* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution- Mechanisms of Evolution
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Kin selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
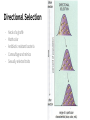
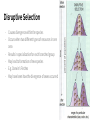
Evolution- Mechanisms of Evolution Biology Miami Arts Charter Introduction - change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations - Gives rise to biodiversity - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GhHOjC4oxh8 Contributions - Lyell: Malthus: overpopulation and resources Lamarck: Acquired traits Wallace: also suggested that evolution of species was caused by this natural selection - suggested that evolution of species was caused by this natural selection - Cowrote paper: On the Tendency of Species to form Varieties; and on the Perpetuation of Varieties and Species by Natural Means of Selection Lyell - Wrote Principles of Geology - one of the first to believe that the world is older than 300 million years based on geological anomalies - idea of uniformitarianism, that the earth was shaped entirely by slow-moving forces still in operation today, acting over a very long period of time - Stratigraphy: studying the layers which would become the different time periods in the history of the world - Tertiary period into three parts, which he named the Pliocene, Miocene, and Eocene. He also renamed the traditional Primary, Secondary and Tertiary periods (now called eras) to Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Malthus - An Essay on the principles of population Population growing exponentially Food grew linearly Lack of resources would lead to famines and death Would unfairly affect the poor Lamarck - early 19th Century a French naturalist theory for how evolution works Lamarckism - proposed that organisms inherited changes caused by use or disuse in its parents. - For example, if a parent giraffe stretches its neck to get at leaves on tall trees, its descendents are born with longer necks, and so giraffes evolve over generations to have long necks Darwin - English naturalist and geologist - Decent from a common ancestor - Branching pattern of evolution resulted from Natural Selection - Struggle for existence Explains the diversity of life Basic mechanism of evolution - On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life: 1859 - Widely accepted by 1870 Natural Selection - Unequal survival and reproduction of organisms due to environmental forces, resulting in the preservation of favorable traits - 4 principles - 1. Variation - Mutations Meiosis - recombination due to crossing-over in 1st division - random movement of chromosomes in 2nd division - Random sex cell selection & fertilization - 2. Differential Reproduction - Environment cannot support unlimited population - Certain phenotypes Traits that are well adapted for the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce - Non-random mating Natural Selection - 3. Heritability - Traits need to be passed onto future generations through genes - 4. Result is descent with modification - When humans select the modification = artificial selection - When the environment selects = Natural Selection How Natural works Natural Selection is Survival of the fittest (REPRODUCTION) There is no agent involved in natural selection. Natural selection is a process of elimination Selection pressure on a population? •Competition for food • Competition for a mate • Changes in the environment • Predators • Parasites Examples of Selection Pressures Predators - variants with adaptations allowing them to escape predators have more offspring - e.g. speed, defensive weapons, camouflage, mimicry Prey/Food - variants with adaptations allowing them to obtain food have more offspring - e.g. Speed, senses for finding prey/food, weapons for killing prey or obtaining food, camouflage for stealth Climate - those who can survive new climate best have more kids - e.g. ice age, change in climate due to migration. Mates - variants with adaptations allowing them to attract a mate to have offspring - e.g. strong, attractive, good provider Predation pressure •Only the darker colored moths survived after the industrial revolution. Selection was for more melanin. Food EXAMPLE - The neck of the Giraffe - Co-evolution with Acacia Trees - Selection pressure is source of food - The Red Queen Hypothesis... Types of Selection - Directional Selection - Natural selection favors one extreme of the population for that trait - often happens when environment changes in a consistent way- e.g.climate gets colder. Types of Selection - Disruptive Selection - Causes species to diverge - Stabilizing Selection - Natural selection favors the average for population selected - Sexual Selection Directional Selection - Neck of a giraffe Moth color Antibiotic resistant bacteria Camouflage and mimics Sexually selected traits Stabilizing Selection - When the extremes of the trait aren’t as well suited - Examples - bird clutch size Tail length in birds - Child birth weight Disruptive Selection - Causes divergence within the species - Occurs when two different types of resources in one area - Results in specialization for each branched group - May lead to formation of new species - E.g. Darwin’s Finches - May have been how the divergence of sexes occurred Camouflage, Mimicry, & Decoys Purpose - escape from predators, sneaking up on prey Camouflage - directional selection favors individuals who most resemble the environment Mimicry - directional selection can favor individuals that most resemble something harmful, unappetizing, or non-threatening Decoys - directional selection can favor individuals that use lures or decoys to attract other animals to be eaten or help them unwittingly