* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport in Human
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
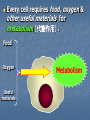
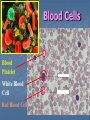
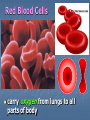
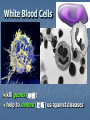
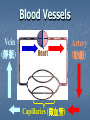
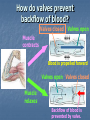
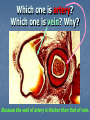
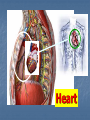
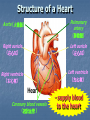
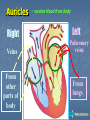
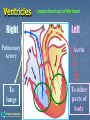
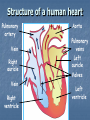
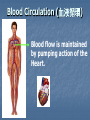
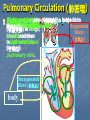
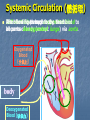
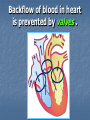
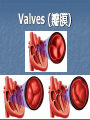
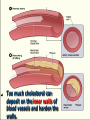
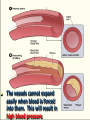
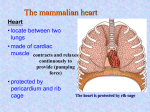
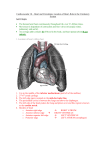
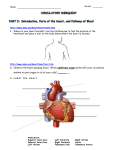
Transport in Human (人類的運輸系統) Every cell requires food, oxygen & other useful materials for metabolism (代謝作用) . Food Oxygen Useful materials Metabolism Metabolism produces toxic waste products which must be removed. Metabolism Toxic waste products e.g. carbon dioxide Many cells are far away from the small intestine and the lung. A transport system is developed to increase the O2efficiency of exchange CO2 and transport of materials. Food Transport System Blood 血液 Blood vessels 血管 Heart 心臟 Blood Cells Blood Platelet White Blood Cell Red Blood Cell Blood Plasma (血漿) (55%) 90% water Dissolved substances: Dissolved food substances Plasma Proteins Wastes Blood cells (血細胞) (45%) Red blood cells White blood cells Blood platelets Red Blood Cells carry oxygen from lungs to all parts of body White Blood Cells kill germs (病菌) help to defend (防衛) us against diseases Blood Platelets involved in blood clotting (凝血作用) are Blood cells are produced by bone marrow (骨髓). Blood Vessels Vein (靜脈) Heart Capillaries (微血管) Artery (動脈) Arteries carry blood from heart to other parts of the body thick wall with muscles branch into capillaries Capillaries the smallest blood vessels reach every part of the body Capillaries have very thin walls => substances can diffuse across their walls are the places for exchange of materials between the blood and the cells CO2, wastes glucose O2 Tissue cell Veins Capillaries join up to form veins. carry blood back to heart thinner walls with less muscles have valves (瓣膜) to prevent backflow of blood (血液倒流) How do valves prevent backflow of blood? Valves closed Valves open Muscle contracts Blood is propelled forward Valves open Valves closed Muscle relaxes Backflow of blood is prevented by valve. Which one is artery? Which one is vein? Why? Because the wall of artery is thicker than that of vein. Heart Structure of a Heart Aorta (大動脈) Pulmonary artery (肺動脈) Right auricle Left auricle Right ventricle Left ventricle (右心耳) (右心室) Coronary blood vessels (冠狀血管 ) (左心耳) (左心室) - supply blood to the heart Auricles Right Veins From other parts of body - receive blood from body Left Pulmonary veins From lungs Heart structure Ventricles Right - pump blood out of the heart Left Pulmonary Artery Aorta To lungs To other parts of body Heart structure Structure of a human heart Pulmonary artery Vein Right auricle Vein Right ventricle Aorta Pulmonary veins Left auricle Valves Left ventricle Blood Circulation (血液循環) Blood flow is maintained by pumping action of the Heart. Pulmonary Circulation (肺循環) Deoxygenated blood returns from Right auricle ventricle contracts pumps blood and pump to blood to O2 (缺氧血) CO 2lungs Gaseous Oxygenated exchange blood Oxygenated body the right through to the pulmonary ventricle right auricle . artery . . (氣體交換) in lungs; flow back to left Blood blood becomes auricle and then (含氧血) oxygenated to left ventricle blood (含氧血) through pulmonary vein. Deoxygenated Blood (缺氧血) body Systemic Circulation (體循環) The blood Left After ventricle flowing flows through pumps backoxygenated to body, the heart. the blood blood to all parts of becomes deoxygenated body (except. lungs) via aorta. Oxygenated Blood (含氧血) body Deoxygenated Blood (缺氧血) Double Circulation (雙循環) Blood flows through the heart twice in one complete circulation Consists of 2 circuits: 1. 2. Connection between heart with lungs . Connection between heart with the rest of the body . Is it possible that blood flows backwards in heart? Why? Backflow of blood in heart is prevented by valves . Valves (瓣膜) Useful Websites http://www.ehc.com/vbody.asp http://www.mercksharpdohme.com/ disease/heart/coronary_health/anato my/home.html Eating for healthy transport system Takes in too much fat in diet will make us put on weight easily Fatty foods also contain a lot of cholesterol Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in the blood. It is used to make cell membranes and some hormones. Eating for healthy transport system Do you remember the chart used in teaching Diet and Health? we can also obtain nutritive values of common food from the website of Centre for Food Safety (食物安全中心): http://www.fehd.gov.hk/niis/prese arch3.html Too much cholesterol can deposit on the inner walls of blood vessels and harden the walls. The vessels cannot expand easily when blood is forced into them. This will result in high blood pressure. Eating for healthy transport system Cholesterol deposits may block the coronary arteries that supply oxygen & nutrients to the heart muscle and coronary heart disease results. The heart may stop beating due to the lack of oxygen and this may cause death. Eating for healthy transport system If there is a blockage or rupture in the brain arteries, stroke may result. This may result in paralysis. To avoid the trap of cholesterol in the body, it is recommended that we limit our average daily cholesterol intake to less than 300 mg.