* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5_slides_olefin_complexes_VIPEr
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Spin crossover wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
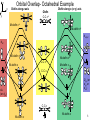
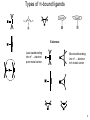
Complexes of alkenes, alkynes, and dienes Created by Margaret L. Scheuermann, Princeton University; Abby R. O’Connor, The College of New Jersey, [email protected]. Copyright Scheuermann and O’Connor, 2014. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercialShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license visit http://creativecommons.org/about/license/ History & Utility First example Popular starting materials and precatalysts: W. C. Zeise, Annalen der Physik, 1831, 21, 497. Review: Hunt. Platin. Met. Rev. 1984, 28, 76. Catalytic intermediates: Alkene hydrogenation^* Alkene dimerization/ oligomerization/ polymerization^* Olefin metathesis^* Mizoroki-Heck^* Wacker Oxidation^ Hydrofunctionalization- Hydroboration/ hydosilylation^/ hydrocyanation^/ hydroamination^/ hydroformylation^/ etc. ^ significant industrial use; * Nobel Prize 2 z x Orbital Overlap- Octahedral Example Olefin along z axis y Olefin C-C σ* Olefin along x (or y) axis M-olefin σ* M-olefin σ* dx2-y2 dz2 M-olefin π* M-olefin π M-olefin π* C-C π* M-olefin π C-C π Dxy (or dyz or dxz) dxz (or dyz) C-C σ M-olefin σ M-olefin σ 3 Types of π-bound ligands Extremes Less backbonding into π*… electron poor metal center More backbonding into π*… electron rich metal center 4 Properties Electron rich metal centers tend to form more stable olefin complexes • late metals • Low oxidation states • high d-electron counts • low overall charge Rotation around metal-olefin bond Orientation determined by steric and electronic factors Bond lengths and angles NMR •As backbonding increases so do geometry differences •C-C bonds get longer • When backbonding is minimal (electron poor metal center) 1H and 13C shifts resemble free olefin • sp2 becomes more sp3-like • sp becomes more sp2-like • can help relieve ring strain Buchwald. JACS 1986, 165, 7441. • When backbonding is significant (electron rich metal center) 1H and 13C resonances shift upfield- smaller δ 5 Synthesis & Reactivity Ligand substitution* β-hydride elimination* Displacement by ligand substitution* Insertion* α β R = H, alkyl, aryl Reduction * Often present in catalytic cycles Nucleophilic attack* (when metal center is a poor π donor) 6





![[1] Conduction electrons in a metal with a uniform static... A uniform static electric field E is established in a...](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008947248_1-1c8e2434c537d6185e605db2fc82d95a-150x150.png)