* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Connection Introduction: Cladistics and Evolution by
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation–evolution controversy wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Mormon views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
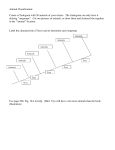
Name _____________________________________________ Date __________________ Block ____________ Evolution Connection Introduction: Cladistics and Evolution by Natural Selection “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution.” -‐ Theodosius Dobzhansky Evolution is such a broad topic that it relates to every unit in biology. In fact, it is often said that biology is difficult to understand unless you study it in the context of evolution. During each unit this year, we will discuss an “evolution connection” in which we will study an aspect of evolution that relates to our unit. Each evolution connection will be a self-contained worksheet. This way, by the end of the year, you will have several packets that collectively represent a whole unit on evolution. We begin our study of biology with a brief introduction to evolution. Use the online resources, along with chapter 1 of your textbook, to answer the following questions. Part I: Evolutionary Relationships and Cladistics http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/Trex/ Begin this activity by going to the website below and selecting “Student Start” You will navigate through all 5 folders in this tutorial, beginning with folder 1. Folder 1: 1. List some distinguishing characteristics of each of the 3 domains of living things. Domain Distinguishing Characteristics Bacteria Archaea Eukaryota 2. What is a common ancestor? 3. How long ago did all living things share a common ancestor? Folder 2: When you have examined the information in this folder, do the knowledge check questions below. (Note: these questions relate to the evolutionary tree below, which is different from the tree on the website.) 4. In the cladogram provided, label the distinct history, shared history, and common ancestor for kangaroo and human. 5. Which organism in the cladogram is most closely related to humans? Explain. Notice: in this typical cladogram, no information is given about relative time between evolutionary events. If the spacing between branches were different, we would call this a phylogenetic tree. Phylogenetic trees are just o ne specific type of cladogram. Folders 3 & 4: 6. What type of information is shown in a cladogram? 7. Fill in the tables below. 8. To which animal is T. rex most closely related? (Circle one) Caiman Parrot Folder 5 9. Use the information gathered in folders 1 – 4 to make inferences about the following: Color vision Warm blooded Feathers Sing to Young Scaly skin Melanin pigment Amniotic egg Few glands in skin Hole in hip socket 3chambered heart 4– chambered heart Caiman + 0 0 + + + + + 0 + 0 Parrot + + + + + + + + + 0 + T. rex Cladistics and phylogeny are related fields of biology that try to map evolutionary relationships between organisms. Using cladistics, all organisms can be classified into 3 major groups, or domains. Examine the phylogenetic tree below. 10. Which two domains are most closely related to one another? Explain your answer. Part II: Evolution by Natural Selection Video: “Who Was Charles Darwin?” http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/teachstuds/svideos.html 11. What characteristics made Darwin especially well suited for science? 12. What did Darwin see and do on his 5-‐year voyage aboard the Beagle? 13. What new idea did Charles Darwin introduce to science? How did it challenge the current understanding of biodiversity? 2. We Can Observe Changing Populations Video: How Does Evolution Really Work? http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/teachstuds/svideos.html 14. What are the four components of natural selection? A. B. C. D. 15. What determines an individual hummingbird’s beak length? 16. What factors in the environment might select for beak length and shape within hummingbird populations? 17. How can hummingbird DNA help Dr. Schneider determine the evolutionary history of hummingbirds?