* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart and Heart Diseases
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
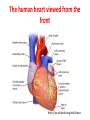
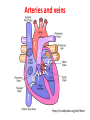
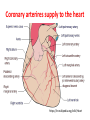
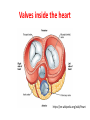
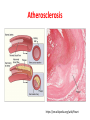
Heart and Heart Diseases Chien-Ming Li, MD, PhD Size and shape • Cone-shaped • 250–350 grams • Size of a fist: 12*8*6 cm The human heart viewed from the front https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart Arteries and veins https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart Coronary arterires supply to the heart https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart Valves inside the heart https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart The cardiac cycle as correlated to the ECG https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart Atherosclerosis https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart Heart diseases 1. Coronary artery diseases or ischemic heart disease 1. Heart failure 2. Valve diseases, septal defect 3. Cardiomyopathy 4. Arrhythmias 5. Pericarditis 1. Coronary artery disease • Caused by atherosclerosis (plague) • May cause chest pain (angina) • A ruptured plaque can cause unstable angina or a heart attack • Complications: cardiac arrest, ventricular rupture • Risk factors: Obesity, high blood pressure, uncontrolled diabetes, smoking and high cholesterol 2. Heart failure • Causes: coronary artery disease, valve disorders, diseases of cardiac muscle • can't beat enough blood to meet the needs of the body • Right heart or the left heart failure • Symptoms or signs: breathlessness due to pulmonary congestion, pulmonary edema), swelling (edema) of the feet, decrease exercise tolerance, enlarged liver, cardiac murmurs 3. Cardiomyopathy • Deterioration of the heart muscle's ability to contract • Causes: alcohol, toxins, sarcoidosis • Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: enlarged heart • Restrictive cardiomyopathy: constrict the outflow tracts of the heart • Dilated cardiomyopathy: impact on the efficiency of its beating 4. Valve disease • Stenosis – Aortic stenosis – Mitral stenosis • Regurgitation – Mitral regurgitation – mitral valve prolapse 4.1. ASD and VSD and PDA • • • • • • • Congenital diseases Patent foramen ovale Ventricular septal defect Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coarctation Tetralogy of Fallot 5. Cardiac arrhythmias • • • • • • Rapid heart rate (tachycardia) > 100 beats/min Slow heart rate (bradycardia) < 60 Asystole: cessation of heart rhythm atrial fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation heart block: abnormal conduction can cause a delay or unusual order of contraction of the heart muscle 6. Pericarditis • Pericardium: surrounds the heart • Pericarditis: inflammation of pericardium • Causes: cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, tuberculosis or Q fever, amyloidosis or sarcoidosis, tumors, high uric acid levels • Complications: pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade