* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Este - Delmar
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
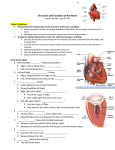
Chapter 26: Glossary The Complete Health History and Physical Examination Alveoli Alveoli are the smallest functional units of the respiratory system, where gas exchange occurs. Angle of Louis (sternal angle) The angle of Louis articulates with the second rib. Apnea Apnea is the absence of spontaneous breathing for 10 or more seconds. Asystole Asystole is the absence of a pulse. Atrioventricular (A-V) node The atrioventricular node is the back-up pacemaker of the heart. If the S-A node fails to initiate an impulse, the A-V node will take over. The A-V node has an intrinsic rate of 40 to 60 impulses per minute. Atrioventricular valves The atrioventricular valves are the mitral and tricuspid valves, which are located between the atria and the ventricles. The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. The mitral valve is located between the left atria and the left ventricle. Bradycardia Bradycardia is a pulse rate slower than 60 beats per minute in an adult. Bradypnea Bradypnea is a respiratory rate less than 12 breaths per minute in an adult. Bruit Bruits are blowing sounds heard when blood flow becomes turbulent in a blood vessel or when blood rushes past an obstruction. Click A click is an abnormal, high-pitched sound heard on systole. Costal angle The costal angle is located where the 10th pair of ribs meets the sternum at the midsternal line. Copyright © 2010 by Delmar, Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Costal margins The costal margins are the medial borders created by the connection of the false ribs. Crescendo Crescendo is a term used to describe sounds that go from soft to loud. Decrescendo Decrescendo is a term used to describe sounds that go from loud to soft. Eupnea Eupnea is a normal respiratory rate, between 12 and 20 breaths per minute. Gallop A gallop is an additional sound that is best heard in early diastole at the apex of the heart. A gallop may or may not be an abnormal finding, depending on the patient's age and whether the patient is pregnant. Heaves A heave is a lifting of the cardiac area secondary to an increased workload. This is an abnormal finding. Hematemesis The vomiting of blood is known as hematemesis. Hyperactive bowel sounds The presence of increased or hyperactive bowel sounds is an abnormal finding that indicates increased bowel motility, possibly due to gastroenteritis, diarrhea, or laxative use. Hypertension Hypertension is blood pressure greater than 140 mm Hg systolic and 90 mm Hg diastolic. Hypoactive bowel sounds The presence of diminished or hypoactive bowel sounds is an abnormal finding that indicates decreased bowel motility, possibly secondary to peritonitis or nonmechanical obstruction. Hypotension Hypotension is blood pressure below the normal range. Copyright © 2010 by Delmar, Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. McBurney's point McBurney's point is located in the RLQ of the abdomen. The elicitation of pain upon palpation at McBurney's point is a positive finding that may indicate appendicitis. Mediastinum The mediastinum is the area between the right and left lungs. Midaxillary line The midaxillary line is the imaginary vertical line drawn from the apex of the axillae and lying midway between the anterior and posterior lines. Midclavicular line The midclavicular line is an imaginary vertical line drawn from the midpoint of the clavicle. Murphy's sign Murphy's sign is used to assess for cholecystitis. To assess Murphy's sign, palpate below the liver margin at the lateral border of the rectus muscle. Ask the patient to take a deep breath. Murphy’s sign is present if the patient complains of pain with palpation. Orthostatic hypotension Orthostatic hypotension results when a patient's blood pressure significantly decreases and the heart rate increases as the patient moves from a lying down to a sitting or standing position. Pansystolic (holosystolic) A murmur that is audible throughout all of systole is referred to as a pansystolic or holosystolic murmur. Precordium The precordium is the area on the anterior surface of the body overlying the heart, great vessels, pericardium, and pulmonary tissue. Pulse deficit A pulse deficit occurs when the apical pulse rate is greater than the radial pulse rate. Rebound tenderness Rebound tenderness is seen when, upon palpation, the patient complains of tenderness or pain as the abdominal wall returns to its normal position. Rebound tenderness may indicate peritoneal irritation. Copyright © 2010 by Delmar, Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Rovsing's sign Rovsing's sign is used to elicit the presence of referred pain, indicative of peritoneal inflammation secondary to appendicitis. To perform this technique, perform deep palpation in the LLQ for 5 seconds. A positive Rovsing's sign is present if the patient feels pain in the RLQ. Sinoatrial (S-A) node The sinoatrial node is the normal pacemaker of the heart. The intrinsic rate of the S-A node is between 60 and 100 impulses per minute. Snap A snap is an abnormal, high-pitched sound heard on diastole. Striae Striae develop when there has been rapid or prolonged stretching of the skin, as in pregnancy or obesity. Suprasternal notch The suprasternal notch is located in the midsternal line above the manubrium. Tachycardia Tachycardia is a pulse rate faster than 100 beats per minute in an adult. Tachypnea Tachypnea is a respiratory rate greater than 20 breaths per minute in an adult. Thrills A thrill is a palpable vibration similar to what one feels when placing a hand on a purring cat. The presence of a thrill is an abnormal finding. Valve regurgitation Valve regurgitation is a backward flow of blood through the heart valve. Valve stenosis Valve stenosis is a narrowing or constricting of a diseased heart valve. Copyright © 2010 by Delmar, Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.