* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.-the-heart-circulatory-system
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
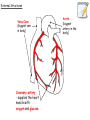
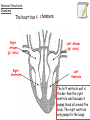
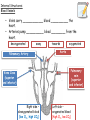
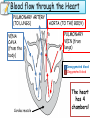
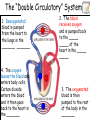
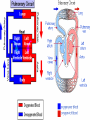
National 5 Biology Key Area 6: The Need for Transport (b) Animal Transport Systems National 4 Biology Key Area 4 Growth and Development of different organisms By the end of this lesson you will be able to .... • Describe the function of the circulatory system in animals • Describe (and be able to identify in a diagram) the features of the heart and associated vessels. – To include right and left atria, left and right ventricles, valves, aorta, vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein and coronary artery. • Describe the pathway of oxygenated blood through the heart, lungs and body. • Describe the pathway of deoxygenated blood through the heart, lungs and body. The Circulatory System • The circulatory system consists of the heart (a muscular pump) and the blood vessels (a system of tubes), which carry essential materials (in the blood) to all parts of the body. External Structures Vena Cava (biggest vein in body) Coronary artery - supplies the heart muscle with oxygen and glucose. Aorta (biggest artery in the body) Internal Structures: Chambers The heart has 4 chambers. Right Atrium (pl. atria) Right Ventricle Left Atrium (pl. atria) Left Ventricle The left ventricle wall is thicker than the right ventricle wall because it pumps blood all around the body. The right ventricle only pumps to the lungs. Internal Structures: Valves • The heart has ___ valves. • Valves help to ________ THE _________ OF BLOOD. • They make sure the blood flows in ____ __________. 4 one direction BACKFLOW PREVENT Valves (between ventricles and vessels) Valves (between atria and ventricles) Internal Structures: Blood Vessels • Veins carry _____________ blood ___________ the heart. • Arteries pump ___________ blood _________ from the heart. deoxygenated away Pulmonary Artery towards oxygenated Aorta Pulmonary vein (superior and inferior) Vena Cava (superior and inferior) Right side – deoxygenated blood (low O2, high CO2) Left side – oxygenated blood (high O2, low CO2) Blood flow through the Heart • http://www.kscience.co.uk/animations/h eart.swf Blood flow through the Heart PULMONARY ARTERY (TO LUNGS) VENA CAVA (from the body) AORTA (TO THE BODY) PULMONARY VEIN (from lungs) Deoxygenated blood Oxygenated blood Cardiac muscle The heart has 4 chambers! The “Double Circulatory” System 1. Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs in the _______ _______ 4. The oxygen leaves the blood and enters body cells. Carbon dioxide enters the blood and it then goes back to the heart in the _______ 2. The blood receives oxygen and is pumped back to the _____ _____ of the heart in the _____ _____ 3. The oxygenated blood is then pumped to the rest of the body in the _______