* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Review
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
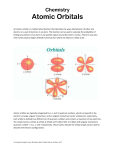
Chapter 13 Review Atomic Models The first model of the atom showing electrons was developed by JJ Thomson. What did he call his model? The Plum Pudding Model Atomic Models Rutherford’s model of the atom included a ________. nucleus Atomic Models The Bohr Model was the first model that showed the electrons located in ________ ________. energy levels Atomic Models Energy levels on a Bohr model are like _______ of a __________. steps of a ladder Atomic Energy A ___________ is the amount of energy required to move from one energy level to the next. quantum Atomic Energy What do electrons usually release when going from the excited state back to the ground state? photons Atomic Models What is the most current model of the atom called? Quantum Mechanical Model Atomic Models The Quantum Mechanical Model is based on who’s equations? Erwin Schrodinger Atomic Sublevels How many sublevels are in energy level 1? 1 sublevel (s) Atomic Sublevels How many sublevels are in energy level 2? 2 sublevels (s,p) Atomic Sublevels How many sublevels are in energy level 3? 3 sublevels (s,p,d) Atomic Sublevels How many sublevels are in energy level 4? 4 sublevels (s,p,d,f) Atomic Orbitals List the 4 sublevels in order of lowest energy to highest energy. s, p, d & f Atomic Orbitals How many orbitals are in the “s” sublevel? 1 orbital Atomic Orbitals How many electrons are in the “s” sublevel? 2 electrons each orbital holds 2 electrons Atomic Orbitals How many orbitals are in the “p” sublevel? 3 orbitals Atomic Orbitals How many electrons are in the “p” sublevel? 6 electrons Atomic Orbitals How many orbitals are in the “d” sublevel? 5 orbitals Atomic Orbitals How many electrons are in the “d” sublevel? 10 electrons Atomic Orbitals How many orbitals are in the “f” sublevel? 7 orbital Atomic Orbitals How many electrons are in the “f” sublevel? 14 electrons Atomic Orbitals What is the shape of the “s” orbital? sphere Atomic Orbitals What is the shape of the “p” orbital? dumb bell Atomic Orbitals What is the shape of the “d” orbital? cloverleaf Energy Levels How many electrons can go in energy level 1? 2 electrons (s) Energy Levels How many electrons can go in energy level 2? 8 electrons (s,p) Energy Levels How many electrons can go in energy level 3? 18 electrons (s,p,d) Energy Levels How many electrons can go in energy level 4? 32 electrons (s,p,d,f) Electron Configurations __________ ___________ states that electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first. Aufbau Principle Electron Configurations __________ _________ __________ states that only 2 electrons can occupy an orbital and they must have opposite spins. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle Electron Configurations ___________ __________ states that electrons fill all orbitals of the same energy before putting 2 electrons in the same orbital. Hund’s Rule Electron Configurations What does the “3” in tell you? the energy level 10 3d Electron Configurations What does the “d” in tell you? the sublevel 10 3d Electron Configurations What 10 3d does the “10” in tell you? the number of electrons Electron Configurations An atom is said to have an ________ when it has 8 electrons in its last energy level. octet Electron Configurations Write the electron configuration for phosphorus. 1s22s22p63s23p3 Electron Configurations Write the electron configuration for Iron. 2 2 6 2 6 2 6 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Electron Configurations Write the electron configuration for bromine. 2 2 6 2 6 2 10 5 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p Electron Configurations What are the 2 exceptions when writing electron configurations? Chromium and Copper Electron Configurations Write the electron configuration for chromium. 2 2 6 2 6 1 5 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Electron Configurations Write the electron configuration for copper. 2 2 6 2 6 1 10 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Energy Levels What is the highest energy level for Chlorine? rd 3 (its in period 3) Energy Levels What is the highest energy level for Gold? th 6 (its in period 6) Orbital Notation Draw the orbital notation for Iron. see additional diagram