* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patterns in Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
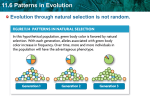
Key concept : Evolution occurs in patterns • Evolution through natural selection is not random. • Natural selection can have direction. • The effects of natural selection add up over time. Convergent Evolution Defined: evolution toward similar traits in unrelated species due to a similar environment. • Ex: Tuna (fish) and dolphins (mammals). They are an unrelated species living in a similar environment, the ocean. • Faced similar evolutionary pressures. Divergent Evolution red fox kit fox ancestor • Defined: Describes evolution toward different traits in closely related species. – Cause: Different environments Coevolution • Defined: Two or more species evolve in response to changes in each other – Evolutionary paths become connected – Both species receive benefits from the other as a result of adaptations. • Ex: Plants and Insects – Plants: provide insects with nectar – Insect: transfers pollen from one plant to another Coevolution Continued… • Coevolution can occur in competitive relationships, sometimes called an evolutionary arms race. – Example: Crab vs. Snail & Bacteria vs. Humans Evolutionary Arms Race Continued… Antibiotic Resistance Bad Good • Antibiotics: chemicals designed to kill bacteria – Produced by other microorganisms to fight bacteria • Antibiotic Resistance: Bacteria are adapting to the use of antibiotics – Overuse & misuse speeds up the process – Importance: Bacteria infections are becoming harder to treat Species Can Become Extinct • Defined: The elimination of a species from Earth. • Mass Extinctions: • Background Extinctions: – Cause: Catastrophic events – Cause: Local changes in environment – Ice Age, Meteorites – Forest fires, habitat destruction. – Destroys many species at global level – Affects a few species in a small area – Very severe – Less severe. – Rare but much more intense – Occur at roughly the same rate as – At least 5 mass extinctions in speciation last 600 million years How Fast Does Evolution Occur? • Gradualism: Slow & steady change of 1 species into another – Small changes continually build over time Punctuated Equilibrium: Long periods of little change are interrupted by shorter periods of rapid change. – Due to sudden environment change – Ex: Mammal diversity exploded after dinosaur extinction Gradualism of the Horse How Fast Does Evolution Occur? To radiate = to s-p-r-e-a-d out • Adaptive radiation: A process of evolution where one species can split into a number of different species. – Ancestral species diversifies into many descendent species – Each adapted to a different environment • Ex: Mammals Review • How is convergent and divergent evolution different? • What is thought to bring different organisms such as fish and dolphins to have evolved a similar body plan? • What is coevolution? • What does a flower gain from a close relationship with a hummingbird? • What does the hummingbird gain? • How is gradualism and punctuated equilibrium different?