* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ES Ch 1 NOTES Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
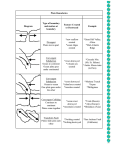
Name___________________________________________ CHAPTER 1 NOTES PACKET Date__________________ 1.1 EARTH HAS SEVERAL LAYERS A) Earth is made up of materials with different____________________________________________. 1) About ________ billion years ago the Earth formed from explosions from comets and asteroids, which along with heat and pressure, turned the Earth into a ball of glowing, melted rock. 2) Over time the materials sank to the center of the Earth and less _______________ material moved towards the surface, forming the Earth’s layers. B) Earth’s layers have different properties. 1) The Earth’s layers vary in composition, _________________________________ and thickness. 2) The Earth’s crust and top of the mantle form the _______________________________ or “rock” layer of the Earth. 3) Below that is the ____________________________, softer rock in the upper mantle called the asthenosphere, which is like hot tar. a) Crust is cool ___________________, 0-700C and 6-70km thick. It’s thinnest under oceans and thickest under continental mountain ranges. b) The mantle is _____________________________ rock, 870-4400C and 2900km thick. It’s like hot, thick paste. c) The outer core is __________________________ metals, 4400-6100C and 2300km thick. d) The inner core is __________________________ metals, 7000-8000C and 2400km in diameter. 1 C) The lithosphere is made up of many _________________________________. 1) It is split into random slabs of rocks called _______________________ plates, which fit together like puzzle pieces. 2) Most of the ___________________ plates contain both continental and oceanic crust. 3) These plates have help to solve the mystery of how continents moved to their present position. 1.2 CONTINENTS CHANGE POSITION OVER TIME A) Continents join together and _______________ apart. 1) Alfred Wegner proposed a _________________________________ on continental drift in the early 1900’s. 2) He stated that the Earth’s continents were once ______________________ as a single landmass and then slowly moved apart. 2 3) Fossil Evidence- fossils of many ____________________________________ creatures have been found on opposite shores, like the Mesosaurus. 4) Coal in Antarctica- coal is formed in _______________________ swamps, from the remains of vegetation that grew as long as 400 million years ago. 5) Geology- Rock layers found in on the _______________________ of one continent may be the same as rock layers on other continents. B) The theory of _____________________________________________________ explains how plates and their continents move. 1) Wegner’s ideas were pushed aside for many years until scientists realized that plate tectonics could connect some of his concepts. 2) In the __________, scientists created maps of the sea floor and noticed that there were underwater mountain ranges called mid-ocean ridges. 3) _____________________________________ is when melted rock rises through cracks in the crust and pushes old crust over as new crust rises. 4) The __________________ crusts oldest age is between 160-180 million years old and the continental crust is around 4 billion years old. 5) Ocean trenches are deep canyons where _____________________________ oceanic crust allows old crust to sink back into the asthenosphere. Old crust is destroyed as quickly as new crust is formed. 3 C) Plates move because of ______________________________________ currents in the asthenosphere, which allows hot, soft rock to rise, it then cools and sinks, then it’s heated and rises again. 1) This plate movement causes major earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain ranges to appear. Most of the world's active volcanoes (triangles) are along the edges of tectonic plates (the lines). 1.3 PLATES MOVE APART A) Tectonic plates have different __________________________________________. 1) Convergent Boundariesplates _______________________ into each other. 4 2) Divergent Boundaries- plates spread apart 3) Transform Boundaries- two _______________ slide past each other. This picture (LEFT) shows the San Andreas Fault in California, which is a transform fault. The aerial view (RIGHT) of the San Andreas Fault (transform) the trees in the orchard (dots) have been offset by the slipping of the plates. The Pacific Plate is to the left and the North American to the right. B) The sea floor spreads apart at ________________________________________ boundaries, which are at mid ocean ridges and rift valleys. 1) Mid ocean ridges form the longest _____________________________ chains on Earth and most contain a rift valley in the center. 2) Magnetic reversals have occurred ___________________________ times over the Earth’s long history. 5 a) Bits of _______________________ in lava will tend to line up with a magnetic orientation pointing at the North Pole. When the lava solidifies, the magnetic orientation is frozen into the rock- essentially; it will have a “north end” and a “south end” on the ocean floor. C) Continents split apart at _______________________________________ plate boundaries. 1) Divergent plate boundaries on continents also produce rift valleys. Great Rift Valley of Africa a. Magma rises through cracks to form ____________________________________ and as the rift valley grows wider, the continent splits apart. b. The valley floor slowly thins and _______________________ until eventually it’s below sea level. c. Water from nearby _____________________________ or rivers may fill the valley and form a sea or lake. D) Hot spots can be used to track ___________________________________ movements. 1) Hot Spots are areas of ___________________________________ activity that develop where magma rises in a plume from the mantle. 2) The _________________________________ plume acts like a blowtorch while the plate moves above it. Hawaii is an example of a hot spot island chain. 6 1.4 PLATES CONVERGE OR SCRAPEPAST EACH OTHER A) Tectonic plates ______________________________________________ at convergent boundaries. 1) _______________________________________-continental collision occurs where two continental plates collide, crumpling and folding rock between them. The collision of India into Asia 50 million years ago caused the Eurasian Plate to crumple up and override the Indian Plate creating the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau 2) _______________________________________-oceanic subductions occur when two oceanic plates collide and the older, denser plate sinks beneath the top plate, forming deep ocean trenches and island arcs. The Mariana’s Trench, for example, is a deep trench created as the result of the Philippine Plate subducting under the Pacific Plate. 3) ______________________________________-continental subduction occurs where an oceanic plate sinks beneath a continental plate, forming a deep ocean trench and volcanic coastal mountains. Off the coast of South America along the Peru-Chile trench, the oceanic Nazca Plate is subducting under the continental part of the South American Plate. In turn, the overriding South American Plate is being lifted up, creating the towering Andes Mountains. 7 B) Tectonic plates _______________________________ past each other at transform boundaries. 1) At transform boundary, two plates move past each other in opposite directions and their edges scrape and grind against each other. 2) __________________________is formed or destroyed and it occurs both on land and the sea floor The San Andres Fault in California is an example. C) The theory of plate tectonics helps geologists today. 1) This allows geologists to understand how _____________________________ and ocean basins formed. 2) Geologists can also __________________________ earthquakes and volcanic activity. 8