* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Function of Marine Ecosystems
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Marine conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
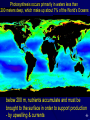
Structure and Function of Marine Ecosystems Challenges of Integrating Ecosystem Knowledge Definitions Key Processes in Marine Ecosystems Status of Ecosystem Science Steven Murawski Ph.D. Director, Office of Science & Technology National Marine Fisheries Service -1- -2- Definitions An ecosystem is a geographically specified system of organisms (including humans), the environment, and the processes that control its dynamics. The environment is the biological, chemical, physical, and social conditions that surround organisms. When appropriate, the term environment should be qualified as biological, chemical, physical, and/or social. -3- Spatial Scales & Boundaries -4- The Trophic Pyramid and Energy Flow Humans Apex Predators Piscivores Forage Fish Zooplankton Phytoplankton 0.01 unit 0.1 unit 1 unit 10 units 100 units 1000 units -5- Photosynthesis occurs primarily in waters less than 200 meters deep, which make up about 7% of the World’s Oceans below 200 m, nutrients accumulate and must be brought to the surface in order to support production -6- by upwelling & currents Scales and Observations -7- Regional Climatology Affects Ecosystems -8- Interactions Between Physical & Biological Components of Ecosystems -9- Harvesting Affects Distributions & Abundances of Species Atlantic cod -10- Surface Production & Dynamics Food-web and particle size models Known Status of Major Species Nutrient Enrichment & Toxics 3-D Structure of Selected Ocean Environments Mapping of Habitats Climate Variation effects on Reversibility of species & ecosystems Human impacts Status of all “important” species Spatially-explicit models of Number of Species in predator-prey systems the Oceans Unknown Valuing Ecosystem Goods & Services Synoptic Maps of the Sea Floor Evolutionary effects of human activities Structure of “pristine” ecosystems Predictive models of many-species interactions Unknowable