* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Notes- teacher copy
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
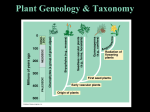
Name ________________________________ Date___________________ Period _______________ Plants Chapter 21-29 AHSGE Std. 10 2 Categories of Plants Characteristics Multicellular Eukaryotic Photosynthetic 6CO2 + 6H20 + Light energy C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2. Have cell walls made of Cellulose. Nonvascular Does not have vascular tissue or true roots leaves, or stems. Vascular Have roots, stem, leaves, xylem, and Phloem. Nonvascular Plants- Reproduction and survival depend on water. They must live in moist environments. Ex: mosses, liverwarts, hornwarts. Fill out this chart Using pg. 577 in the book. Plants Nonvascular Division Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts Origins Adaptations Liverworts were the first land plants. - Have rhizoids to help anchor the stem in soil. - Grow in clumps or masses - have leaves that form structures that protect reproductive cells. Originated 440 million Years ago. Non-seed Vascular - club moss - Horse tails - Ferns - Devonian Period - 375 million yrs ago Seed Vascular - - 360 million yrs ago during the Paleozoic Era. - Conifers= 250 million yrs ago. Cycads Ginkgo Biloba Gnetophyta Conifers Anthophyta - seeds surrounded by a fruit or carried on scales of a cone. - Can grow in a wide variety of habitats. Name ________________________________ Date___________________ Period _______________ Vascular Plants Examples: Ferns, Club mosses Vascular tissue—tissue in plant that transports food/water Vascular refers to veins. Xylem: transports water and minerals Phloem: transports food/nutrients not all plants have vascular tissue Is a basis for dividing plants into different phyla Seedless Vascular Plants have vascular system, but do not produce seeds ex: fern Leaves= fronds Produce spores 3 divisions Lycophyta – club mosses Arthrophyta- horsetails Pterophyta- ferns Vascular Seed Plants Seed—protective structure where embryonic plant can be stored until conditions are favorable for growth. Two types of seed plants Gymnosperms (4 phyla) Angiosperms (1 large phylum) Gymnosperms Seeds are not protected by a fruit Examples: Ginkgo biloba Conifers—plants with seeds inside cones and needle-like leaves Pines, firs, cedars, redwoods Angiosperms Flowering Plants Seeds are protected by fruit Produce fruits with 1 or more seeds Fruit—ripened ovary of flower Fruit aid in seed dispersal Examples: maple trees, apple trees, wildflowers, herbs, azaleas, grass, oak trees, poplar trees Name ________________________________ Date___________________ Period _______________ Two types of Angiosperms Monocot Ex: corn, grass Dicot Ex. trees, shrubs, sunflowers , most flowers In multiples of 3’s One cotyledons Usually netlike In a ring Flower Structure Plant Adaptations to Living on Land cuticles—_waxy coating on the outside of plant that prevents water loss Leaves—broad flat structures (usually) that trap light for photosynthesis Roots—structures that allow plants to obtain water/nutrients from soil Stem- plant organ that provides support for growth and food storage. spores and seeds—structures that keep reproductive cells from drying out. Xylem- transports water & dissolved substances Phloem—transports dissolved food/nutrients. Plant Tissues Stomata-Controls the exchange of gases; Helps control water loss. Guard Cells-control the opening & closingof the stomata Flowers are reproductive structures for angiosperms Produce fruit and seeds Pistil Name ________________________________ Date___________________ Period _______________ Petal S: located at center of Structure: leaf like, flower, top of stem usually colorful structures at F: female reproductive top of stem part Style—the “stalk” that Function: attract supports stigma pollinators Stigma—top of style; sticky or hairy structure that traps pollen grains Stamen Ovary—enlarged base of S: located inside of petals pistil; contains one egg F: male reproductive part • Anther—top part of stamen, produces pollen • Filament—“stalk” that supports anther Sepal S: leaf like, usually green structure that encircle flower stem below petal F: to protect developing flower Process of Angiosperm Reproduction Pollination—transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma Happens before fertilization Pollen is transferred to stigma by wind or animals After pollen lands, a pollen tube grows Pollen tube—extension that allows sperm to reach egg inside ovary Angiosperms have “double fertilization” meaning one sperm fertilizes egg and other sperm joins with another cell to form endosperm (nutrients). Seeds contain both endosperm and embryonic plant