* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indian Literature
Survey
Document related concepts
Atharvaveda wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
Namaste Sada Vatsale wikipedia , lookup
Dharmaśāstra wikipedia , lookup
Dayananda Saraswati wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Mahabharata wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
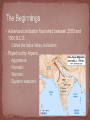
Advanced civilization flourished between 2500 and 1500 B.C.E. Called the Indus Valley civilization Wiped out by Aryans Aggressive Nomadic Warriors Superior weapons Evolved from Aryan beliefs Way of life, not just religion No written doctrines or sets of rules No single prophet or religious leader Many, many gods Many believe that all the gods are aspects of a single essence or immortal spirit Three deities stand out – called Trimurti Brahma (creator) Vishnu (protector) Shiva (destroyer/preserver) dharma: from Sanskrit, “to hold” – fulfill the duties of station in life, however lofty or humble karma: from Sanskrit, “action” – actions in life; good or bad karma leads to good or bad reincarnation reincarnation: rebirth of deceased person’s soul into new body; when a soul is sufficiently purified, it is united with Brahman, or the ultimate spiritual reality Social class Five basic ranks Brahmans: scholars, priests, teachers Kshatriyas: rulers and warriors Vaisyas: merchants, farmers, artisans Sudras: menial work Dalits (untouchables) Excluded altogether Dispose of dead animals; clean up human waste Believed to pollute others by touch or sight Founded during end of Vedic period Buddha means “Enlightened One” Siddhartha Gautama Prince Gave up rich life for spiritual peace Life is an endless cycle of suffering caused by desire for earthly goods Practice yoga (“union”) – self-denial, meditation, breathing practices, nonviolent behavior Rejects social stratification of Hinduism 8th century AD Constant fighting between Islamic and Hindu dynasties – lasted centuries! Ended in partition between Muslims and Hindus in 1947: Pakistan for Muslims India for Hindus Vedic: 1500-500 BCE Named for the Vedas, or sacred hymns Classical: 500 BCE to AD 1000 Wrote in Sanskrit संस्कृतम ् Means “perfect speech” Considered a sacred language Rig-Veda “hymns of the supreme sacred knowledge” regarded as divinely inspired Mahabharata epic story about two rival families Bhagavad-Gita interrupts the Mahabharata divided into 18 sections of “teachings”