* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Only(features(that(result(from(common(ancestry(reflect( evolutionary
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
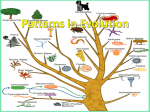
• Only(features(that(result(from(common(ancestry(reflect( evolutionary(changes( • Homologies:(phenotypic(and(genetic(similarities(from(a(shared( ancestry( • Analogy:(similarity(between(2(species(that(is(due(to(convergent( evolution(rather(than(common(ancestors((homology)( • Analogous(structures(that(arose(independently(are(also(called( homoplasies( • The(more(elements(that(are(similar(in(2(complex(structures,(the( greater(the(chance(of(homology(( • Molecular(homoplasy:(coincidental(matches( • Molecular(systematics:(uses(DNA(data(of(the(molecules(to( determine(evolutionary(relationships( • Cladistics:(place(species(into(groups((clades)(which(includes(an( ancestral(species(and(all(its(descendants(((( • A(taxon(only(equals(a(clade(if(it’s(monophyletic:(consists(of(an( ancestral(species(and(all(its(descendants( • Paraphyletic:(an(ancestral(species(and(some((not(all)(of(its( descendants( • Polyphyletic:(taxa(with(different(ancestors( • Phyletic=(tribe( • Shared(ancestral(character:(character(that(originated(in(an( ancestor(of(the(taxon( • Shared(derived(character:(shared(by(all(taxa(but(not(found(in( their(ancestors,(evolutionary(novelty(unique(to(a(clade( • Outgroup:(species/group(of(species(from(an(evolutionary( lineage(that(is(known(to(have(diverged(before(the(lineage(that( includes(the(species(we(are(studying( • Branching(patterns(are(all(relative( • Maximum(parsimony:(first(investigate(the(simplest(explanation( that(is(consistent(with(the(facts( • Phylogenies(based(on(DNA;(most(parsimonious(tree(requires( the(fewest(base(changes( • Maximum(likelihood:(given(certain(probability(rules(about(how( DNA(sequences(change(over(time,(a(tree(can(be(formed(that( reflects(the(most(likely(sequence(of(evolutionary(events( (usually(complex)( • Likelihood(of(a(tree(depends(on(the(assumptions(on(which(it’s( based( • Phylogenetic(trees(represent(hypothesis( • Gene(duplication:(more(genes(in(the(genome,(therefore(more( opportunities(for(further(evolutionary(change( • Orthologous(genes:(found(in(different(species,(and(their( divergence(tracks(back(to(the(speciation(events(that(produced( the(species( • Paralogous(genes:(results(from(gene(duplication,(multiple( copies(of(these(genes(have(diverged(from(one(another(within(a( species( • Molecular(clock:(measurement(of(the(absolute(time(of( evolutionary(change(based(on(the(observation(that(some(genes( and(other(regions(of(genomes(appear(to(evolve(at(constant( rates( • Average(rate(of(evolution:(number(of(genetic(differences( against(the(dates(of(evolutionary(branch(points(that(are(known( from(the(fossil(record( • Possibility(that(some(mutations(have(become(fixed(by(genetic( drift((neither(beneficial(or(detrimental)( • Neutral(theory:(much(evolutionary(change(in(genes(and( proteins(have(no(effect(on(fitness(and(therefore(is(not( influenced(by(natural(selection( • Molecular(clock(assumes(that(the(estimated(evolutionary( divergence(has(been(constant(all(along( • Horizontal(gene(transfer:(genes(are(transferred(from(one( genome(to(another(through(mechanisms,(such(as(exchange(of( transposable(elements(and(plasmids,(viral(infection(and(fusion( of(organisms( ( • Linnaeaus’(binomial(classification(system(gives(organisms(2( part(names:(a(genus(and(a(epithet(part( • In(the(Linnaean(system,(species(are(grouped(in(increasingly( broad(taxa:(related(genera(are(place(in(the(same(family,( families(in(orders,(orders(in(classes(etc( • Systematists(depict(evolutionary(relationships(as(branching( phylogenetic(trees.(Many(systematists(propose(that( classification(be(based(entirely(on(evolutionary(relationships( • Unless(branch(lengths(are(proportional(to(time(or(amount(of( genetic(change,(a(phylogenetic(tree(indicates(only(patterns(of( descent( • Much(information(can(be(learned(about(species(from(its( evolutionary(history;(hence,(phylogenies(are(useful(in(a(wide( range(of(applications(( • Organisms(with(similar(morphologies(or(DNA(sequences(are( likely(to(be(more(closely(related(than(organisms(with(very( different(structures(and(genetic(sequences( • Computer(programs(are(used(to(align(comparable(DNA( sequences(and(to(distinguish(molecular(homologies(from( coincidental(matches(between(taxa(that(diverged(long(ago( • Branch(lengths(can(ne(drawn(proportional(to(the(amount(of( evolutionary(change(or(time( • Among(phylogenies,(the(most(parsimonious(tree(is(the(one(that( requires(the(fewest(evolutionary(changes.(The(most(likely(tree( is(the(one(based(on(the(most(likely(pattern(of(changes( • Well]supported(phylogenetic(hypothesis(are(consistent(with(a( wide(range(of(data( • Distnaly(related(species(can(have(orthologous(genes.(The(small( variation(in(gene(number(in(organisms(of(varying(complexity( suggests(that(genes(are(versatile(and(may(have(multiple( functions((( • Past(classification(systems(have(given(way(to(the(current(view( of(the(tree(of(life,(which(consists(of(3(domains( 1. Bacteria( 2. Archaea( 3. Eukarya( • Phylogenies(based(on(rRNA(genes(suggest(that(eukaryotes(are( most(closely(related(to(archaea,(while(data(from(some(other( genes(suggests(a(closer(relationship(to(bacteria( • Other(genetic(analyses(suggest(that(eukaryotes(arose(as(a( fusion(between(a(bacterium(and(an(archaean,(leading(to(a(“ring( of(life”(in(which(eukaryotes(are(equally(closely(related(to( bacteria(and(archaea( ( CHAPTER(27:(BACTERIA(AND(ARCHAEA( • Many(prokaryotes(can(tolerate(extreme(environments( • Ability(to(adapt(to(a(broad(range(of(environments(explains(why( they(are(so(abundant( • Prokaryote(populations(have(been(subject(to(natural(selection( in(all(kinds(of(environments,(resulting(in(their(enormous( diversity(today( • Prokaryotes:(mostly(unicellular(although(the(cells(of(some( species(remain(attached(to(each(other(after(cell(division( • Much(smaller(than(eukaryotic(cells(( • Well]organised,(achieving(all(of(an(organisms(life(functions( within(a(single(cell( 1. Sphereical( 2. Rod]shaped( 3. Spiral(( • In(a(hypertonic(environment(most(prokaryotes(lose(water(and( shrink(away(from(their(wall((they(lay(dormant)( • Salt(can(be(used(as(a(preservative(as(it(causes(prokaryotes(to( lose(water,(preventing(them(from(rapidly(multiplying( • Eukaryote(cell(wall:(cellulose(or(chitin( • Prokaryote(cell(wall((bacteria):(peptidodglycan:(polymer(of( modified(sugars(cross]linked(by(short(polypeptides( • Archaeal(cell(wall:(variety(of(polysaccharides(and(proteins((no( peptidoglycan)( • Gram(stain:(classification(of(many(bacterial(species(into(2( groups(based(on(differences(in(cell]wall(composition( • Stained(with:( 1. Crystal(violet(dye(and(iodine( 2. Rinsed(in(alcohol( 3. Stained(with(red(dye((eg(safranin)( • Gram]positive:(simpler(walls(with(a(relatively(large(amount(of( peptidoglycan( • Gram]negative:(less(peptidoglycan,(structurally(more(complex,( outer(membrane((lipopolysaccharides)(( • More(resistant(to(antibiotics((due(to(wall)( • Cell]wall(of(many(prokaryotes(are(surrounded(by(a(sticky(layer( of(polysaccharides(and(protein(called(a(capsule( • Fimbriae:(hair]like(appendages(that(allow(prokaryotes(to(stick( together( • About(50%(of(prokaryotes(are(capable(of(taxis:(directed( movement(towards(or(away(from(a(stimulus( • Prokaryote(flagella(are(1/10(the(size(of(eukaryotic(flagella(and( are(not(covered(by(an(extension(of(the(plasma(membrane( • Bacteria(flagellum:(motor,(hook,(filament((42(kinds(of(proteins)( • Only(half(of(these(are(necessary(for(function( • Exaptation:(existing(structures(take(on(new(functions(through( descent(with(modification(( • Prokaryotes(lack(compartmentalisation(found(in(eukaryotes( • Prokaryotes(have(less(DNA(than(eukaryotes(