* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mobile Communication
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Communications in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
PSTN network topology wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mobile phone wikipedia , lookup
Mobile telephony wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in India wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
History of smart antennas wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Norwegian Public Safety Network wikipedia , lookup
Mobile television wikipedia , lookup
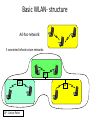
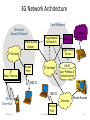
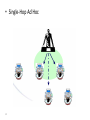
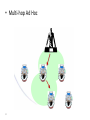
Cellular Networks 1 What is mobility? Spectrum of mobility, from the network perspective: no mobility mobile wireless user, using same access point high mobility mobile user, connecting/ disconnecting from wired network . mobile user, passing through multiple access point while maintaining ongoing connections (like cell phone) 6-2 Cellular Network Basics • There are many types of cellular services. • Cellular network/telephony is a radio-based technology; • Radio waves are electromagnetic waves that antennas propagate • Most signals are in the 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequency bands Cell phones operate in this frequency range (logarithmic scale) 3 Components of cellular network architecture MSC cell connects cells to wide area net manages call setup handles mobility covers geographical region base station (BS) mobile users attach to network through BS air-interface: physical and link layer protocol between mobile and BS Mobile Switching Center Public telephone network, and Internet Mobile Switching Center wired network In a cellular network, a geographical region is divided into service areas called “cells.” A cell is represented as a hexagon. At the center of a cell, is a Base Transceiver Station (BTS or BS) that serves users within the cell. Each cell is allocated a certain number of channels operating at a certain frequency. Base Station: It is a BS consisting of a transceiver that receives or transmits signals over the radio interface. It serves one cell only. BS controller (BSC): controls one or more BSs. Mobile switching center (MSC) sets up and maintains calls made in the network. An MSC connects the cellular network to the fixed telephone network infrastructure (i.e., the Public Switched Telephone Network [PSTN]). It performs all switching and signaling functions for MSs located in its area. Databases When you subscribe to a mobile telephony service, your information is stored in a database called: a Home Location Register (HLR). The HLR plays an important role in providing you with the services offered by your Service Provider. Databases Home Location Register (HLR), stores data of participants, which are reported in an HLR-area – Semi-permanent data: • Call number • identity (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) - IMSI: MCC = Mobile Country Code (262 for .de) + MNC = Mobile Network Code • Personal data (name, address, mode of payment) • Service profile ( call transfer, Roaming-limits etc.) – Temporary data: • • • • MSRN (Mobile Subscriber Roaming Number) (country, net, MSC) VLR-address, MSC-address Authentication Sets of AuC Charge data The Visitor Location Register (VLR) VLR is a database in a mobile communications network associated to a Mobile Switching Centre (MSC). The VLR contains the exact location of all mobile subscribers currently present in the service area of the MSC. This information is necessary to route a call to the right base station. Deleted when the subscriber leaves the service area. Databases Visitor Location Register (VLR) • local database of each MSC with following data: – IMSI, MSISDN – service profile – Accounting information – TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) pseudonym for data security – MSRN – LAI (Location Area Identity) – MSC-address, HLR-address Mobile Communication Networks Mobile Communication Networks UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System): European Standard for future digital Mobile Radio Networks GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications): worldwide standard for digital, cellular Mobile Radio Networks 802.11: International standard for Wireless Local Networks Bluetooth, Zigbee. Mobile Communication Tied to electro-magnetic radio transmission radio transmission orbital (satellite) terrestrial beam radio broadcast radio cellular equatorial orbit non-equatorial orbit non-cellular Principles: – Propagation and reception of electro-magnetic waves – Multiplex – Satellite orbits/Sight- and overlap areas GSM: Properties • Cellular radio network (2nd Generation) • Digital transmission, data communication up to 9600 Bit/s • Roaming (mobility between different net operators, international) • good transmission quality (error detection and -correction) • Scalable (large number of participants possible) • Security mechanisms (authentication, authorization, encryption) • Good resource use (frequency and time division multiplexing) • Integration within ISDN and fixed network Wireless Local Networks, WLAN Why do we need Wireless LANs? Advantages • No cables • Flexibility • Ad-hoc-networks Disadvantages • High error vulnerability on the transmission link in comparison to Standard-LANs • National restrictions, no international standards at used frequency bands (Industrial Scientific Medical (ISM)- Band) • Security, costs Basic WLAN- structure Ad-hoc-network: 3 connected infrastructure networks: STA4 AP AP AP - Access Point AP STA5 Mobile IP (Internet Protocol) Internet Protocol (IP) • IP is the principal communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. • Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet. • IP has the task of delivering packets from the source host to the destination host solely based on the IP addresses in the packet headers. • The first major version of IP, Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is the dominant protocol of the Internet (IPv6). Problem definition of classical IP • Computer mobility in heterogenic networks • Relocation between different IP-subnets • Goal: transparent migration and localization, compatibility to IP, no changes of existing routers • Idea: introduction of temporary/ actual IP-addresses • Mapping of permanent to temporary IP-addresses using localization technique Requirements to MobileIP Transparency: – mobile computer is permanently reachable via its previous “home-address” – can change its network access point freely – can also communicate after coupling/uncoupling Compatibility: – mobile computer can also communicate with each “nonmobileIP”-computer – no changes to existing computer/routers Security: – all registering messages must be authenticated 3G Network Architecture Core Network Wireless Access Network Mobile Access Router Programmable Softswitch IP Base Stations Gateway Application Server IP Intranet Access Point Telephone Network IP Intranet (HLR) User Profiles & Authentication 802.11 802.11 3G Air Interface Sridhar Iyer Internet Wired Access Access Point IIT Bombay 23 What is 802.11? • A family of wireless LAN (WLAN) specifications developed by a working group at the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) • Defines standard for WLANs using the following four technologies – – – – Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) Infrared (IR) Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) • Versions: 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11e, 802.11f, 802.11i Performance • 802.11a maximum rate of 54Mbps in the 5 GHz band • 802.11b maximum rate of 11Mbps at in the 2.4 GHz spectrum band • 802.11g is a new standard for data ratesup to 54 Mbps at 2.4 GHz. Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Introduction • Two types of wireless networks: – Infrastructured network: • Base stations are the bridges • A mobile host will communicate with the nearest base station • Handoff is taken when a host roams from one base to another 27 – Ad hoc network: • infrastructureless: no fixed base stations • without the assistance of base stations for communication • Due to transmission range constraint, –two units need multi-hop routing for communication • quickly and unpredictably changing topology 28 • MANET = Mobile Ad Hoc Networks – a set of mobile hosts, each with a transceiver – no base stations; no fixed network infrastructure – multi-hop communication – needs a routing protocol which can handle changing topology 29 • Single-Hop Ad Hoc 30 • Multi-hop Ad Hoc 31 Typical Ad-Hoc applications • Personal area networking – cell phone, laptop, ear phone, wrist watch • Military environments – soldiers, tanks, planes • Civilian environments – car network • meeting rooms – sports stadiums – boats, small aircraft • Emergency operations – search-and-rescue – policing and fire fighting 32 • The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a standardized network protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for dynamically distributing network configuration parameters, such as IP addresses for interfaces and services. • With DHCP, computers request IP addresses and networking parameters automatically from a DHCP server, reducing the need for a network administrator or a user to configure these settings manually. How do you contact a mobile friend: Consider a friend frequently changing addresses, how do you find her? I wonder where Alice moved to? • search all phone books? • call her parents? • expect her to let you know where he/she is? 6-34 Mobility: approaches • Let routing handle it: routers advertise permanent address of mobile-nodes-in-residence via usual routing table exchange. – routing tables indicate where each mobile located – no changes to end-systems • Let end-systems handle it: – indirect routing: communication from correspondent to mobile goes through home agent, then forwarded to remote – direct routing: correspondent gets foreign address of mobile, sends directly to mobile 6-35 Mobility: approaches • Let routing handle it: routers advertise permanent address of mobile-nodes-in-residencenot via usual routing table exchange. scalable – routing tables indicate where each mobile located to millions of – no changes to end-systems mobiles • Let end-systems handle it: – indirect routing: communication from correspondent to mobile goes through home agent, then forwarded to remote – direct routing: correspondent gets foreign address of mobile, sends directly to mobile 6-36 GSM: handoff with common MSC • Handoff goal: route call via new base station (without interruption) • reasons for handoff: VLR Mobile Switching Center old routing old BSS new routing new BSS – stronger signal to/from new BS (continuing connectivity, less battery drain) – load balance: free up channel in current BS GSM: handoff with common MSC VLR Mobile Switching Center 2 4 1 8 old BSS 5 7 3 6 new BSS 1. Old BS informs MSC of impending handoff, provides list of 1+ new BSs 2. MSC sets up path (allocates resources) to new BS 3. new BS allocates radio channel for use by mobile 4. new BS signals MSC, old BS: ready 5. old BS tells mobile: perform handoff to new BS 6. mobile, new BS signal to activate new channel 7. mobile signals via new BS to MSC: handoff complete. MSC reroutes call 8 MSC-old-BS resources released 6-38 GSM: handoff between MSCs • anchor MSC: first MSC visited during call home network correspondent Home MSC anchor MSC PSTN MSC MSC MSC – call remains routed through anchor MSC • new MSCs add on to end of MSC chain as mobile moves to new MSC • IS-41 allows optional path minimization step to shorten multi-MSC chain (a) before handoff 6-39 GSM: handoff between MSCs anchor MSC: first MSC visited during cal home network correspondent Home MSC call remains routed through anchor MSC new MSCs add on to end of anchor MSC PSTN MSC MSC MSC MSC chain as mobile moves to new MSC IS-41 allows optional path minimization step to shorten multi-MSC chain (b) after handoff 6-40