* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Therapy - (www.forensicconsultation.org).
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Index of psychology articles wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Dodo bird verdict wikipedia , lookup
Process-oriented psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Relationship counseling wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Lifetrack Therapy wikipedia , lookup
Vladimir J. Konečni wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Humanistic psychology wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Equine-assisted therapy wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
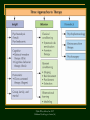
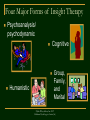
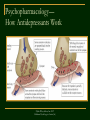
Psychology in Action (8e) by Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 15: Therapy Karen Huffman, Palomar College ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Lecture Overview Insight Therapies Behavior Therapies Biomedical Therapies Therapy and Critical Thinking ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Introductory Definitions Psychotherapy: techniques employed to improve psychological functioning and promote adjustment to life Three Major Approaches to Therapy: Insight (personal understanding) Behavior (maladaptive behaviors) Biomedical (mental illness and medical treatments, such as drugs) ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Four Major Forms of Insight Therapy Psychoanalysis/ psychodynamic Cognitive Humanistic Group, Family, and Marital ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Psychoanalysis/Psychodynamic Psychoanalysis: Freudian therapy designed to bring unconscious conflicts into consciousness ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Psychoanalyis/Psychodynamic Five Major Techniques of Psychoanalysis: 1. Free association Dream analysis Analyzing resistance Analyzing transference Interpretation 2. 3. 4. 5. ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Psychoanalysis/Psychodynamic Evaluation of psychoanalysis: Limited applicability and lack of scientific credibility Psychodynamic Therapy: briefer, more directive, and more modern form of psychoanalysis that focuses on conscious processes and current problems ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Cognitive Cognitive Therapy: focuses on faulty thinking and beliefs Improvement comes from insight into negative self-talk (unrealistic things a person has been telling himself or herself) Cognitive Restructuring (process of changing destructive thoughts or inappropriate interpretations) ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Cognitive (Continued) 1. 2. Two Major Cognitive Therapies: Albert Ellis’s Rational-Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) Aaron Beck’s Cognitive-Behavior Therapy ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Cognitive (Continued) Ellis’s Rational-Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT): eliminates self-defeating beliefs through rational examination ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Cognitive (Continued) Beck’s Cognitive-Behavior Therapy: confronts and changes behaviors associated with destructive cognitions Depressive Thinking Patterns: selective perception overgeneralization magnification all-or-nothing thinking ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Cognitive (Continued) Evaluation of cognitive therapy: Pro: Considerable success with a range of problems Con: Criticized for overemphasizing rationality, ignoring unconscious dynamics, minimizing importance of the past, etc. ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Humanistic Humanistic therapy: Maximizes personal growth through affective restructuring (emotional readjustment) Key assumption: People with problems are suffering from a blockage or disruption of their normal growth potential, which leads to a defective self-concept. ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Humanistic (Cont.) Rogers’s Client-Centered Therapy: emphasizes client’s natural tendency to become healthy and productive Techniques include: Empathy Unconditional positive regard Genuineness Active listening ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Humanistic (Continued) Evaluation of humanistic therapy: Pro: Evidence for success Con: Basic tenets, such as selfactualization, difficult to test scientifically ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Insight Therapies: Group, Family, and Marital Therapies Group Therapy: a number of people meet together to work toward therapeutic goals Family and Marital Therapies: work to change maladaptive family and couple interaction patterns ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies Behavior Therapy: group of techniques based on learning principles used to change maladaptive behaviors Three foundations of behavior therapy: Classical conditioning Operant conditioning Observational learning ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies: Classical Conditioning Systematic Desensitization: gradual process of extinguishing a learned fear (or phobia) by working through a hierarchy of fearful stimuli while remaining relaxed ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies: Classical Conditioning ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies: Classical Conditioning Aversion Therapy: pairing an aversive (unpleasant) stimulus with a maladaptive behavior ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies: Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning Techniques Used to INCREASE Adaptive Behaviors: Shaping--successive approximations of target behavior are rewarded (includes role-playing, behavior rehearsal, assertiveness training) Tokens: symbolic rewards used to immediately reinforce desired behavior ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies: Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning Techniques Used to DECREASE Maladaptive Behaviors: Extinction: withdrawal of attention Punishment: adding or taking away something (e.g., time-out) ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies: Observational Learning Modeling: watching and imitating models that demonstrate desirable behaviors Participant Modeling: combining live modeling with direct and gradual practice ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Behavior Therapies (Continued) Evaluation of behavior therapies: Pro: Strong evidence for success with a wide range of problems Con: Questioned and criticized for generalizability and ethics ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Biomedical Therapies Biomedical Therapy: uses physiological interventions, such as drugs, to reduce or alleviate symptoms of psychological disorders Three forms of biomedical therapy: Psychopharmacology Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) Psychosurgery ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Biomedical Therapies: Psychopharmacology Four major categories of drugs: • Antianxiety (increases relaxation, reduces anxiety and muscle tension) Antipsychotic (treats hallucinations and other symptoms of psychosis) Mood Stabilizer (treats manic episodes and depression) Antidepressant (treats symptoms of depression) • • • ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Biomedical Therapies: Psychopharmacology ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Psychopharmacology— How Antidepressants Work ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Biomedical Therapies (Continued) Electroconvulsive Therapy: based on passing electrical current through the brain and used when other methods have not been successful Psychosurgery: operative procedures on the brain designed to relieve severe mental symptoms that have not responded to other forms of treatment ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking Therapy Essentials--Five Common Goals ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking: Gender and Cultural Diversity • • • • • • Cultural Similarities in Therapy: naming a problem qualities of the therapist establishing credibility placing the problems in a familiar framework applying techniques to bring relief a special time and place ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking: Gender and Cultural Diversity (Cont.) Cultural Differences: Therapies in individualistic cultures emphasize independence, the self, and control over one’s life. Therapies in collectivist cultures emphasize interdependence. ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking: Gender and Cultural Diversity (Cont.) Key considerations for women and therapy: 1. Higher rate of diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders Stresses of poverty Stresses of multiple roles Stresses of aging Violence against women 2. 3. 4. 5. ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking: Institutionalization Institutionalization— Criteria for involuntary commitment: – Dangerous to self or others Believed to be in serious need of treatment No reasonable alternatives – – ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking: Institutionalization (Continued) Deinstitutionalization: discharging as many people as possible from state hospitals and discouraging admissions • Community services such as community mental health (CMH) centers work to cope with the problems of deinstitutionalization. ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Therapy and Critical Thinking: Evaluating and Finding Therapy Forty to 90 % who receive therapy are better off than people who do not. Guidelines for Finding a Therapist: Take time to “shop around.” If in a crisis, call 24-hour hotlines or college counselin centers. • • • If others’ problems affect you, get help yourself. ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e) Psychology in Action (8e) by Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation End of Chapter 15: Therapy Karen Huffman, Palomar College ©John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e)