* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Connect Innovate UK
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
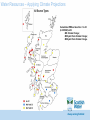
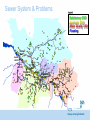
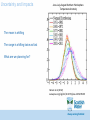
Catchment Management: Impacts of Climate Change – ‘Setting the scene’ Dr Mark Williams Scottish Water/ UK Water Industry Research Ltd Always serving Scotland Our Purpose • Protecting public health • Protecting and enhancing our environment • Facilitating economic growth, affordability Resilience to environmental change is key The role of UK Water Industry Research (UKWIR) ● ‘One voice’ industry research ● New and emerging issues ● UK WIR Areas that do not conflict with company interests UKWIR Key Collaborative Outputs Water Resource Planning Tools ● ● ● UK WIR Shared with Regulators / Government Underpins sectoral approach for agreement with regulators for business planning Consistent reporting on Climate Change Risk Assessments CC Risk Assessment And Adaptation Planning Impacts and Responses for Water and Wastewater treatment Impact on Customer Demand Water Resources Huge number of water resource zones (300+) Reasonable level of resilience, but climate vulnerability assessment indicates some issues Central (50% probability) estimate of the change in mean precipitation (%) by 2050 (high emissions scenario) UKWIR Tools enable UKCP09 Complex Hydrologically Modelled Sources e.g. large reservioirs, rivers, boreholes etc Smaller sources, simplistic models e.g. small rivers/streams etc Convert raw data to evotranspiration and flows Joint probabilities: Temperature and Precipitation Joint probabilities: Temperature and Precipitation Impact on chosen level of service (1 in 40) in 2030s and beyond Develop and test wet/dry scenarios – cumulative flow issues Impact on Demand Impact on chosen level of service (1 in 40) in 2030s and beyond Impact on Demand Detailed hydrological assessment – incorporate into models General planning assumptions Water Resources – Applying Climate Projections Cumulative WRZs at less than 1 in 40 (in 2039/40) with: •NO Climate Change; •MID yield from Climate Change; •MIN yield from Climate Change. Scottish Water Adaptation Studies Monitoring • Range and type of monitoring better understood • Significant gap – we do not have the data to understand how things are changing Surface Water Management Planning • Identified extent to which this will support CC adaptation • To be taken forward as part of SWMP work CC Risk Assessment • Focus on understanding CC risks, failure nodes, detailed asset case study • Further underpinned need for real data • Need to extend – CC projection changes, Scotland’s Risk Assessment 2015-21 Adaptation Plan Water Resource Planning – integrating CC Customer and asset flood risk management Surface Water Management Planning Monitoring – projects: raw water quality raw water quantity drainage and sewer flows/loads – trends Risk assessment updates and feed into Scotland’s Risk Assessment Catchment Management - Water Quality Contaminants and Sources Contaminants • Pesticides • Colour • Metals • Nutrients • Sediment • Hydrocarbons Sources Land based activities Pathways Catchment specific • Agriculture Receptors • WTW • Customers • Public amenities • Engineering works • Forestry activities Primary Benefits – Improved drinking water quality/treatment and value for money Secondary Benefits • Environmental (quality, energy, carbon) • Land users e.g. save land chemical inputs •Catchment resilience Catchment Management Team Area (WTW) Issue River Ugie (Forehill) Pesticides River Deveron (Turriff) Pesticides Loch of Lintrathen (Clatto) Nutrients Loch Ascog (Loch Ascog) Nutrients Dumfries Basin (Cargen & Terregles borehole) Nitrates Lochgoin/ Craigendunton Reservoirs (Amlaird) Colour Monitoring in priority catchments River Ugie catchment Issues encountered Water Environment Management Plan (WEMP) • Improved drinking water quality/treatment • Net cost/carbon benefit • Environmental benefit (improved biodiversity) • Benefit land users e.g. save soils, save chemical inputs • Partnership working • Climate change – resilience, naturalising watercourses The ‘ideal’ – resilient, natural watercourses The Urban Challenge? Original objective: integrate climate models into drainage models BUT: Drainage planning is based on local statistical rainfall models Climate models based on statistical probabilities Applying climate projections to local models = too much uncertainty Need REAL DATA! Morning 30th July 2002 River Clyde at Glasgow Green On 30 July 2002 Glasgow’s average monthly rainfall fell in just 10 hours. This led to significant flooding across the city as the sewerage and drainage systems struggled to cope with the extreme weather conditions. Overland flow Surcharging Sewers Ponding in low spots MGSDP Partnership Partnership through Collaboration Sewer System & Problems Legend Satisfactory CSO Aesthetic CSO Water Quality CSO Flooding Dalmuir WwT Erskine WwTW Partick WwPS Paisley WwTW Shieldhall WwTW Kinning Park WwPS Dalmarnock WwTW Daldowie WwTW Surface Water Management Green Corridors GCC Flood Prevention Scheme - Ruchill 2030 A FIT FOR PURPOSE SERVICE A FIT FOR PURPOSE ASSET BASE WITH WORK ROUND CONTINGENCIES IN PLACE INVESTMENT DECISIONS (Ready for PR29etc) DEVELOP DESIGN SPECIFICATION FOR ASSETS BASED ON CLIMATE CHANGE QUANTIFY UNCERTAINTY TOOLS AND MODELS AVAILABLE INVESTMENT DECISIONS (Ready for PR24 etc) RESEARCH INTO TOOLS AND MODELS FEEDBACK FROM GOVERNMENT 2020 INVESTMENT DECISIONS (Ready for PR19/SR20/PC) DEVELOP DESIGN SPECIFICATION FOR ASSETS BASED ON CLIMATE CHANGE QUANTIFY UNCERTAINTY TOOLS AND MODELS AVAILABLE RESEARCH INTO TOOLS AND MODELS FEEDBACK FROM GOVERNMENT 2015 INVESTMENT DECISIONS (Ready for PR14/SR15/PC) DEVELOP DESIGN SPECIFICATION FOR ASSETS BASED ON CLIMATE CHANGE QUANTIFY UNCERTAINTY TOOLS AND MODELS AVAILABLE 2010 UK WIR DEVELOP DETAILED UNDERSTANDING OF ASSET BASE CAPABALITY RESEARCH INTO TOOLS AND MODELS DIRECTION FROM GOVERNMENT ASSETS APPROPRIATELY ADAPTED TO SECURE SERVICES RESILIENT TO CLIMATE CHANGE Uncertainty and Impacts June-July-August Northern Hemisphere Temperature Anomaly The mean is shifting The range is shifting twice as fast What are we planning for? Hansen et al (2012) www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1205276109