* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introduction to white blood cells
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
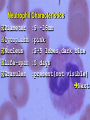
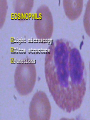
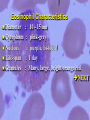
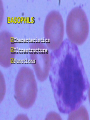
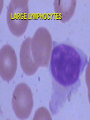
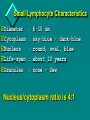
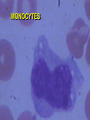
INTRODUCTION TO WHITE BLOOD CELLS developed by Liz Fracalanza Tina Goodyear Hugh B. Fackrell Dept of Biological Sciences University of Windsor Windsor, ON Canada OBJECTIVES To examine the formed elements of blood To define the structure and function of the cellular elements To differentiate between the various blood cells Introduction Blood may be separated into a clear fluid composed of either serum or plasma and formed elements which contain cells and cell fragments Next Formed Elements of Blood Leucocytes (white blood cells) Erythrocytes (red blood cells) Thrombocytes (platelets) Frequency of W.B.C in Human Blood WBC neutrophil lymphocyte monocyte eosinophil basophil % 54-69 25-33 3-7 1-3 0-0.75 number/mm3 2700-6900 1250-3300 150-700 50-300 0-75 Next Structure and function of the cellular elements NEUTROPHILS Characteristics Ultrastructure Functions Distribution Neutrophil Characteristics Diameter :9 -16um Cytoplasm :pink Nucleus :2-5 lobes,dark blue Life-span :5 days Granules :present(not visible) Next Next Neutrophil Functions Respond chemotactically to various stimuli (complement, lymphokines and bacterial membrane components) Phagocytosis of foreign particles and microbes NEXT Distribution of Neutrophils Approximately one-half of the neutrophils found in the body are attached to the endothelial lining of the blood vessels, poised to cross the blood vessel wall and attack an infection Next EOSINOPHILS Light microscopy Ultra structure Functions Eosinophil Characteristics Diameter : Cytoplasm : Nucleus : Life-span : Granules : 10 - 15 um pink-grey purple, bi-lobed 1 day Many, large, bright orange/red NEXT Eosinophil Ultrastructure Eosinophil Function Chemotactic response to complement, antibodies and histamine Active against parasites by phagocytosis and secretion of granular contents next BASOPHILS Characteristics Ultrastructure Functions Basophil Characteristics Diameter :10 -15 um Cytoplasm :basophilic (blue) Nucleus :not usually seen may be lobed Granules :many, large, dark purple, covers nucleus next Basophil EM Basophil Ultrastructure Basophil Functions Secretes substances during an allergic reaction Secretes large amounts of heparin, which is an anticoagulant Secretes histamine, which participates in constriction of the blood vessels, bronchioles and intestines next LARGE LYMPHOCYTES Large Lymphocyte Characteristics Diameter :10 - 18 um Cytoplasm :sky-blue - deep-blue may be vacuolated Nucleus :mono-nuclear, dense chromatin, dark blue Granules : may be few Nucleus/cytoplasm ratio is 1:1 SMALL LYMPHOCYTES Small Lymphocyte Characteristics Diameter : Cytoplasm : Nucleus : Life-span : Granules : 6-10 um sky-blue - dark-blue round, oval, blue about 10 years none - few Nucleus/cytoplasm ratio is 4:1 Lymphocyte Ultrastructure Lymphocyte Function Lymphocytes can behave as one of three major cell types: 1. T lymphocytes 2. B lymphocytes 3. Natural Killer cells T LYMPHOCYTES Helper T Cells Cytotoxic T cells T cell Ultrastructure Helper T lymphocytes aids in stimulation of antibody production by B-lymphocytes Cytotoxic T lymphocytes Destroy invading cells or cancer cells by direct contact. Induce apoptosis B Lymphocytes production and secretion of antibodies participation in “memory immunity” once transformed into a plasma cell, it contains more rough endoplasmic reticulum Plasma Cell Natural Killer Cells Directly destroys virally infected cells and tumour cells Null Cell MONOCYTES Monocyte Characteristics Diameter :12-20um Cytoplasm :light grey-blue, may be vacuolated Nucleus :purple, patchy (mesh-like) Life-span :3 days Granules :fine May not be visible) Nucleus : Cytoplasm (N:C) : 1:1 next Monocyte Functions Phagocytosis - ingests and destroys fungi, bacteria and damanged or degenerated cells Stimulates the immune response by presenting the products of phagocytosis to lymphocytes Attracts neutrophils to the damaged site by secreting chemical attractants Aids in maintenance of blood vessels next Monocyte Ultrastructure