchy, red scaly patches that may blister or ooze; redder on outside with normal skin tone inside (like a ring) “Barber’s itch”