* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bohr Model and Quantum Model
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
James Franck wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
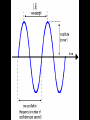
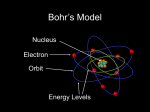
CHEMISTRY “ELECTRONS IN ATOMS” proposed that the energy of the electron in the H atom was quantized allowed energy levels for the electron = ORBITS (electron can only have certain amounts of energy, not any possible amount) RULE 1: Electrons can orbit only at certain allowed distances from the nucleus. RULE 2: Atoms radiate energy when an electron jumps from a higher-energy orbit to a lower-energy orbit. Also, an atom absorbs energy when an electron gets boosted from a low-energy orbit to a highenergy orbit. Ground state-the original energy level of an electron before becoming excited Excited state-describe an electron that has become excited Photons are a particle of radiation or an individual quantum of light Quantum is a finite quantity of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom Using the Bohr’s Model of the atom, if an electron in an atom of hydrogen goes from energy level 6 to energy level 2, what is the wavelength and frequency of the EM radiation emitted? Which transition occurs when a hydrogen atom emits light with a wavelength of 434 nm? A) The electron jumps from n=2 to n=4 B) The electron jumps from n=2 to n=5 C) The electron falls from n=4 to n=2 D) The electron falls from n=5 to n=2 applied known wave equations to electrons In 1926 the Quantum Model was formed It states that electrons do not have precise orbits or paths Electrons move about in a cloud around the nucleus in what appears to be a random pattern The Quantum Model only predicts where an electron is likely to be found Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Heisenberg stated that you may know the location of an electron or the velocity of electron but you may not know both simultaneously In the quantum model, the nucleus is not surrounded by orbits, but by atomic orbitals Atomic Orbitals: a 3-D (three dimensional) region around the nucleus where a certain electron can be located Electrons emits energy in the form of radiation Low energy electrons are found near the nucleus; high energy electrons are found further away from the nucleus The Quantum Model is based on understanding the behavior of light Light is composed of Electromagnetic (EM) waves EM spectrum shows all forms of radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum Encompasses all forms of electromagnetic radiation, with the only differences in the types of radiations is their frequencies and wavelengths. The Speed of Light remains the same always. Waves Wavelength: () the distance between wave crests measured in m or nanometers (nm) Amplitude: height of wave from origin to crest Trough-the lowest point on a wave Crest-the highest point on a wave Frequency Frequency: () the number of wave cycles that pass a given point in a given time Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz) 1 Hertz = 1/s