* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12-4 Marketing: An Introduction Types of Retailers
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
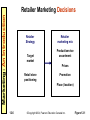
Marketing: An Introduction Retailing and Wholesaling •Chapter Twelve •Lecture Slides –Express Version •Course •Professor •Date Marketing: An Introduction Looking Ahead • After studying this chapter you should be able to: • Explain the roles of retailers and wholesalers in the distribution channel • Describe the major types of retailers and give examples of each • Identify the major types of wholesalers and give examples of each • Explain the marketing decisions facing retailers and wholesalers 12-2 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Marketing: An Introduction Types of Retailers • Amount of service – Self-service retailers – Limited-service retailers – Full-service retailers • Product line – Specialty stores • Narrow product line, deep assortment – Department stores • Wide variety of product lines – Supermarkets • Wide variety of food, laundry, household products – Convenience stores • Limited line of high-turnover goods – Superstores • Large assortment of food and non-food items 12-3 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Marketing: An Introduction Types of Retailers (continued) – Category killer • Big box specialty store – Service retailers • Provide services rather than tangible goods • Relative prices – Discount stores – Off-price retailers • Independents • Factory outlets • Warehouse clubs • Retail organization – – – – – 12-4 Corporate chains Voluntary chain Retailer cooperative Franchise organizations Merchandising conglomerates ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Marketing: An Introduction Franchising Systems • Characteristics of a franchise system – The franchiser owns the trademark and licenses it for a fee to franchisees – The franchisee pays to belong to the system – The franchiser provides a packaged system for marketing and operations • Pro: – Turn-key system for entrepreneur – National support for promotions – Rapid expansion for franchiser using other people’s money and risk – Recognized name equals instant business • Con: – You get what you pay for – Owner has less freedom in decision making – Contracts can be one-sided and difficult to break 12-5 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Marketing: An Introduction Retailer Marketing Decisions Retailer Strategy Target market Retailer marketing mix Product/service assortment Prices Retail store positioning Promotion Place (location) 12-6 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Figure 12-1 Marketing: An Introduction Future of Retailing • Wheel of retailing concept – – – – New retailers begin as low margin, low price Become popular by offering alternative Later evolve by adding service and better goods Become the higher priced, higher margin retailers they first replaced • Growth of non-store retailing – – – – – – – Direct mail Catalogues Telephone shopping TV Shopping shows E-commerce via the Internet Home and office parties Door-to-door personal selling • Importance of technology 12-7 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Marketing: An Introduction Functions of Wholesalers • • • • • • • • • 12-8 Selling and promoting Buying and assortment building Bulk breaking Warehousing Transportation Financing Risk bearing Market information Management services and advice ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Marketing: An Introduction Types of Wholesalers • Merchant wholesalers – – – – – – – – – – Full-service wholesalers Wholesale merchants Industrial distributors Limited-service wholesalers Cash and carry wholesalers Truck wholesalers (truck jobbers) Drop shippers Rack jobbers Producers’ cooperatives Mail-order wholesalers • Agents and brokers – Brokers – Agents – Manufacturers’ agents 12-9 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. continued Marketing: An Introduction Types of Wholesalers (continued) – Selling agents – Purchasing agents – Commission merchants • Manufacturer’s sales branches & offices – Sales branches – Sales offices – Purchasing offices Wholesaler Strategy Wholesaler marketing mix Target market Product/service assortment Prices Promotion Place (location) Service positioning 12-10 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc. Figure 12-2 Marketing: An Introduction Looking Back • Retailer and wholesaler roles in distribution channel • Types of retailers • Types of wholesalers • Marketing decisions required by retailers and wholesalers 12-11 ©Copyright 2004, Pearson Education Canada Inc.