* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Teacher`s guide
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
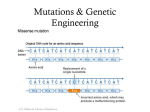
SUBJECT GRADE LEARNING UNIT SCIENCE 1OTH HOW ARE THE WORLD COMPONENTS RELATED? LEARNING OBJECT CURRICULAR AXIS STANDARD COMPETENCIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES Does evolution by natural selection occur currently? Living environment Compare cases of current species that illustrate different actions of natural selection. Establish relationships among mutation, natural selection and heredity. To establish relationships among variability, heredity, natural selection and time. To identify examples of the law of natural selection that can be found in nearby areas, taking into account the important aspects of this law. To recognize the importance of natural selection for the evolution process of the living organisms. To ask and answer questions related to evolution in a conversation. SKILLS/ KNOWLEDGE Skill 1. Explain how controlled reproduction changes organisms. Skill 2. Explain how fortuitous mutations help the process of change in organisms through natural selection. Skill 3. Give examples of evidence of evolutionary change from comparative anatomy. Skill 4. Research biochemical and genetic studies that reveal the molecular similarities among different organisms. Skill 5. Argue how natural selection can lead to pesticides resistance. Skill 6. Consult studies showing natural selection today. Skill 7 To practice the use of nouns, adjectives and adverbs as a tool to review studied topics. LEARNING FLOW Activity 1 • • • • • • • Skill Introduction Evolution Important Genetic variability and mutations Mutations: raw material of evolutionary change Learning activity Activity 2 • • • • • • • Skill Introduction Retaking the evolution process Natural selection Important Examples of natural selection Learning activity Activity 3 • • Skills Introduction • • • Controlled reproduction or artificial selection Did You know that…? Natural selection and pesticides Learning activity Activity 4 • • • • • • • Skill Introduction Compared anatomy: evidence of evolutionary change Important Evidences coming from Homology. Similar characteristics: convergent evolution Learning activity Activity 5 • • • • • • • • Skill Introduction Did you know that…? DNA Milestones Central dogma of molecular Biology Molecular biology techniques Genomic biology Learning activity Summary Homework Bibliography Glossary Vocabulary Box English Review Topic ASSESSMENT GUIDELINE The student will be able to understand the role of natural selection and mutations in evolution, show current examples of natural selection, its similarity to artificial selection and understand how sciences like compared anatomy provided evidence for evolutionary theory. Likewise, the student is expected to know the main current techniques for the study of genetics. Stage Learning Activities Learning flow The teacher will read the introduction to his/her students, then he/she will listen to the answers and ideas of students on the topic, and a brief explanation of the topic will be given. Introduction The Aedes aegypti (mosquito that transmits Zika), as well as many other insects, lays a lot of eggs throughout its life (between 150-200 eggs each time). Have you ever asked yourself? Why despite this fact, they do not have overly large population sizes, or at least do not correspond to the number of eggs laid? 157 years ago, scientist Charles Darwin (1819-1882) postulated the evolution theory, which will allow you to understand many questions like the above. Development The teacher presents the theme Activity 1 Skill 2. Explain how fortuitous mutations help the process of change in organisms through natural selection. . Evolution Dear teacher, you will start the class with the introduction, making a brief review of the structure of DNA, and population genetics to contextualize the student about the importance of genetics in the process of evolution. Introduction Figure 2. Example of natural selection in beetles. Figure 2. The colors of litter beetles are similar to dry leaves; this facilitates camouflage. (Retrieved from: www.gimnasiomodernocastilla.edu.co) Teacher, it is essential to make the students understand that natural conditions play an important role in the evolution of living beings. Important Genetic variability and mutations Very Important… We must take into account that natural conditions are not always the same; that is why a favorable combination of alleles is not always favorable in the environment. In this context, natural selection makes the favorable combination change, and then, evolution occurs. DEVELOPMENT Teacher, the importance of genetic variability and mutations for the evolutionary process will be explained next. Rely on the image to clarify the students’ doubts. Genetic variability and mutations Figure 3. Genetic variability of Heliconius numata specie in the Colombian Amazon. Retrieved from: Rueda, N. (pp. 80) 2016. Teacher, next we will go in detail about the role of mutations of the species. Please, rely on the text and image to expand the topic to students. Mutations: raw material of evolutionary change Figure 4. Mutation generated in an apple. Mutations Figure 4. Example of a mutation. Retrieved from: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/0_0_0/evo_18_sp Learning Activity Teacher, to complete the learning activity, it is necessary to have understood how fortuitous mutations help the process of change in organisms through natural selection. A matching exercise has been proposed to this end. Please support the students by answering their questions. Instruction: There are two columns, A and B. Column A contains 9 words and Column B 9 definitions. Drag the words from Column A to match the definitions of Column B, as appropriate. Be careful, you can drag only one word per term. Column A Evolution Population genotype Learning Activity Mutation Genetic variability Somatic mutation Germinal mutation Natural selection Column B Intergenerational change of allele frequencies in populations. Differential reproduction of genotypes of a biological population. Change in the organization of DNA. Change in the DNA of germinal cells. Set of genes within a population. Change in the DNA of a somatic cell. Range of allelic variants of a genotype. Answer Key: Evolution: intergenerational change of allele frequencies in populations. Population genotype: set of genes within a population. Mutation: change in the organization of DNA. Genetic Variability: range of allelic variants of a genotype. Somatic mutation: change in the DNA of a somatic cell. Germinal mutation: change in the DNA of germinal cells. Natural selection: differential reproduction of genotypes of a biological population.. Compare your answers with a classmate. Practice asking and answering questions, for example: Student A: What is the intergenerational change of allele frequencies in populations? Student B: That intergenerational change corresponds to… Activity 2 The teacher presents the theme Skill Introduction Skill 6: Consult studies showing natural selection today. Teacher, the objective of this activity is that students understand the process of natural selection and find examples today. The following example in butterflies and moths from Colombia seeks to introduce students to the subject. Please, expand in the example. Introduction One of the following images is not a butterfly. Which is the false butterfly? Why does a living being seek to resemble another? Figure 6. Example of mimicry in Colombia. Figure 6. Butterfly species of the genus Heliconius and its mimetic Moth in the Colombian Amazon. Retrieved from: Rueda, N., (pp. 112). 2016 Taking up the evolution Answer key: b process Development Dear teacher, the subject begins to develop, taking up important aspects of the process of evolution. Use the image as support to explain the topic. Resuming the evolution process Figure 7: processes that explain the dynamics of evolutionary change. Natural selection Figure 7: Changes in allele frequencies over time, occurring as a result of different evolutionary processes. The example of natural selection represents a case of directional selection in which allele A is benefited. The mutation case shows the appearance of two new alleles. In the case of migration, individuals carrying the allele A are introduced into the population. In the case of genetic drift, in the new population, resulting in a drastic reduction of the population size, the allelic frequencies are changed to the detriment of the allele A. Retrieved from: http://curtisbiologia.com/files/images/23-04.jpg Teacher, we will talk about the process of natural selection next. Please, rely on the text and image, give an additional explanation. Natural selection 1. There is diversity of characters 2. There is differential reproduction 3. There is heredity 4. Final result Very important… Whenever there is variation, differential reproduction and heredity, the result is evolution b selection. It is just that simple. All examples retrieved from: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/0_0_0/evo_25 Teacher, there are three examples of natural selection in Colombia. Please, help the students to understand the process through examples, and if necessary, give other examples about the process to make it as clear as possible. Examples of natural selection 1. Orchids: they have varied striking shapes to attract their pollinators. Individuals that manage to attract more pollinators will leave more offspring, leading to evolution by natural selection. Variety of orchids of Colombia. Retrieved http://www.sabedoriaglobal.com.br/orquideas-especies-imagens/ from: 2. Birds: they have beaks and wings with different Examples natural selection of shapes and sizes. Variability in the peaks is given by need for different food. So each particular population has evolved selecting the most favorable type of peak, which will allow them to find the food that is more common in their habitat. In this way, they can leave more offspring; in the case of the colors of their wings, natural selection favors the more attractive wings of males. This will allow them to mate with more females and leave more offspring. Variety of beaks and wings in birds. Retrieved from: http://rincondelecturas.com/lecturas/20036-aves/20036-aves.php 3. Moor plants: the different populations of the species of these plants, some individuals had the genetic information for production, for example, white hair on their leaves. This feature allowed them to survive longer, since they did not burn excessively; therefore, these individuals left more offspring and thus, the populations evolved adapting to the habitat. Frailejon plants (Espeletia sp.). Retrieved http://www.imeditores.com/banocc/paramos/fotos.php?id=149 from: Teacher, before starting the learning activity, make a summary of the topics covered so that the students understand how natural selection occurs; in this way, they can consult studies demonstrating selection today. Learning activity To do this learning activity, it is necessary to understand how natural selection works, in order to consult studies showing natural selection today. A matching exercise has been proposed to this end. Instructions: Fill in the blanks with the words below; this exercise will help you review what you have learned. Each word must be used only one time. Words: orchids, inherit, birds, butterflies, differential reproduction, offspring, moor, plants, variation, heredity, variability. Colombia is the first country in biodiversity of _____ (1) and __________ (2), the second in biodiversity of ______ (3) and _____ (4), and one of the few countries with the ___________ (5) ecosystem. Flowers have __________ (6) in their shapes and colors, which are striking to attract their pollinators. Individuals that attract more pollinators will leave more ___________ (7), and therefore, ___________ (8) their genes. Natural selection is defined as the ____________________ (9) of individuals carrying different genotypes of a population. If there is ___________ (10), differential reproduction and _________(11), the result will be evolution by natural selection. It is just that simple. Answer key: Learning activity 1. Birds 2. Orchids 3. Plants 4. Butterflies 5. Moor 6. Variability 7. Offspring 8. Will inherit 9. differential reproduction 10. Variation 11. Heredity Activity 3 Skills Skill 1. Explain how controlled reproduction changes organisms. Skill 5. Argue how natural selection can lead to resistance to pesticides Introduction Dear teacher, the aim of this activity is that students understand the role of artificial selection and pesticides in agriculture, and animal husbandry. Rely on the text and image to complement the explanation. Introduction Figure N.8 Corn varieties of the Caribbean and Santander Regions in Colombia. Figure N.8 These varieties have emerged from the artificial selection of farmers. Retrieved from: http://maicesdelnansa.blogspot.com.co/2013/10/organizacio nes-colombianas-intentan.html Dear teacher, the subject of artificial selection is extended in this section. Rely on the example given to clarify the doubts of students. If necessary, give other examples. Controlled reproduction or artificial selection Figure 9: Potato Varieties in Colombia. Figure 9: There are 5,000 varieties of potatoes in the world, and there are 100 varieties in Colombia. That is evolution through artificial selection. Retrieved from: http://contextoganadero.com/agricultura/colombia-tiene-5-nuevasvariedades-de-papa Did you know that…? Native potatoes began to become extinct. "Producers began working with commercial materials and made monocultures, which harmed the conservation of potatoes, base of food security for communities for a long time." Dear teacher, expand the information and give an example to show the relationship between natural selection and pesticides. Natural selection and pesticides Dear teacher, the goal of the learning activity is that the students understand how we can make changes to organisms through controlled reproduction. Please, support the students solving their questions. Learning activity To do this learning activity, it is necessary to understand how controlled reproduction modifies the organisms. To this end, an activity called “find the sentence” has been proposed. Instruction: Organize each sentence in correct and logical order. The message will help you review the studied topics. 1. Artificial selection, of organisms, the controlled reproduction, is basically. 2. are selection pressures, regarding what characteristics, The decisions made, in the population, by a breeder, he wants to select. . 3. must be allowed, in larger size, only the reproduction, for several generations, of large individuals, To obtain cattle Answer key: 1. Artificial selection is basically the controlled reproduction of organisms. 2. The decisions made by a breeder regarding what characteristics he wants to select in the population are selection pressures. 3. To obtain cattle in larger size, only the reproduction of large individuals must be allowed for serveral generations. Activity 4 Skill 3: give examples of evidence of evolutionary change from comparative anatomy. Dear teacher, in this activity the student is expected to understand how scientists found the evidence supporting the evolutionary process in human beings from sciences such as comparative anatomy. Rely on the image, the question posed and the text to introduce the subject. Introduction: one of the embryos is human, which one? Figure 6: The photos show that homologies among vertebrates are clearly evident at the beginning of development. Retrieved from : https://www.google.com.co/search?q=anatomia+c omparada&biw=1138&bih=505&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&sqi=2&ved=0ah UKEwjdjbD4haHMAhXFJh4KHYXvCoQQ_AUIBigB#tbm=isch&q=embrion+pez&im gdii=DuNw9PwliMcL9M%3A%3BDuNw9PwliMcL9M%3A%3BNJqaXtrlvfmmM%3A&imgrc=DuNw9PwliMcL9M%3A. Answer: F Comparative anatomy Comparative anatomy: evidence of evolutionary change Very important… if two structures have the same function through similar means, and also the same origin, they are analogous and homologous structures simultaneously. DEVELOPMENT Teacher, the purpose of this section is that the students understand what homologous structures are, and why they are evidence of the evolutionary process that some organisms have experienced through the years, as well as, the fact that they had the same common ancestor. There are some examples below. Rely on the image to resolve the doubts of the students. Evidence coming from Homology Figure 11. Vertebrate homologies. Homologies Figure 11: The various bones of the image structures are displayed in color to indicate the fundamental similarities in their structure and organization. Retrieved from: http://curtisbiologia.com/files/images/23-04.jpg Traducción: Tretrápodo (antecesor): tetrapod (antecessor) Cocodrilo: Crocodile Cuervo: Crow Ballena: Whale Murcielago: Bat Caballo: Horse Humano: Human Dear teacher, the aim of this activity is to give the students examples of similar structures and how they demonstrate convergent evolution. Support the avatar’s explanation and solve any student doubts about the examples. Similar features: convergent evolution Teacher, start explaining the activities and objectives to be obtained with the development of the activity. Students are expected to associate the main concepts to their meanings. Learning activity convergent evolution To do this learning activity, it is necessary to understand how comparative anatomy found evidence of evolutionary change that allowed scientists to have a more robust theory of evolution. Instruction: Matching activity. Drag the words from column A to the definitions and/or examples from column B, as appropriate. There are 5 words closely related to the definitions and/or example of B column. Be careful: only one word can be dragged per definition. Column A Comparative anatomy, analogy, homology, convergent evolution, similar selective pressures. Column B Learning activity 1. The acquisition of equivalent characteristics through independent evolutionary histories is ___________________. 2. The same type and arrangement of the bones in vertebrates is an example of ______________structures. 3. The comparative study of body structures of different species of animals belonging to the same group is called____________________________. 4. The acquisition of equivalent characteristics occurs through independent evolutionary histories, because these organisms are subject to ___________________________________. 5. The wings of butterflies, birds and bats are examples of _______________.structures Answer key: Activity5 Skill 1. Convergent evolution, 2. Homologous, 3. Compared anatomy 4. Similar selective pressures, 5. Analogous Skill 4. Research biochemical and genetic studies that reveal the molecular similarities among different organisms. Skill 7 To practice the use of nouns, adjectives and adverbs as a tool to review studied topics. Introduction Introduction Dear teacher, address the issue from "did you know that…?” Please, help the students to understand the arguments presented in the avatar, check their answers and if necessary, complement them so that the students understand what the activity is about. Did you know that…? The genome comprises the entire genetic material of an organism, and consists of deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. The genome is the instructions manual for life where we can find the genes that form proteins, which in turn perform the functions of an organism. Its size is variable and generally depends on the total number of base pairs. For example, the human genome (Homo sapiens) and the mouse’s (Mus musculus) contain 3 billion base pairs, while the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) contains 180 million base pairs, and the Escherichia coli bacterium contains 4.7 million base pairs. Did you know that scientists managed to sequence (to know the order) the entire human genome? What year did you think it happened? Answer key: 2004 History of DNA DEVELOPMENT Dear teacher, the objective of this activity is that students understand how genetics science has been developing over time, and know the most relevant scientists who contributed to it. Rely on computer graphics and go in detail where necessary. DNA Milestones Teacher, the objective of this activity is to extend the important discovery of the double structure of DNA. Rely on the text and the hyperlink that will allow the student to see this structure interactively. Central Dogma of molecular Biology Watch a simulation of DNA structure in http://biomodel.uah.es/model4/dna/dnapairs.htm this link : Teacher, the aim of this activity is that students know the main techniques used to study the DNA of organisms, considering that the most common is the PCR. A hyperlink will show the students a video that allows them to better understand this technique. Please, help the student to understand the topic. Molecular Biology techniques Molecular 1. Restriction enzymes (Cut biology 2. DNA Cloning (Copy and paste 3. PCR: Cloning without bacteria 4. Sanger Model: Genome sequencing The following video has been proposed to deepen in the subject of molecular biology: PCR: Polymerase chain Reaction (IQOG-CSIC) (2014). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TalHTjA5gKU Teacher, the objective is that the students know the most modern techniques to solve questions about genetics, DNA, evolution, among others. Rely on the text to help the students understand these techniques. Genomic Technology 1. DNA automated sequencing 2. Subcloning "Shotgun" Figure 12. Genomics discovery of a new species. Techniques Figure 12. The figure shows the parent species of the new species and H. heurippa. Retrieved from: www.butterfliesofamerica.com Teacher, the aim of the activity is that by answering true or false, the students review the contents studied. Help the students during activity resolving their questions. Learning activity To do this learning activity, it is necessary to understand how biochemical and genetic studies may reveal similarities among different organisms. In addition, it is also important to know well the techniques used to solve research questions in genetics and molecular Biology. Instruction: Choose T (True) or F (False), as appropriate. a) The genome comprises the entire genetic material of an organism and consists of deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA ____. b) The central dogma of molecular biology is the discovery by Watson and Crick of the double helix structure of DNA ______. c) More DNA fragments can be analyzed quickly and easily by means of molecular biology techniques than with genomics techniques____. d) New species may be discovered through the molecular biology techniques and genomics _____. Genomic Technology e) The automation of processes has not positively contributed to progress in the study of DNA _____. Answers: a) T. This terms comprises what is known as DNA. b) T. This discovery opened molecular biology. c) F. It is on the contrary. Genomics techniques are more modern and have streamlined the process of DNA analysis. d) T. Yes. One it is one of the most used applications. e) F. Automation has been very positive for this science, as it provides fast and prevents unintentional human error in these processes. LANGUAGE PRACTICE Complete the following paragraph using the nouns, adjectives and adverbs from the box: frequencies populations Learning activity evolution individual favorable partle The theory of evolution has been explained ____________ by the Darwinian theories, and Mendelian genetics. Both theories were joined and people began to think, not only about the ___________ genotypes, but also in the ______________, which must be understood as the set of genes of all the population. When genes are analyzed over several generations, it can be observed that the ______________ of some alleles change from one generation to the next one, at the expense of others whose frequency decreases. This happens because if an individual has a ____________ combination of alleles in the genotype, and this combination gives an advantage over other individuals, then the contribution to the gene pool of the next generation will be higher. Therefore, ___________ is the intergenerational change of allele frequencies in populations. Answer key: The theory of evolution has been explained partly by the Darwinian theories, and Mendelian genetics. Both theories were joined and people began to think, not only about the individual genotypes, but also in the populations, which must be understood as the set of genes of all the population. When genes are analyzed over several generations, it can be observed that the frequencies of Summary homework some alleles change from one generation to the next one, at the expense of others whose frequency decreases. This happens because if an individual has a favorable combination of alleles in the genotype, and this combination gives an advantage over other individuals, then the contribution to the gene pool of the next generation will be higher. Therefore, evolution is the intergenerational change of allele frequencies in populations Dear teacher, use this information to present the summary of the topics covered. Homework The objective of this activity is, first of all, that the student answers the OA question: Does evolution by natural selection occur currently? It focuses mainly on activity N. 2, which deals with the skills: "Consult studies showing natural selection today" and "argue how natural selection can lead to pesticide resistance"; for this end, it is important that the student has understood activity N. 2, developed the learning activity, shared his/her concerns with the teacher, and likewise, that he/she has participated actively with the examples of the activity, understood and proposed others, if possible. When students finish, they must ask you any questions that arose during the development and hand in their work. The next test evaluates your understanding of the studied topics. It contains multiple-choice, true-or-false, and matching questions. To succeed in the evaluation, you must review, understand and complete all the information provided in the four learning activities. 1. Moorland plants have white hairs. How can you explain this fact according to Darwinian theories? a) The plants developed white hairs to reflect the sun rays and not to die burned by the cold. b) In the moor, all the plants are better adapted and leave more offspring than elsewhere. c) The mutations cause the moor plants to be white and not another color. d) None of the above statements is correct. Answer key: a), within the population of moor plant, there were individuals with genes encoding for leaves covered by white hairs, allowing them to reflect the sun rays. This enables them to survive longer and leave more offspring; with the passage of time, most of the individuals in the population have white hairs. This is an example of evolution by natural selection, according to Charles Darwin. 2. Choose true or false for each sentence: a) The wing of a bat and a human arm are analogous organs. b) The genotype of an individual is what can be observed with the naked eye. c) The natural conditions are not always the same; for that reason, a favorable combination of alleles may not always be favorable. d) All mutations are relevant to evolution. Answers key a) T: They are analogous organs because they have a similar function in different mediums. b) F: The characteristics of an individual that can be seen with the naked eye are the Phenotype. c) T: The natural conditions of a habitat are constantly changing; therefore, the same individuals with the same allele combinations are not always favorable. d) F: There are mutations that are not inherited as those in somatic cells; therefore, they do not contribute to evolution. 3. Match the terms (A) to the definitions (B): Column A Analogy Evolution Homology Phenotype Column B It is the appearance of an individual. Similar morphological structures without common origin. Similar morphological structures with common ancestral origin. Intergenerational change of species. Answer key: 1. Analogy: similar morphological structures without common origin. 2. Evolution: Intergenerational change of species. 3. Homology: similar morphological structures with common ancestral origin. 4. Phenotype: It is the appearance of an individual. Choose the correct option: 4. In some cases, human beings have chosen to pair certain farm animals within a species. For example, by allowing the reproduction of only the larger cattle over many generations, there have been very large cattle breeds. This process is known as: a) Natural Selection. b) Mutation c) Artificial selection d) None of the above Answer key: C). The humans guide the selection, not nature. 5. The dynamics of evolutionary change that occurs at the level of populations can be explained by: a) Natural selection b) Mutation c) Genetic drift d) Gene flow resulting from migration e) The mating pattern f) All of the above g) A and b Answer key: evolutionary change can occur for any of the processes mentioned in the answers or a combination of some of them. Glossary Dear teacher, the glossary will help your students reinforce important concepts addressed in the OA. Genetic population: the set of all alleles of all genes of individuals that constitute it. Phenotype: an individual’s appearance and biological function. Genotype: an individual’s genetic constitution. Evolution: Intergenerational change in a population. Mutation: change occurring in genotype. Natural selection: the process by which the environment exerts pressure on the gene pool of populations and thus, the evolutionary change is determined. Analogy: they are structures that have a similar function based on the same medium, but whose origin is generally different. Homologies: they are structures that are morphologically similar because they derive from a common ancestral structure. Genomics: the science that focuses on the study of genomes and the genes they contain, their functions and the interactions among themselves and with the environmental factors. Vocabulary box Offspring: n. New individual organisms that result from the process of sexual or asexual reproduction Allele: n. Alternative form of a gene or base pair sequence that occurs on a chromosome Somatic mutation: n. A mutation that occurs in a somatic cell. Germinal mutation: n. Genetic alterations occurring in cells destined to develop into germ cells Gene pool: n. All the genes and their different alleles that are present in a population of a particular species of organism Habitat: n. The place in which an organism lives, which is characterized by its physical features or by the dominant plant types Pesticide: n. A chemical (such as an insecticide, fungicide, rodenticide, herbicide, or germicide) that is used to kill or control pests, such as insects, weeds, or micro-‐organisms. Selection pressures: n. The extent to which organisms possessing a particular characteristic are either eliminated or favored by environmental demands. It indicates the degree of intensity of natural selection. Retrieved from: http://www.oxfordreference.com English review topic Nouns, adjectives and adverbs Bibliography Teacher, to expand the information, please rely in the following bibliography, likewise your students will be able to explore it. Curtis, H., Barnes, N., Schnek, A., Massarini, A. (2008). Biología. 7° Ed. – Buenos aires: Médica Panamericana. Equipo de Comprendiendo la Evolución. (2016). Evolución 101. Retrieved from: http://evolution.berkeley.edu Botánica online – SL- (2016). Selección natural en las aves parásitas. Retrieved from: http://www.botanical-online.com/animales/seleccionnatural-aves-parasitas.htm). SIB Colombia. (2016). Biodiversidad en http://www.sibcolombia.net/web/sib/cifras. Colombia. Retrieved from: IMeditores, Banco de Occidente. (2016) Estrategias adaptativas de la Vegetación. Retrieved from: http://www.imeditores.com/banocc/paramos/cap5.htm Evolutionibus. (2016) La resistencia a los from:http://evolutionibus.eresmas.net/ddt.html pesticidas. Retrieved Bedoya, F., Battilana, C. G. (2006). Genómica y proteómica: Un paso más. Acta Med Per 23(3). López-López, Marisol; López Gutiérrez, Antonio Ulises; Sainz Espuñes, Teresita del Rosario; RosalesTorres, Ana Ma. (2005). ¿Qué sabe usted acerca de...Genómica?. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Farmacéuticas, vol. 36, núm. 1, enero-marzo, pp. 42-44. Universidad Veracruzana. (2016) Biología molecular. Retrieved from:https://www.uv.mx/veracruz/cess/servicios/biologia-molecular/ Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto.(2016).Aedes aegypti. Retrieved from::https://www.unrc.edu.ar/unrc/trabajo/docs/dengue-ilustraciones.pdf Gimnasio moderno castilla. (2016). La evolución – Que es la selección natural-. Retrieved from:: www.gimnasiomodernocastilla.edu.co. Rueda, N. (2016). Parámetros poblacionales y aportes para la conservación de las especies del género Heliconius KLUK, 1780 en hábitats de diferente grado de conservación de la Amazonia Colombiana. (Tesis de Maestría en Biología). Universidad Nacional de Colombia. Understandingevolution. (2016). Las mutaciones. Retrieved from::http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/0_0_0/evo_18_sp Understandingevolution. (2016). La selección artificial. Retrieved from::http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/_0_0/evo_30_sp Curtis, H., Barnes, N., Schnek, A., Massarini, A. (2008). Biología. 7° Ed. – Buenos aires: Médica Panamericana. Retrieved from:: http://curtisbiologia.com/files/images/23-04.jpg Antes del fin. (2016). La teoría de la recapitulación. Retrieved from:: http://antesdelfin.com/recapitulacion.html Curtis, H., Barnes, N., Schnek, A., Massarini, A. (2008). Biología. 7° Ed. – Buenos aires: Médica Panamericana. Retrieved from:: http://curtisbiologia.com/files/images/23-04.jpg Universidad nacional a distancia. (2016). Tecnología del ADN recombinante. Retrieved from:: http://bitecnologiaunad.blogspot.com.co/2012/05/marcoteorico.html Butterflies of América. (2016). Mariposas del género Heliconius. Retrieved from::www.butterfliesofamerica.com Contexto ganadero. (2016). Variedad de papa Colombiana. Retrieved from:: http://contextoganadero.com/agricultura/colombia-tiene-5-nuevasvariedades-de-papa Maíces del Nansa. (2016). Variedad de maíces de Colombia. Retrieved from:: http://maicesdelnansa.blogspot.com.co/2013/10/organizacionescolombianas-intentan.html PCR: Reacción en Cadena de la Polimerasa https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TalHTjA5gKU (IQOG-CSIC) (2014).