* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
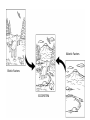
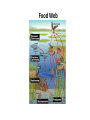
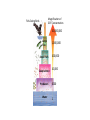
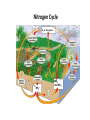
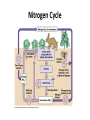
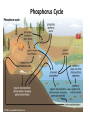
Ecology Figure 3-2 Ecological Levels of Organization Levels of Organization Section 3-1 Go to Section: Species Diversity Section 6-3 Percent of Living Organisms Insects 54.4% Protists 4.2% Other Animals 19.7% Plants 18% Fungi 3.4% Go to Section: Bacteria 0.3% Interest Grabber Section 4-2 Fitting In • Organisms not only live together in ecological communities, but they also constantly interact with one another. These interactions, which include predation and competition, help shape the ecosystem in which they live. • 1. Based on your own experiences, define predation. Give one example of predation. • 2. Based on your own experiences, define competition. Give one example of competition. Go to Section: Abiotic and Biotic Factors Section 4-2 Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors ECOSYSTEM Go to Section: Habitat vs. Niche • Habitat- place where an organism lives • Niche- the use of its habitat and its function/ role in the community Niche • Fundamental niche- the entire range where an organism could survive. • Realized niche- actual area in a community that an organism occupies due to competition. Figure 4-5 Three Species of Warblers and Their Niches Section 4-2 Cape May Warbler Feeds at the tips of branches near the top of the tree Bay-Breasted Warbler Feeds in the middle part of the tree Spruce tree Go to Section: Yellow-Rumped Warbler Feeds in the lower part of the tree and at the bases of the middle branches Section 3-2 Go to Section: Food Web Ecological Pyramids Section 3-2 Energy Pyramid Shows the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level. Organisms use about 10 percent of this energy for life processes. The rest is lost as heat. Biomass Pyramid Represents the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level. Typically, the greatest biomass is at the base of the pyramid. Go to Go to Section: Section: Pyramid of Numbers Shows the relative number of individual organisms at each trophic level. Biomagnification Movement of toxin through a food chain. Increases 10x/level Figure 6-16 Biological Magnification of DDT Section 6-3 Magnification of DDT Concentration Fish-Eating Birds 10,000,000 Large Fish Small Fish 100,000 Zooplankton 10,000 Producers Water Go to Section: 1,000,000 1000 1 Water Cycle Figure 3-13 The Carbon Cycle Section 3-3 Carbon Cycle CO2 in Atmosphere CO2 in Ocean Go to Section: Section 3-3 Nitrogen Cycle N2 in Atmosphere NH4+ Go to Section: NO3and NO2- Nitrogen Cycle Phosphorus Cycle