* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Farmer-managed natural regeneration wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
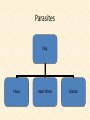
SYMBIOSIS How are our relationships comparable to ecology? Interest Grabber Section 4-2 Fitting In • Organisms not only live together in ecological communities, but they also constantly interact with one another. These interactions, which include predation and competition, help shape the ecosystem in which they live. • 1. Based on your own experiences, define predation. Give one example of predation. • 2. Based on your own experiences, define competition. Give one example of competition. Go to Section: What is symbiosis? • Symbiosis: is a close ecological relationship between the individuals of two (or more) different species. • Mutualism: cooperative relationship in which both species derive some benefit. • Example: Pollination • Parasitism: one individual known as the parasite, feeds on another individual, known as the host. • Endoparasite- Internal • Ectoparasite- External • Commensalism: interaction in which one species benefits and the other is not affected. How do we understand Symbiosis? • Every ecosystem has many different symbiotic relationships. Each fills a niche. All symbiotic relationships are specific to the organisms. You can’t replace one with another. Parasites Dog Fleas Heart Worm Giardia Commensalism 1. An orchid lives on a tropical tree. It lives on the tree to reach the sunlight. Mutualism 1. There is a bird, the Egyptian plover, which cleans crocodile teeth by eating the left over food particles in the crocodile’s mouth. Abiotic and Biotic Factors Section 4-2 Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors ECOSYSTEM Go to Section: Habitat vs. Niche • Habitat- place where an organism lives • Niche- the use of its habitat and its function/ role in the community Niche • Fundamental niche- the entire range where an organism could survive. • Realized niche- actual area in a community that an organism occupies due to competition. Figure 4-5 Three Species of Warblers and Their Niches Section 4-2 Cape May Warbler Feeds at the tips of branches near the top of the tree Bay-Breasted Warbler Feeds in the middle part of the tree Spruce tree Go to Section: Yellow-Rumped Warbler Feeds in the lower part of the tree and at the bases of the middle branches Biomagnification Movement of toxin through a food chain. Increases 10x/level Figure 6-16 Biological Magnification of DDT Section 6-3 Magnification of DDT Concentration Fish-Eating Birds 10,000,000 Large Fish Small Fish 100,000 Zooplankton 10,000 Producers Water Go to Section: 1,000,000 1000 1