* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture #12 Date ______
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
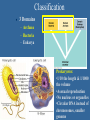
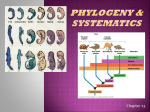
Ch. 26: Classification & Phylogenetics The Major Lineages of Life Characteristic Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Nuclear Envelope No No Yes Membraneenclosed organelles No No Yes Introns No Yes Yes Histones associated w/DNA No Yes Yes Circular chromosome Yes Yes No Taxonomy The tracing of evolutionary relationships (phylogenetic tree) Linnaeus Binomial nomenclature: – Genus, species epithet – Homo sapiens Taxon (taxa): a group of organisms in the same clade (ancestor + all descendants) Phylogenetic Trees Systematics: classifying organisms according to their evolutionary relationships Fossils, morphology, molecular evidence Protista: (not “true” kingdom) Bacteria: (not “true” kingdom) The only “true” clade Constructing a Cladogram Homology vs. Analogy... Homology: likenesses attributed to common ancestry (inheritance) Analogy: functional similarities; not indicative of close evolutionary relationships Convergent evolution: species from different evolutionary branches that resemble one another due to similar ecological roles Homologous Structures Human Cat Whale Bat A Cladogram: the basis of a phylogenetic tree Cladograms are based on shared characters Classification 3 Domains – Archaea – Bacteria – Eukarya Prokaryotes: •1/10 the length & 1/1000 the volume •Asexual reproduction •No nucleus or organelles •Circular DNA instead of chromosomes, smaller genome