* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download High Frequency of Recombination (Hfr)
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
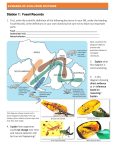
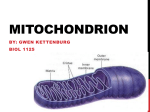
This Week • Start Mt DNA experiment, • Start High Frequency of Recombination (HFR) experiment, • Continue Arabidopsis Developmental Screen. Arabidopsis flower • Wild-type, – perianth, • calyx (4 sepals), • corolla (4 petals), – androecium, • 6 stamens, – gynoecium, • 2 carpels. Model Flower System Floral Transition Mutants Inhibitory Conditions • Circadian clock mutants, • Photoreceptor mutants, • Hormone mutants, • Homeotic mutants, mutant wild type • Others. Inducing Conditions High Frequency of Recombination (Hfr) ...bacteria exhibiting a high frequency of recombination, – an alteration DNA sequence such that the genotype of subsequent individuals differs from the parent, …specifically, strains with a chromosome integrated F factor that is able to mobilize and transfer part of the chromosome to the F- cell. Hfr Cells F factor ...F factor integration site, ...host (bacteria chromosome) integration site. Bacterial Chromosome Inserted F plasmid - F Pilus Attaches to F Cell Hfr DNA is Cut F factor and Chromosomal DNA are Transferred Recombination Requires Crossing over Double Crossover DNA not Incorporated into Chromosome are Digested F factor inserts in different regions of the bacterial chromosome, Also inserts in different orientations. Origin of Replication Hfr strain H 1 2 3 Order of transfer thr azi ton lac pur gal his gly thi thr thi gly his gal pur lac ton azi lac pur gal his gly thi thr azi ton gal pur lac ton azi thr thi gly his Indicates direction of transfer. F factor Aa A aA Hfr F- Hfr DNA that is not incorporated in the F- strand, and DNA that has crossed out of the F- strand is digested. F factor A transfers first. A A Hfr F- A transfers last. A Hfr A F- Leading Gene: the first gene transferred is determined empirically. Hfr strain H 1 2 3 Order of transfer thr azi ton lac pur gal his gly thi thr thi gly his gal pur lac ton azi lac pur gal his gly thi thr azi ton gal pur lac ton azi thr thi gly his E. coli Map • 0 minutes is at the threonine, • 100 minutes is required to transfer complete genome, pp. 3 assignment due 11/15/2005 car::tn10 (0.6) tetR car (0.6) tetS 1st Selection: tetR, nalR Mitochondrial DNA - 16, 569 bp, multiple copies per mt, 100 - 1000 mt per cell, 37 genes; - 22 oxidative phosphorylation, - 13 tRNA, - 2 rRNA, - Mitochondrial Control Region. Mitochondrial Inheritance • In mammals, 99.99% of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is inherited from the mother, • The sperm carries its mitochondria around a portion of its tail and has only about 100 mitochondria compared to 100,000 in the oocyte, • As the cells develop, more and more of the mtDNA from males is diluted out. – less than one part in 104 or 0.01% of the mtDNA is paternal. Mitochondrial Control Region • control region, – single promoter on each strand initiates transcription, – ori, • D-loop, – replication loop topography, • hypervariable region, – mutation rate 10x greater than genome. Mitochondrial Mutation Rate Electron leak from the ETC (1 3 %) result in the formation of superoxide. Protection Pathway Hydroxyl radical production Mitochondrial Control Region • Hair follicle DNA extraction, • PCR, • Sequencing (at Cold Spring Harbor), • Sequence analysis here at WWU.